s - Wyższa SzkoÅa Filologiczna we WrocÅawiu
s - Wyższa SzkoÅa Filologiczna we WrocÅawiu
s - Wyższa SzkoÅa Filologiczna we WrocÅawiu
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
On the variability of vocalic inventory in Black South African English 47<br />
2. The vocalic inventory of BSAE<br />
Bertus Van Rooy (2008: 179) argues that BSAE is characterized by the<br />
absence of the tense/lax contrast and that of central vo<strong>we</strong>ls, at least in the<br />
mesolectal variety. His findings point to the fact that mesolectal speakers of<br />
BSAE have five contrastive vo<strong>we</strong>l phonemes, namely /i/, /ɛ/, /a/, /N/ and /u/.<br />
Acrolectal speakers have some other vo<strong>we</strong>ls as <strong>we</strong>ll, which, as expected, bring<br />
their variety closer to the native varieties of English, but there are some features<br />
which are common along the lectal continuum. These and other features of the<br />
BSAE vocalic system are discussed in what follows.<br />
2.1. The monophthongs<br />
According to Van Rooy (2008), drawing on Van Rooy and Van Huyssteen<br />
(2000), the monophthongs of BSAE are the ones in Table 1; the mergers are<br />
illustrated by their association with the same vo<strong>we</strong>l in BSAE:<br />
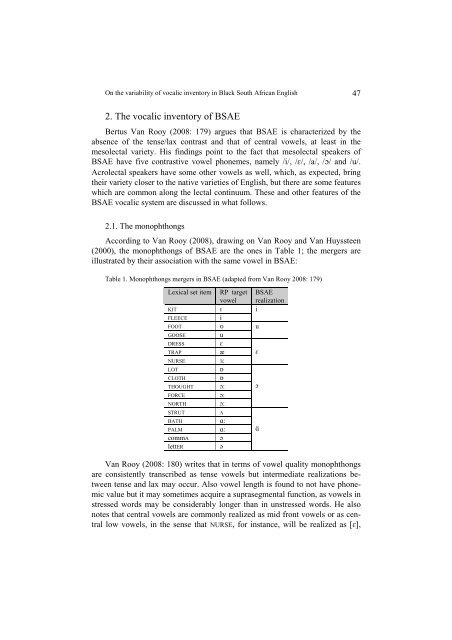
Table 1. Monophthongs mergers in BSAE (adapted from Van Rooy 2008: 179)<br />
Lexical set item<br />
KIT<br />
FLEECE<br />
FOOT<br />
GOOSE<br />
DRESS<br />
TRAP<br />
NURSE ɜ:<br />
LOT<br />
ɒ<br />
CLOTH<br />
ɒ<br />
THOUGHT ɔ:<br />
FORCE ɔ:<br />
NORTH ɔ:<br />
STRUT<br />
RP target<br />
vo<strong>we</strong>l<br />
ɪ<br />
i<br />
ʊ<br />
u<br />
ɛ<br />
æ<br />
ʌ<br />
BATH ɑ:<br />
PALM ɑ:<br />
commA<br />
lettER<br />
ə<br />
ə<br />
BSAE<br />
realization<br />
i<br />
u<br />
ɛ<br />
ɔ<br />
ɑ‚<br />
Van Rooy (2008: 180) writes that in terms of vo<strong>we</strong>l quality monophthongs<br />
are consistently transcribed as tense vo<strong>we</strong>ls but intermediate realizations bet<strong>we</strong>en<br />
tense and lax may occur. Also vo<strong>we</strong>l length is found to not have phonemic<br />
value but it may sometimes acquire a suprasegmental function, as vo<strong>we</strong>ls in<br />
stressed words may be considerably longer than in unstressed words. He also<br />
notes that central vo<strong>we</strong>ls are commonly realized as mid front vo<strong>we</strong>ls or as central<br />
low vo<strong>we</strong>ls, in the sense that NURSE, for instance, will be realized as [ɛ],