Alberto Risueño Pérez - Gredos - Universidad de Salamanca
Alberto Risueño Pérez - Gredos - Universidad de Salamanca
Alberto Risueño Pérez - Gredos - Universidad de Salamanca
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
632<br />
Leukemia<br />
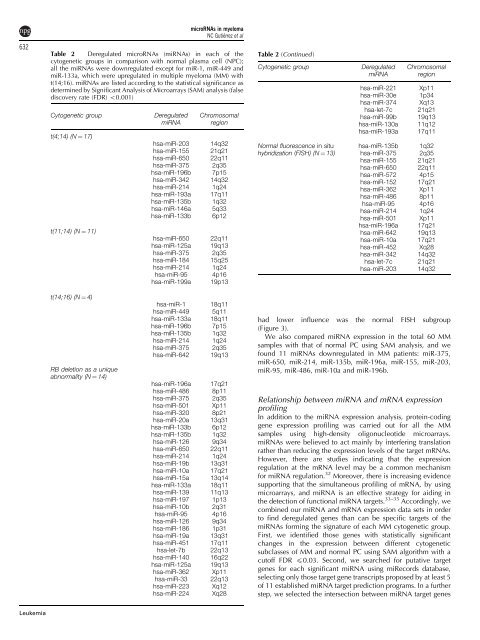
Table 2 Deregulated microRNAs (miRNAs) in each of the<br />
cytogenetic groups in comparison with normal plasma cell (NPC);<br />
all the miRNAs were downregulated except for miR-1, miR-449 and<br />
miR-133a, which were upregulated in multiple myeloma (MM) with<br />
t(14;16). miRNAs are listed according to the statistical significance as<br />
<strong>de</strong>termined by Significant Analysis of Microarrays (SAM) analysis (false<br />
discovery rate (FDR) o0.001)<br />
Cytogenetic group Deregulated<br />
miRNA<br />
t(4;14) (N ¼ 17)<br />
t(11;14) (N ¼ 11)<br />
t(14;16) (N ¼ 4)<br />
RB <strong>de</strong>letion as a unique<br />
abnormality (N ¼ 14)<br />
microRNAs in myeloma<br />
NC Gutiérrez et al<br />
Chromosomal<br />
region<br />
hsa-miR-203 14q32<br />
hsa-miR-155 21q21<br />
hsa-miR-650 22q11<br />
hsa-miR-375 2q35<br />
hsa-miR-196b 7p15<br />
hsa-miR-342 14q32<br />
hsa-miR-214 1q24<br />
hsa-miR-193a 17q11<br />
hsa-miR-135b 1q32<br />
hsa-miR-146a 5q33<br />
hsa-miR-133b 6p12<br />
hsa-miR-650 22q11<br />
hsa-miR-125a 19q13<br />
hsa-miR-375 2q35<br />
hsa-miR-184 15q25<br />
hsa-miR-214 1q24<br />
hsa-miR-95 4p16<br />
hsa-miR-199a 19p13<br />
hsa-miR-1 18q11<br />
hsa-miR-449 5q11<br />
hsa-miR-133a 18q11<br />
hsa-miR-196b 7p15<br />
hsa-miR-135b 1q32<br />
hsa-miR-214 1q24<br />
hsa-miR-375 2q35<br />
hsa-miR-642 19q13<br />
hsa-miR-196a 17q21<br />
hsa-miR-486 8p11<br />
hsa-miR-375 2q35<br />
hsa-miR-501 Xp11<br />
hsa-miR-320 8p21<br />
hsa-miR-20a 13q31<br />
hsa-miR-133b 6p12<br />
hsa-miR-135b 1q32<br />
hsa-miR-126 9q34<br />
hsa-miR-650 22q11<br />
hsa-miR-214 1q24<br />
hsa-miR-19b 13q31<br />
hsa-miR-10a 17q21<br />
hsa-miR-15a 13q14<br />
hsa-miR-133a 18q11<br />
hsa-miR-139 11q13<br />
hsa-miR-197 1p13<br />
hsa-miR-10b 2q31<br />
hsa-miR-95 4p16<br />
hsa-miR-126 9q34<br />
hsa-miR-186 1p31<br />
hsa-miR-19a 13q31<br />
hsa-miR-451 17q11<br />
hsa-let-7b 22q13<br />
hsa-miR-140 16q22<br />
hsa-miR-125a 19q13<br />
hsa-miR-362 Xp11<br />
hsa-miR-33 22q13<br />
hsa-miR-223 Xq12<br />
hsa-miR-224 Xq28<br />
Table 2 (Continued )<br />
Cytogenetic group Deregulated<br />
miRNA<br />
Chromosomal<br />
region<br />
hsa-miR-221 Xp11<br />
hsa-miR-30e 1p34<br />
hsa-miR-374 Xq13<br />
hsa-let-7c 21q21<br />
hsa-miR-99b 19q13<br />
hsa-miR-130a 11q12<br />
hsa-miR-193a 17q11<br />
Normal fluorescence in situ hsa-miR-135b 1q32<br />
hybridization (FISH) (N ¼ 13) hsa-miR-375 2q35<br />
hsa-miR-155 21q21<br />
hsa-miR-650 22q11<br />
hsa-miR-572 4p15<br />
hsa-miR-152 17q21<br />
hsa-miR-362 Xp11<br />
hsa-miR-486 8p11<br />
hsa-miR-95 4p16<br />
hsa-miR-214 1q24<br />
hsa-miR-501 Xp11<br />
hsa-miR-196a 17q21<br />
hsa-miR-642 19q13<br />
hsa-miR-10a 17q21<br />
hsa-miR-452 Xq28<br />
hsa-miR-342 14q32<br />
hsa-let-7c 21q21<br />
hsa-miR-203 14q32<br />
had lower influence was the normal FISH subgroup<br />
(Figure 3).<br />
We also compared miRNA expression in the total 60 MM<br />
samples with that of normal PC using SAM analysis, and we<br />
found 11 miRNAs downregulated in MM patients: miR-375,<br />
miR-650, miR-214, miR-135b, miR-196a, miR-155, miR-203,<br />
miR-95, miR-486, miR-10a and miR-196b.<br />
Relationship between miRNA and mRNA expression<br />
profiling<br />
In addition to the miRNA expression analysis, protein-coding<br />
gene expression profiling was carried out for all the MM<br />
samples using high-<strong>de</strong>nsity oligonucleoti<strong>de</strong> microarrays.<br />
miRNAs were believed to act mainly by interfering translation<br />
rather than reducing the expression levels of the target mRNAs.<br />
However, there are studies indicating that the expression<br />
regulation at the mRNA level may be a common mechanism<br />
for miRNA regulation. 32 Moreover, there is increasing evi<strong>de</strong>nce<br />
supporting that the simultaneous profiling of mRNA, by using<br />
microarrays, and miRNA is an effective strategy for aiding in<br />
the <strong>de</strong>tection of functional miRNA targets. 33–35 Accordingly, we<br />
combined our miRNA and mRNA expression data sets in or<strong>de</strong>r<br />
to find <strong>de</strong>regulated genes than can be specific targets of the<br />
miRNAs forming the signature of each MM cytogenetic group.<br />
First, we i<strong>de</strong>ntified those genes with statistically significant<br />
changes in the expression between different cytogenetic<br />
subclasses of MM and normal PC using SAM algorithm with a<br />
cutoff FDR p0.03. Second, we searched for putative target<br />
genes for each significant miRNA using miRecords database,<br />
selecting only those target gene transcripts proposed by at least 5<br />
of 11 established miRNA target prediction programs. In a further<br />
step, we selected the intersection between miRNA target genes