You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
87 Elementos de cálculo, volumen 1<br />
De un modo parecido definimos la notación<br />
lim f(x) = −∞<br />
x→c<br />
(el límite de f(x) cuando x tiende a c es menos infinito).<br />
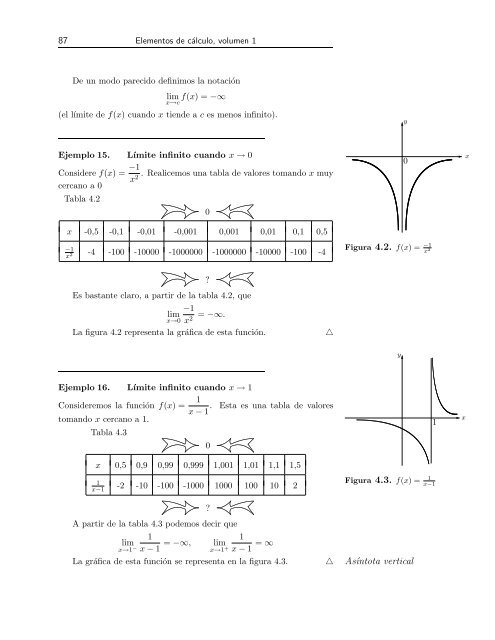
Ejemplo 15. Límite infinito cuando x → 0<br />
Considere f(x) = −1<br />
. Realicemos una tabla de valores tomando x muy<br />
x2 cercano a 0<br />
Tabla 4.2<br />
.<br />
.<br />
.<br />
.<br />
. 0<br />
.<br />
x -0,5 -0,1 -0,01 -0,001 0,001 0,01 0,1 0,5<br />
−1<br />
x 2 -4 -100 -10000 -1000000 -1000000 -10000 -100 -4<br />
.<br />
.<br />
.<br />
.<br />
. ?<br />
.<br />
Es bastante claro, a partir de la tabla 4.2, que<br />
−1<br />
lim = −∞.<br />
x→0 x2 La figura 4.2 representa la gráfica de esta función. △<br />
Ejemplo 16. Límite infinito cuando x → 1<br />
Consideremos la función f(x) = 1<br />
.<br />
x − 1<br />
tomando x cercano a 1.<br />
Esta es una tabla de valores<br />
Tabla 4.3<br />
.<br />
.<br />
.<br />
.<br />
. 0<br />
.<br />
x 0,5 0,9 0,99 0,999 1,001 1,01 1,1 1,5<br />
1<br />
x−1 -2 -10 -100 -1000 1000 100 10 2<br />
.<br />
.<br />
.<br />
.<br />
. ?<br />
.<br />
A partir de la tabla 4.3 podemos decir que<br />
lim<br />
x→1 −<br />
1<br />
= −∞, lim<br />
x − 1 x→1 +<br />
1<br />
= ∞<br />
x − 1<br />
y<br />
✻<br />
0<br />
Figura 4.2. f(x) = −1<br />
x 2<br />
y<br />
✻<br />
Figura 4.3. f(x) = 1<br />
x−1<br />
La gráfica de esta función se representa en la figura 4.3. △ Asíntota vertical<br />
1<br />
✲ x<br />
✲ x