Download - Academy Publisher
Download - Academy Publisher
Download - Academy Publisher
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
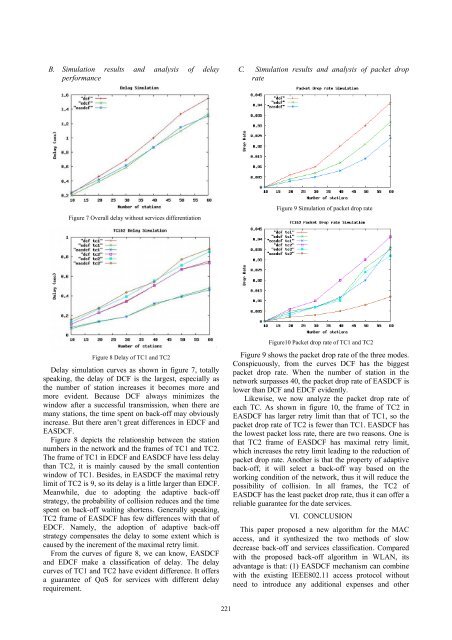
B. Simulation results and analysis of delay<br />
performance<br />
C. Simulation results and analysis of packet drop<br />
rate<br />
Figure 7 Overall delay without services differentiation<br />
Figure 9 Simulation of packet drop rate<br />
Figure 8 Delay of TC1 and TC2<br />
Delay simulation curves as shown in figure 7, totally<br />
speaking, the delay of DCF is the largest, especially as<br />
the number of station increases it becomes more and<br />
more evident. Because DCF always minimizes the<br />
window after a successful transmission, when there are<br />
many stations, the time spent on back-off may obviously<br />
increase. But there aren’t great differences in EDCF and<br />
EASDCF.<br />
Figure 8 depicts the relationship between the station<br />
numbers in the network and the frames of TC1 and TC2.<br />
The frame of TC1 in EDCF and EASDCF have less delay<br />
than TC2, it is mainly caused by the small contention<br />
window of TC1. Besides, in EASDCF the maximal retry<br />
limit of TC2 is 9, so its delay is a little larger than EDCF.<br />
Meanwhile, due to adopting the adaptive back-off<br />
strategy, the probability of collision reduces and the time<br />
spent on back-off waiting shortens. Generally speaking,<br />
TC2 frame of EASDCF has few differences with that of<br />
EDCF. Namely, the adoption of adaptive back-off<br />
strategy compensates the delay to some extent which is<br />
caused by the increment of the maximal retry limit.<br />
From the curves of figure 8, we can know, EASDCF<br />
and EDCF make a classification of delay. The delay<br />
curves of TC1 and TC2 have evident difference. It offers<br />
a guarantee of QoS for services with different delay<br />
requirement.<br />
Figure10 Packet drop rate of TC1 and TC2<br />
Figure 9 shows the packet drop rate of the three modes.<br />
Conspicuously, from the curves DCF has the biggest<br />
packet drop rate. When the number of station in the<br />
network surpasses 40, the packet drop rate of EASDCF is<br />
lower than DCF and EDCF evidently.<br />
Likewise, we now analyze the packet drop rate of<br />
each TC. As shown in figure 10, the frame of TC2 in<br />
EASDCF has larger retry limit than that of TC1, so the<br />
packet drop rate of TC2 is fewer than TC1. EASDCF has<br />
the lowest packet loss rate, there are two reasons. One is<br />
that TC2 frame of EASDCF has maximal retry limit,<br />
which increases the retry limit leading to the reduction of<br />
packet drop rate. Another is that the property of adaptive<br />
back-off, it will select a back-off way based on the<br />
working condition of the network, thus it will reduce the<br />
possibility of collision. In all frames, the TC2 of<br />
EASDCF has the least packet drop rate, thus it can offer a<br />
reliable guarantee for the date services.<br />
VI. CONCLUSION<br />
This paper proposed a new algorithm for the MAC<br />
access, and it synthesized the two methods of slow<br />
decrease back-off and services classification. Compared<br />
with the proposed back-off algorithm in WLAN, its<br />
advantage is that: (1) EASDCF mechanism can combine<br />
with the existing IEEE802.11 access protocol without<br />
need to introduce any additional expenses and other<br />
221