- Page 2:
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF Evolution
- Page 5 and 6:
Encyclopedia of Evolution Copyright
- Page 8 and 9:
Contents Foreword ix Acknowledgment
- Page 10:
Foreword The theory and facts of ev
- Page 14 and 15:
IntroduCtIon What you do not know a
- Page 16:
other issues coming along with it.
- Page 20 and 21:
adaptation Adaptation is the fit of
- Page 22 and 23:
from the allometric patterns of gro
- Page 24 and 25:
considered as an example. (The taxo
- Page 26 and 27:
English) were a resounding success,
- Page 28 and 29:
Some Centers of the Evolution of Ag
- Page 30 and 31: helps the DNA insert into the host
- Page 32 and 33: Even within a single patient, HIV e
- Page 34 and 35: then into the insect body; carbon d
- Page 36 and 37: chromosomes (they are diploid) whil
- Page 38 and 39: genetic basis. About 35,000 years a
- Page 40 and 41: emained dormant and sprouted after
- Page 42 and 43: Further Reading Wise, Steven M. Rat
- Page 44 and 45: Because the DNA of many archaebacte
- Page 46 and 47: Koi and goldfish have been bred tha
- Page 48 and 49: Barringer Crater, Arizona, was form
- Page 50 and 51: y a silent wall of darkness advanci
- Page 52 and 53: Skeleton of “Lucy,” the Austral
- Page 54: Further Reading Alemseged, Zerxenay
- Page 57 and 58: acteria, evolution of Examples of t
- Page 59 and 60: 0 Bates, Henry Walter advantage. Th
- Page 61 and 62: ehavior, evolution of In another sp
- Page 63 and 64: ig bang make nests with horizontal
- Page 65 and 66: iodiversity How Much Do Genes Contr
- Page 67 and 68: iodiversity Biodiversity (as indica
- Page 69 and 70: 0 biogeography Another problem with
- Page 71 and 72: iogeography Biogeography of Selecte
- Page 73 and 74: iogeography their species through d
- Page 75 and 76: iology design) or adaptation to the
- Page 77 and 78: iology D. Response to environment.
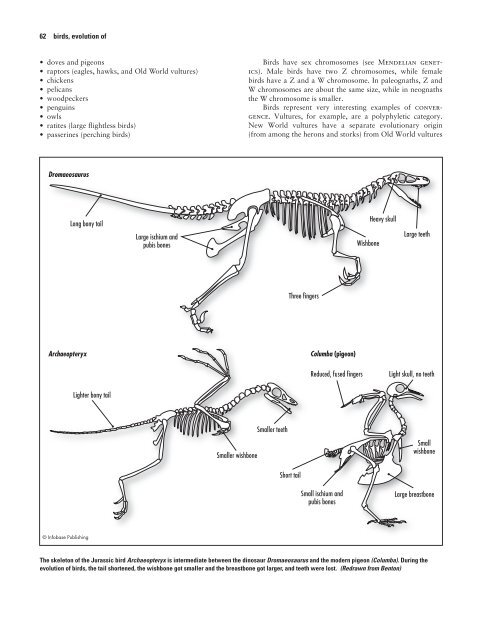
- Page 79: 0 birds, evolution of • The foot.
