Dernière édition Attention: Le pdf pèse environ 17 - BFH-TI - Berner ...
Dernière édition Attention: Le pdf pèse environ 17 - BFH-TI - Berner ...
Dernière édition Attention: Le pdf pèse environ 17 - BFH-TI - Berner ...
- Keine Tags gefunden...
Sie wollen auch ein ePaper? Erhöhen Sie die Reichweite Ihrer Titel.
YUMPU macht aus Druck-PDFs automatisch weboptimierte ePaper, die Google liebt.
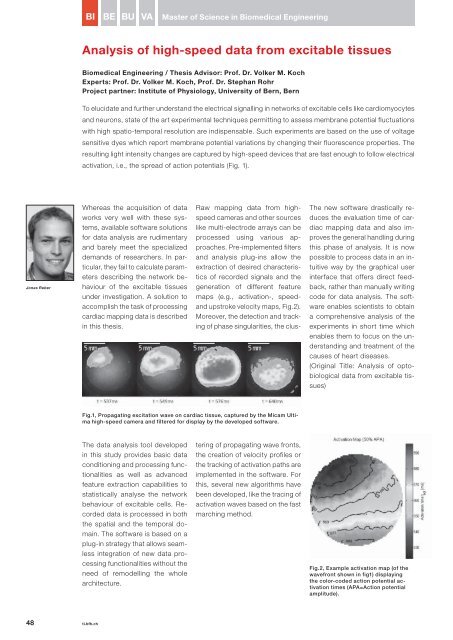
BIBEBUVAMaster of Science in Biomedical EngineeringAnalysis of high-speed data from excitable tissuesBiomedical Engineering / Thesis Advisor: Prof. Dr. Volker M. KochExperts: Prof. Dr. Volker M. Koch, Prof. Dr. Stephan RohrProject partner: Institute of Physiology, University of Bern, BernTo elucidate and further understand the electrical signalling in networks of excitable cells like cardiomyocytesand neurons, state of the art experimental techniques permitting to assess membrane potential fluctuationswith high spatio-temporal resolution are indispensable. Such experiments are based on the use of voltagesensitive dyes which report membrane potential variations by changing their fluorescence properties. Theresulting light intensity changes are captured by high-speed devices that are fast enough to follow electricalactivation, i.e., the spread of action potentials (Fig. 1).Jonas ReberWhereas the acquisition of dataworks very well with these systems,available software solutionsfor data analysis are rudimentaryand barely meet the specializeddemands of researchers. In particular,they fail to calculate parametersdescribing the network behaviourof the excitable tissuesunder investigation. A solution toaccomplish the task of processingcardiac mapping data is describedin this thesis.Raw mapping data from highspeedcameras and other sourceslike multi-electrode arrays can beprocessed using various approaches.Pre-implemented filtersand analysis plug-ins allow theextraction of desired characteristicsof recorded signals and thegeneration of different featuremaps (e.g., activation-, speedandupstroke velocity maps, Fig.2).Moreover, the detection and trackingof phase singularities, the clus-The new software drastically reducesthe evaluation time of cardiacmapping data and also improvesthe general handling duringthis phase of analysis. It is nowpossible to process data in an intuitiveway by the graphical userinterface that offers direct feedback,rather than manually writingcode for data analysis. The softwareenables scientists to obtaina comprehensive analysis of theexperiments in short time whichenables them to focus on the understandingand treatment of thecauses of heart diseases.(Original Title: Analysis of optobiologicaldata from excitable tissues)Fig.1, Propagating excitation wave on cardiac tissue, captured by the Micam Ultimahigh-speed camera and filtered for display by the developed software.The data analysis tool developedin this study provides basic dataconditioning and processing functionalitiesas well as advancedfeature extraction capabilities tostatistically analyse the networkbehaviour of excitable cells. Recordeddata is processed in boththe spatial and the temporal domain.The software is based on aplug-in strategy that allows seamlessintegration of new data processingfunctionalities without theneed of remodelling the wholearchitecture.tering of propagating wave fronts,the creation of velocity profiles orthe tracking of activation paths areimplemented in the software. Forthis, several new algorithms havebeen developed, like the tracing ofactivation waves based on the fastmarching method.Fig.2, Example activation map (of thewavefront shown in fig1) displayingthe color-coded action potential activationtimes (APA=Action potentialamplitude).48 ti.bfh.ch