Air quality expert group - Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in ... - Defra
Air quality expert group - Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in ... - Defra
Air quality expert group - Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in ... - Defra
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
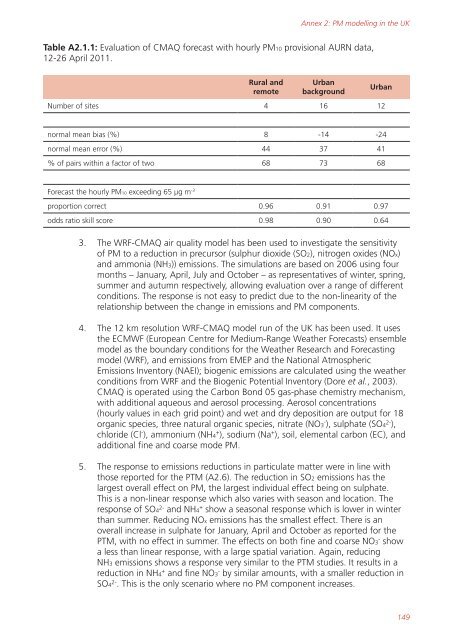
Table A2.1.1: Evaluation of CMAQ forecast with hourly PM10 provisional AURN data,<br />
12-26 April 2011.<br />
Rural and<br />
remote<br />
Urban<br />
background<br />
Number of sites 4 16 12<br />
normal mean bias (%) 8 -14 -24<br />
normal mean error (%) 44 37 41<br />
% of pairs with<strong>in</strong> a factor of two 68 73 68<br />
Forecast the hourly PM10 exceed<strong>in</strong>g 65 µg m -3<br />
Annex 2: PM modell<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the UK<br />
Urban<br />
proportion correct 0.96 0.91 0.97<br />
odds ratio skill score 0.98 0.90 0.64<br />
3. The WRF-CMAQ air <strong>quality</strong> model has been used to <strong>in</strong>vestigate the sensitivity<br />
of PM to a reduction <strong>in</strong> precursor (sulphur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx)<br />
and ammonia (NH3)) emissions. The simulations are based on 2006 us<strong>in</strong>g four<br />
months – January, April, July and October – as representatives of w<strong>in</strong>ter, spr<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
summer and autumn respectively, allow<strong>in</strong>g evaluation over a range of different<br />
conditions. The response is not easy to predict due to the non-l<strong>in</strong>earity of the<br />
relationship between the change <strong>in</strong> emissions and PM components.<br />
4. The 12 km resolution WRF-CMAQ model run of the UK has been used. It uses<br />
the ECMWF (European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts) ensemble<br />
model as the boundary conditions for the Weather Research and Forecast<strong>in</strong>g<br />
model (WRF), and emissions from EMEP and the National Atmospheric<br />
Emissions Inventory (NAEI); biogenic emissions are calculated us<strong>in</strong>g the weather<br />
conditions from WRF and the Biogenic Potential Inventory (Dore et al., 2003).<br />
CMAQ is operated us<strong>in</strong>g the Carbon Bond 05 gas-phase chemistry mechanism,<br />
with additional aqueous and aerosol process<strong>in</strong>g. Aerosol concentrations<br />
(hourly values <strong>in</strong> each grid po<strong>in</strong>t) and wet and dry deposition are output for 18<br />
organic species, three natural organic species, nitrate (NO3 - ), sulphate (SO4 2- ),<br />
chloride (Cl - ), ammonium (NH4 + ), sodium (Na + ), soil, elemental carbon (EC), and<br />
additional f<strong>in</strong>e and coarse mode PM.<br />
5. The response to emissions reductions <strong>in</strong> <strong>particulate</strong> <strong>matter</strong> were <strong>in</strong> l<strong>in</strong>e with<br />
those reported for the PTM (A2.6). The reduction <strong>in</strong> SO2 emissions has the<br />
largest overall effect on PM, the largest <strong>in</strong>dividual effect be<strong>in</strong>g on sulphate.<br />
This is a non-l<strong>in</strong>ear response which also varies with season and location. The<br />
response of SO4 2- and NH4 + show a seasonal response which is lower <strong>in</strong> w<strong>in</strong>ter<br />
than summer. Reduc<strong>in</strong>g NOx emissions has the smallest effect. There is an<br />
overall <strong>in</strong>crease <strong>in</strong> sulphate for January, April and October as reported for the<br />
PTM, with no effect <strong>in</strong> summer. The effects on both f<strong>in</strong>e and coarse NO3 - show<br />
a less than l<strong>in</strong>ear response, with a large spatial variation. Aga<strong>in</strong>, reduc<strong>in</strong>g<br />
NH3 emissions shows a response very similar to the PTM studies. It results <strong>in</strong> a<br />
reduction <strong>in</strong> NH4 + and f<strong>in</strong>e NO3 - by similar amounts, with a smaller reduction <strong>in</strong><br />
SO4 2- . This is the only scenario where no PM component <strong>in</strong>creases.<br />
149