- Page 83 and 84: Burgess shale early career. By heat
- Page 85 and 86: Burgess shale jointed legs, Anomalo
- Page 87 and 88: Cambrian period occurred when anima
- Page 89 and 90: 0 Cenozoic era opens the way to an
- Page 91 and 92: Chicxulub Pritchard, J., and Dolph
- Page 93 and 94: cladistics The above examples used
- Page 95 and 96: coevolution descent, and that scien
- Page 97 and 98: coevolution Coevolution of Organism
- Page 99 and 100: 0 coevolution What Are the “Ghost
- Page 101 and 102: coevolution What Are the “Ghosts
- Page 103 and 104: commensalism Wilson, Michael. Micro
- Page 105 and 106: continental drift was an animal tha
- Page 107 and 108: continental drift During geological
- Page 109 and 110: 0 convergence bee-pollinated flower
- Page 111 and 112: convergence Both birds and bats hav
- Page 113 and 114: creationism explained these observa
- Page 115 and 116: creationism used to justify militar
- Page 117 and 118: creationism • In the early 21st c
- Page 119 and 120: 00 Cretaceous period however, other
- Page 121 and 122: 0 Cro-Magnon evolution had occurred
- Page 123 and 124: 0 Cro-Magnon areas, perforated shel
- Page 125 and 126: 0 Cuvier, Georges Cuvier held stron
- Page 127 and 128: 0 Darwin Awards Darwin Awards “Th
- Page 129 and 130: 0 Darwin, Charles forever. It would
- Page 131 and 132:
Darwin, Charles and animals did hav
- Page 133 and 134:
Darwin’s finches has its own uniq
- Page 135 and 136:
Dawkins, Richard ate the pulp. More
- Page 137 and 138:
developmental evolution Part II. In
- Page 139 and 140:
0 Devonian period gene from an inve
- Page 141 and 142:
dinosaurs what DeVries thought were
- Page 143 and 144:
diseases, evolution of • Thyreoph
- Page 145 and 146:
disjunct species have happened? Som
- Page 147 and 148:
DNA (evidence for evolution) genes,
- Page 149 and 150:
0 DNA (evidence for evolution) seco
- Page 151 and 152:
DNA (raw material of evolution) DNA
- Page 153 and 154:
DNA (raw material of evolution) The
- Page 155 and 156:
Dobzhansky, Theodosius Mice have tw
- Page 157 and 158:
duplication, gene prominent brow ri
- Page 159 and 160:
0 ecology Second, organisms can con
- Page 161 and 162:
Eldredge, Niles they possess no str
- Page 163 and 164:
eugenics grieving, or experiencing
- Page 165 and 166:
eugenics because government officia
- Page 167 and 168:
eukaryotes, evolution of of the sor
- Page 169 and 170:
0 Eve, mitochondrial within cells,
- Page 171 and 172:
evolutionary ethics the ability to
- Page 173 and 174:
evolutionary ethics Can an Evolutio
- Page 175 and 176:
evolutionary medicine Can an Evolut
- Page 177 and 178:
evolutionary medicine variable in t
- Page 179 and 180:
0 extinction past (a genetic bottle
- Page 181 and 182:
fishes, evolution of his obvious vi
- Page 183 and 184:
Flores Island people Christopher St
- Page 185 and 186:
fossils and fossilization The grain
- Page 187 and 188:
founder effect Further Reading Fort
- Page 189 and 190:
0 Gaia hypothesis nitrogen oxide (N
- Page 191 and 192:
Galton, Francis constituted a premi
- Page 193 and 194:
gene pool Cocos Island is too small
- Page 195 and 196:
Gould, Stephen Jay animals, and the
- Page 197 and 198:
Gray, Asa he had long accepted Lyel
- Page 199 and 200:
0 group selection used the carbon t
- Page 201 and 202:
gymnosperms, evolution of began per
- Page 204 and 205:
Haeckel, Ernst (1834-1919) German E
- Page 206 and 207:
The initial divergence between homi
- Page 208 and 209:
Although Homo ergaster, the presume
- Page 210 and 211:
tions were spreading through Africa
- Page 212 and 213:
Selected Examples of Homo heidelber
- Page 214 and 215:
sunlight of tropical regions, and t
