Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
68 Elementos de cálculo, volumen 1<br />
En funciones definidas “por partes”, como la anterior, si se quiere<br />
verificar la existencia del límite en el punto o puntos donde se parte,<br />
deben calcularse separadamente los dos límites laterales y corroborarse<br />
si son iguales o no.<br />
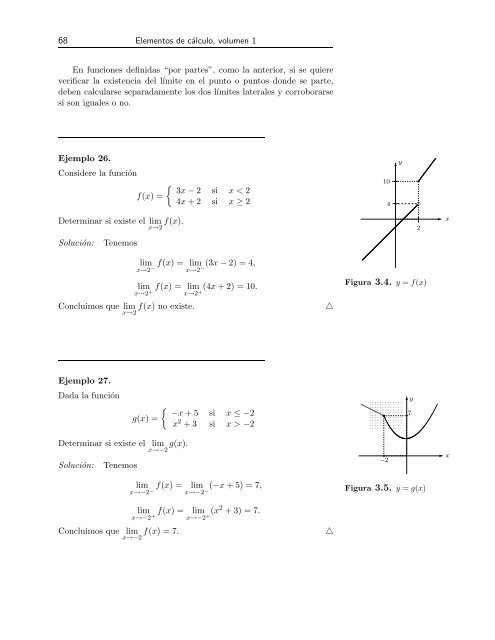
Ejemplo 26.<br />
Considere la función<br />
f(x) =<br />
Determinar si existe el lim<br />
x→2 f(x).<br />
Solución: Tenemos<br />
lim<br />
x→2<br />
lim<br />
x→2<br />
3x − 2 si x < 2<br />
4x + 2 si x ≥ 2<br />
f(x) = lim − 2) = 4,<br />
− −(3x<br />
x→2<br />
f(x) = lim + 2) = 10.<br />
+ +(4x<br />
x→2<br />
Concluimos que lim<br />
x→2 f(x) no existe. △<br />
Ejemplo 27.<br />
Dada la función<br />
g(x) =<br />
Determinar si existe el lim<br />
x→−2 g(x).<br />
Solución: Tenemos<br />
lim<br />
x→−2<br />
−x + 5 si x ≤ −2<br />
x 2 + 3 si x > −2<br />
f(x) = lim + 5) = 7,<br />
− −(−x<br />
x→−2<br />
lim f(x) = lim<br />
x→−2 + x→−2 +(x2 + 3) = 7.<br />
Concluimos que lim f(x) = 7. △<br />
x→−2<br />
10<br />
4<br />
✻ y<br />
Figura 3.4. y = f(x)<br />
. . . . . . . . . . . . . y<br />
. . . . . . . . . . . . . ✻<br />
. . . . . . . . . . . . .<br />
. . . . . . . . . . . . .<br />
. . . . . . . . . . . . .<br />
. . . . . . .<br />
. . . . . . 7<br />
. . . . . . . . . . . . .<br />
. . . . . . . . . . . . .<br />
. . . . . . . . . . . . .<br />
. . . . . . . . . . . . .<br />
. . . . . . . . . . . . .<br />
−2<br />
Figura 3.5. y = g(x)<br />
<br />
❝<br />
2<br />
♣<br />
✲<br />
x<br />
✲ x