Download - Academy Publisher
Download - Academy Publisher
Download - Academy Publisher
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
is paramount for results evaluation and reliability of<br />
performance of the entire network. Therefore, we<br />
authenticate performance improvement in three aspects,<br />
throughput, average delay and packet drop rate.<br />
V. RESULTS AND ANALYSIS<br />
A. Simulation results and analysis of throughput<br />
A. Simulation parameters setting<br />
For Simple, simulation model conforms to<br />
IEEE802.11b standard, transfer rate of 2Mbit/s for all<br />
simulations. The following is other parameters’ setting:<br />
●Transmission delay: 1μs<br />
●Timeslot size: 20μs<br />
●SIFS: 10μs<br />
●back-off stages: 5<br />
●In each scenario, the number of station increases<br />
from 10 to 60 at the increment of 10.<br />
B. Simulation scenarios setting<br />
Simulation scenarios as shown in figure 4.<br />
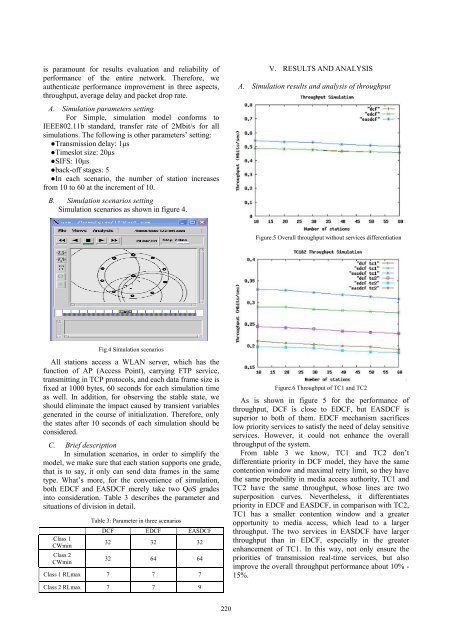
Figure.5 Overall throughput without services differentiation<br />
Fig.4 Simulation scenarios<br />
All stations access a WLAN server, which has the<br />
function of AP (Access Point), carrying FTP service,<br />
transmitting in TCP protocols, and each data frame size is<br />
fixed at 1000 bytes, 60 seconds for each simulation time<br />
as well. In addition, for observing the stable state, we<br />
should eliminate the impact caused by transient variables<br />
generated in the course of initialization. Therefore, only<br />
the states after 10 seconds of each simulation should be<br />
considered.<br />
C. Brief description<br />
In simulation scenarios, in order to simplify the<br />
model, we make sure that each station supports one grade,<br />
that is to say, it only can send data frames in the same<br />
type. What’s more, for the convenience of simulation,<br />
both EDCF and EASDCF merely take two QoS grades<br />
into consideration. Table 3 describes the parameter and<br />
situations of division in detail.<br />
Class 1<br />
CWmin<br />
Class 2<br />
CWmin<br />
Table 3: Parameter in three scenarios<br />
DCF EDCF EASDCF<br />
32 32 32<br />
32 64 64<br />
Class 1 RLmax 7 7 7<br />
Class 2 RLmax 7 7 9<br />
Figure.6 Throughput of TC1 and TC2<br />
As is shown in figure 5 for the performance of<br />
throughput, DCF is close to EDCF, but EASDCF is<br />
superior to both of them. EDCF mechanism sacrifices<br />
low priority services to satisfy the need of delay sensitive<br />
services. However, it could not enhance the overall<br />
throughput of the system.<br />
From table 3 we know, TC1 and TC2 don’t<br />
differentiate priority in DCF model, they have the same<br />
contention window and maximal retry limit, so they have<br />
the same probability in media access authority, TC1 and<br />
TC2 have the same throughput, whose lines are two<br />
superposition curves. Nevertheless, it differentiates<br />
priority in EDCF and EASDCF, in comparison with TC2,<br />
TC1 has a smaller contention window and a greater<br />
opportunity to media access, which lead to a larger<br />
throughput. The two services in EASDCF have larger<br />
throughput than in EDCF, especially in the greater<br />
enhancement of TC1. In this way, not only ensure the<br />
priorities of transmission real-time services, but also<br />
improve the overall throughput performance about 10% -<br />
15%.<br />
220