- Page 216 and 217:
win, Hooker could not pay his own w
- Page 218 and 219:
gene transfer from a bacterium, per
- Page 220 and 221:
to evolutionary science. He also ap
- Page 222 and 223:
Examples of Intergeneric Crosses Re
- Page 224 and 225:
ice ages The term ice ages usually
- Page 226 and 227:
America had not been connected sinc
- Page 228 and 229:
migrated into Europe and displaced
- Page 230 and 231:
ence their intelligence. There is a
- Page 232 and 233:
This does not mean that all of the
- Page 234 and 235:
e exactly the right ones. Bovine in
- Page 236 and 237:
Van Till, Howard J. “E. coli at t
- Page 238 and 239:
food particles with whiplike struct
- Page 240 and 241:
would readily interbreed and produc
- Page 242 and 243:
ased, to eat small plankton near th
- Page 244 and 245:
isotopes When evaporation from the
- Page 246:
Java man See Homo erectus. Johanson
- Page 249 and 250:
0 Kenyanthropus chemist Henri Becqu
- Page 251 and 252:
language, evolution of is not consi
- Page 253 and 254:
language, evolution of Italian, Por
- Page 255 and 256:
Lascaux caves Some of the original
- Page 257 and 258:
Leakey, Richard Richard Leakey, in
- Page 259 and 260:
0 life history, evolution of it inv
- Page 261 and 262:
life history, evolution of is: sele
- Page 263 and 264:
life history, evolution of Why Do H
- Page 265 and 266:
life history, evolution of Why Do H
- Page 267 and 268:
Linnaean system The tree of life us
- Page 269 and 270:
0 living fossils admired. The genus
- Page 271 and 272:
Lysenkoism about evolution. When Da
- Page 273 and 274:
Malthus, Thomas intelligent design)
- Page 275 and 276:
mammals, evolution of the reptilian
- Page 277 and 278:
markers another precocious and crea
- Page 279 and 280:
0 Mars, life on • The spacecraft
- Page 281 and 282:
Maynard Smith, John producing a 200
- Page 283 and 284:
meiosis Zoology. He became director
- Page 285 and 286:
Mendel, Gregor of the fertilized eg
- Page 287 and 288:
Mendelian genetics an American gene
- Page 289 and 290:
0 Mendelian genetics the environmen
- Page 291 and 292:
microevolution Stanley Miller did o
- Page 293 and 294:
missing links Batesian mimicry. Nam
- Page 295 and 296:
mitochondrial DNA Hominin skulls ha
- Page 297 and 298:
molecular clock these scientists di
- Page 299 and 300:
0 mutualism function of the protein
- Page 301 and 302:
natural selection Fact 1. Populatio
- Page 303 and 304:
natural selection Three types of na
- Page 305 and 306:
natural theology different kinds of
- Page 307 and 308:
Neandertals different species of hu
- Page 309 and 310:
0 Neolithic Neandertals lived short
- Page 311 and 312:
new synthesis In contrast to progen
- Page 313 and 314:
noncoding DNA Some regulatory molec
- Page 315 and 316:
origin of life they refer to life t
- Page 317 and 318:
origin of life Are Humans Alone in
- Page 319 and 320:
00 origin of life It is often said
- Page 321 and 322:
0 Origin of Species (book) ribose);
- Page 323 and 324:
0 Orrorin ———. On the Origin
- Page 325 and 326:
0 Paley, William in the Chordata) e
- Page 327 and 328:
0 peppered moths There remained som
- Page 329 and 330:
0 Permian extinction produced in la
- Page 331 and 332:
Permian period upon the exploitatio
- Page 333 and 334:
Piltdown man found in slightly diff
- Page 335 and 336:
plate tectonics The Earth’s surfa
- Page 337 and 338:
population Percent of Mammal Genera
- Page 339 and 340:
0 population genetics Vandermeer, J
- Page 341 and 342:
population genetics If allele A is
- Page 343 and 344:
Precambrian time at least some gene
- Page 345 and 346:
progress, concept of arboreal prima
- Page 347 and 348:
promoter Each chromosome contains t
