Air quality expert group - Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in ... - Defra
Air quality expert group - Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in ... - Defra
Air quality expert group - Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in ... - Defra
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>PM2.5</strong> <strong>in</strong> the UK<br />
156<br />
NO3 – concentration (µg m -3 )<br />
25<br />
20<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
0<br />
Jan-08<br />
Daily NO3 – of <strong>PM2.5</strong> at N Kens<strong>in</strong>gton<br />
Feb-08 Mar-08 Apr-08 May-08 Jun-08 Jul-08 Aug-08 Sep-08 Oct-08 Nov-08 Dec-08<br />
observed modelled<br />
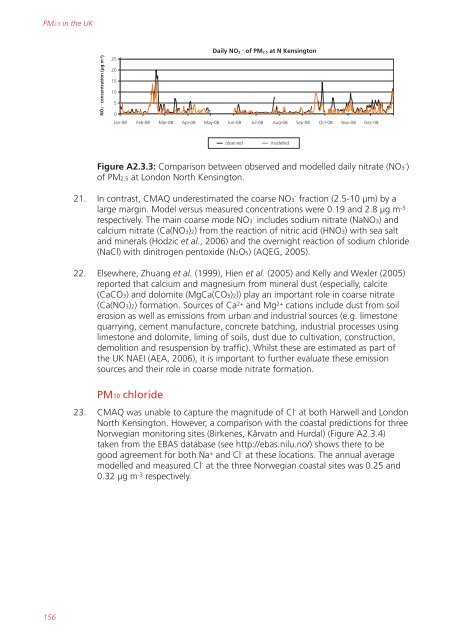
Figure A2.3.3: Comparison between observed and modelled daily nitrate (NO3 - )<br />
of <strong>PM2.5</strong> at London North Kens<strong>in</strong>gton.<br />
21. In contrast, CMAQ underestimated the coarse NO3 - fraction (2.5-10 µm) by a<br />
large marg<strong>in</strong>. Model versus measured concentrations were 0.19 and 2.8 µg m -3<br />
respectively. The ma<strong>in</strong> coarse mode NO3 - <strong>in</strong>cludes sodium nitrate (NaNO3) and<br />
calcium nitrate (Ca(NO3)2) from the reaction of nitric acid (HNO3) with sea salt<br />
and m<strong>in</strong>erals (Hodzic et al., 2006) and the overnight reaction of sodium chloride<br />
(NaCl) with d<strong>in</strong>itrogen pentoxide (N2O5) (AQEG, 2005).<br />
22. Elsewhere, Zhuang et al. (1999), Hien et al. (2005) and Kelly and Wexler (2005)<br />
reported that calcium and magnesium from m<strong>in</strong>eral dust (especially, calcite<br />
(CaCO3) and dolomite (MgCa(CO3)2)) play an important role <strong>in</strong> coarse nitrate<br />
(Ca(NO3)2) formation. Sources of Ca 2+ and Mg 2+ cations <strong>in</strong>clude dust from soil<br />
erosion as well as emissions from urban and <strong>in</strong>dustrial sources (e.g. limestone<br />
quarry<strong>in</strong>g, cement manufacture, concrete batch<strong>in</strong>g, <strong>in</strong>dustrial processes us<strong>in</strong>g<br />
limestone and dolomite, lim<strong>in</strong>g of soils, dust due to cultivation, construction,<br />
demolition and resuspension by traffic). Whilst these are estimated as part of<br />
the UK NAEI (AEA, 2006), it is important to further evaluate these emission<br />
sources and their role <strong>in</strong> coarse mode nitrate formation.<br />
PM10 chloride<br />
23. CMAQ was unable to capture the magnitude of Cl - at both Harwell and London<br />
North Kens<strong>in</strong>gton. However, a comparison with the coastal predictions for three<br />
Norwegian monitor<strong>in</strong>g sites (Birkenes, Kårvatn and Hurdal) (Figure A2.3.4)<br />
taken from the EBAS database (see http://ebas.nilu.no/) shows there to be<br />
good agreement for both Na + and Cl - at these locations. The annual average<br />
modelled and measured Cl - at the three Norwegian coastal sites was 0.25 and<br />
0.32 µg m -3 respectively.