Download - Academy Publisher
Download - Academy Publisher
Download - Academy Publisher
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
navigation and control system of intelligent vehicle.<br />
Some typical path such as S-path and different angle<br />
curve road are chosen in test. The picture of intelligent<br />
vehicle searching path in the S-path test is shown in<br />
Fig.7. The maximum speed for this road conditions is<br />
1.6m / s. The picture of intelligent vehicle driving at<br />
turning is shown in Fig.8. The maximum speed for this<br />
road conditions is 1.6m / s.<br />
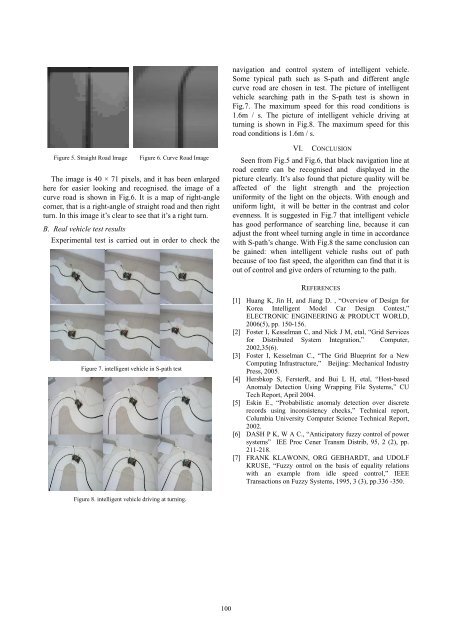
Figure 5. Straight Road Image<br />
Figure 6. Curve Road Image<br />
The image is 40 × 71 pixels, and it has been enlarged<br />
here for easier looking and recognised. the image of a<br />
curve road is shown in Fig.6. It is a map of right-angle<br />
corner, that is a right-angle of straight road and then right<br />
turn. In this image it’s clear to see that it’s a right turn.<br />
B. Real vehicle test results<br />
Experimental test is carried out in order to check the<br />
VI. CONCLUSION<br />
Seen from Fig.5 and Fig.6, that black navigation line at<br />
road centre can be recognised and displayed in the<br />
picture clearly. It’s also found that picture quality will be<br />
affected of the light strength and the projection<br />
uniformity of the light on the objects. With enough and<br />
uniform light, it will be better in the contrast and color<br />
evenness. It is suggested in Fig.7 that intelligent vehicle<br />
has good performance of searching line, because it can<br />
adjust the front wheel turning angle in time in accordance<br />
with S-path’s change. With Fig.8 the same conclusion can<br />
be gained: when intelligent vehicle rushs out of path<br />
because of too fast speed, the algorithm can find that it is<br />
out of control and give orders of returning to the path.<br />
REFERENCES<br />
Figure 7. intelligent vehicle in S-path test<br />
[1] Huang K, Jin H, and Jiang D. , “Overview of Design for<br />
Korea Intelligent Model Car Design Contest,”<br />
ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING & PRODUCT WORLD,<br />
2006(5), pp. 150-156.<br />
[2] Foster I, Kesselman C, and Nick J M, etal, “Grid Services<br />
for Distributed System Integration,” Computer,<br />
2002,35(6).<br />
[3] Foster I, Kesselman C., “The Grid Blueprint for a New<br />
Computing Infrastructure,” Beijing: Mechanical Industry<br />
Press, 2005.<br />
[4] Hersbkop S, FersterR, and Bui L H, etal, “Host-based<br />
Anomaly Detection Using Wrapping File Systems,” CU<br />
Tech Report, April 2004.<br />
[5] Eskin E., “Probabilistic anomaly detection over discrete<br />
records using inconsistency checks,” Technical report,<br />
Columbia University Computer Science Technical Report,<br />
2002.<br />
[6] DASH P K, W A C., “Anticipatory fuzzy control of power<br />
systems” IEE Proc Cener Transm Distrib, 95, 2 (2), pp.<br />
211-218.<br />
[7] FRANK KLAWONN, ORG GEBHARDT, and UDOLF<br />
KRUSE, “Fuzzy ontrol on the basis of equality relations<br />
with an example from idle speed control,” IEEE<br />
Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 1995, 3 (3), pp.336 -350.<br />
Figure 8. intelligent vehicle driving at turning.<br />
100