- Page 349 and 350:
0 punctuated equilibria and persist
- Page 351 and 352:
punctuated equilibria Gradualism wa
- Page 353 and 354:
Quaternary period epoch of the Quat
- Page 355 and 356:
ecapitulation would cause some of t
- Page 357 and 358:
eligion, evolution of pathogens nev
- Page 359 and 360:
0 reproductive systems Catkins of m
- Page 361 and 362:
eproductive systems Scobell has inv
- Page 363 and 364:
eproductive systems fact, there is
- Page 365 and 366:
eptiles, evolution of Blanckenhorn,
- Page 367 and 368:
esistance, evolution of ineffective
- Page 369 and 370:
0 respiration, evolution of There i
- Page 372 and 373:
Sagan, Carl (1934-1996) American As
- Page 374 and 375:
tain features are universally recog
- Page 376 and 377:
The testing of hypotheses accumulat
- Page 378 and 379:
the results are sufficiently intere
- Page 380 and 381:
een wrong: His hypothesis of the co
- Page 382 and 383:
Comparison of Inherit the Wind with
- Page 384 and 385:
and others form more complex struct
- Page 386 and 387:
endonuclease gene is then used as a
- Page 388 and 389:
e able to do the same thing. Second
- Page 390 and 391:
mosomes come in groups of five rath
- Page 392 and 393:
eliminated—that is, if sexual rec
- Page 394 and 395:
one, free of parasites, is likely t
- Page 396 and 397:
nesses of resource acquisition and
- Page 398 and 399:
Zahavi, Amotz. The Handicap Princip
- Page 400 and 401:
and it is not happening extensively
- Page 402 and 403:
this, too, is a genetically based u
- Page 404 and 405:
monkeyflowers of the genus Mimulus)
- Page 406 and 407:
Further Reading Abrahamson, Warren
- Page 408 and 409:
comes from the unfertilized egg, ra
- Page 410:
of the bacteriophages. Therefore, h
- Page 413 and 414:
technology Technological and Cultur
- Page 415 and 416:
thermodynamics • Plants. The flow
- Page 417 and 418:
thermodynamics return to their orig
- Page 419 and 420:
00 Triassic period more resulting l
- Page 422 and 423:
unconformity An unconformity is a g
- Page 424 and 425:
sissippi River is getting shorter e
- Page 426:
ago. This was the birth of the Sun.
- Page 429 and 430:
0 vestigial characteristics algae.
- Page 432 and 433:
Wallace, Alfred Russel (1823-1913)
- Page 434 and 435:
genetic inferiority of the lower cl
- Page 436 and 437:
that point onward he questioned the
- Page 438 and 439:
Carl R. Woese pioneered the use of
- Page 440 and 441:
Darwin’s “One LOng argument”:
- Page 442 and 443:
the young seedlings must compete wi
- Page 444 and 445:
Traits can reappear after even hund
- Page 446 and 447:
ated: It has been an advantage in o
- Page 448 and 449:
chapter 10. On the imperfection of
- Page 450 and 451:
out in competition with the species
- Page 452 and 453:
languages. Linguists classify all R
- Page 454:
My theory has been much maligned. T
- Page 458 and 459:
Index Note: Boldface page numbers i
- Page 460 and 461:
asexual propagation 370-371 Ashfall
- Page 462 and 463:
Bryan, William Jennings creationism
- Page 464 and 465:
ird evolution 62-63 cladistics 72-7
- Page 466 and 467:
divergence molecular clock 278-279
- Page 468 and 469:
extinction 159-160. See also mass e
- Page 470 and 471:
Gondwana (Gondwanaland) 68, 84, 86,
- Page 472 and 473:
Huxley, Julian S. 200 eugenics 146
- Page 474 and 475:
Mendelian genetics and 268 Spencer,
- Page 476 and 477:
Origin of Species (Darwin) 433-434
- Page 478 and 479:
ocean currents 179, 207 Oceanian re
- Page 480 and 481:
polar cells 368 Polkinghorne, John
- Page 482 and 483:
Sanger, Frederick 55 Sanger, Margar
- Page 484 and 485:
spores 264, 370 spotted hyena (Croc
- Page 486 and 487:
useless characteristics 409 Ussher,