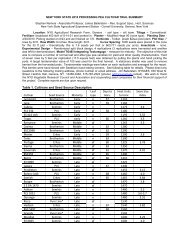
conference schedule and program with abstracts - Horticulture ...
conference schedule and program with abstracts - Horticulture ...
conference schedule and program with abstracts - Horticulture ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
P-50<br />
Estimation of protein spot variability in 2-D gels<br />
G.R. Cramer* 1 , L.G. Deluc 1,3 , K. Spreeman 1 , K. Schegg 1 , A.Y. Fennell 2<br />
1 Department of Biochemistry <strong>and</strong> Molecular Biology, University of Nevada, Reno, Nevada,<br />
USA; 2 Dept. of <strong>Horticulture</strong>, Forestry, L<strong>and</strong>scape & Parks, South Dakota State University,<br />
Brookings, South Dakota, USA; 3 Current address: Department of <strong>Horticulture</strong>, Oregon State<br />
University, Corvalis, Oregon, USA<br />
*Corresponding author: cramer@unr.edu<br />
A common method for quantifying proteins is to separate them by two-dimensional<br />
polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (2-D PAGE) <strong>and</strong> quantify the intensity of the spots <strong>with</strong><br />
image analysis software. Protein spot variability can be quite high averaging about 60 to 80% for<br />
three biological replicates. Gel to gel variability is quite high requiring the researcher to make<br />
many technical replicates <strong>and</strong> select from the best of the gels made. Our lab decided to determine<br />
where most of this variability came from. We designed an experiment to determine if the<br />
variability came from the biological replicates, protein extractions or the custom made 2-D<br />
PAGE gels. A total of 27 gels were run; there were 3 gels of 3 extractions of 3 biological<br />
replicates of Cabernet Sauvignon shoot tips. Nearly 500 common protein spots were quantified<br />
on all 27 gels. Variability was quantified <strong>with</strong> the coefficient of variation (CV). The average CV<br />
was highest for the gels <strong>and</strong> lowest for the biological replicates, averaging 55, 33 <strong>and</strong> 25% for<br />
gels, extractions <strong>and</strong> biological replicates, respectively. The CV ranged from 5 to 122% for some<br />
protein spots indicating that for many proteins it is difficult to get good quantitative data for<br />
comparative purposes. The variability of this method limits the number of proteins that can be<br />
quantified adequately <strong>and</strong> inflates the cost <strong>and</strong> labor due to the replacement of bad gels. A<br />
similar analysis was performed on buds of Seyval <strong>and</strong> Vitis riparia. The average CV of 861 spots<br />
was 68%. Difference Gel Electrophoresis (DIGE) is designed to reduce this variability <strong>and</strong> we<br />
tested DIGE on bud samples to determine if protein spot variability was significantly reduced. A<br />
comparison of the two methods will be discussed.<br />
128