Alberto Risueño Pérez - Gredos - Universidad de Salamanca
Alberto Risueño Pérez - Gredos - Universidad de Salamanca
Alberto Risueño Pérez - Gredos - Universidad de Salamanca
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
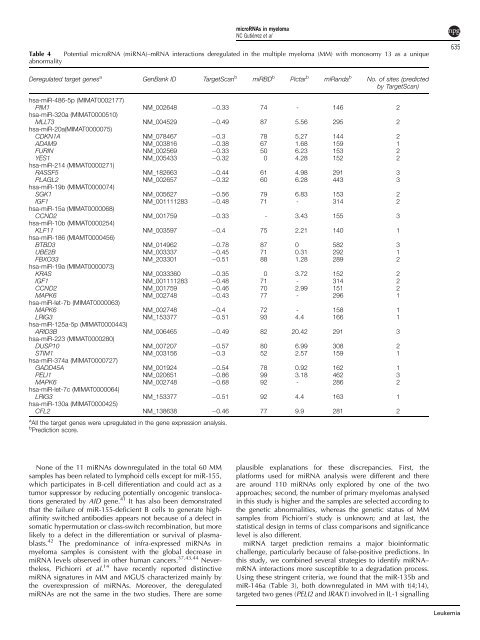
Table 4 Potential microRNA (miRNA)–mRNA interactions <strong>de</strong>regulated in the multiple myeloma (MM) with monosomy 13 as a unique<br />
abnormality<br />
Deregulated target genes a<br />
GenBank ID TargetScan b<br />
None of the 11 miRNAs downregulated in the total 60 MM<br />
samples has been related to lymphoid cells except for miR-155,<br />
which participates in B-cell differentiation and could act as a<br />
tumor suppressor by reducing potentially oncogenic translocations<br />
generated by AID gene. 41 It has also been <strong>de</strong>monstrated<br />
that the failure of miR-155-<strong>de</strong>ficient B cells to generate highaffinity<br />
switched antibodies appears not because of a <strong>de</strong>fect in<br />
somatic hypermutation or class-switch recombination, but more<br />
likely to a <strong>de</strong>fect in the differentiation or survival of plasmablasts.<br />
42 The predominance of infra-expressed miRNAs in<br />
myeloma samples is consistent with the global <strong>de</strong>crease in<br />
miRNA levels observed in other human cancers. 37,43,44 Nevertheless,<br />
Pichiorri et al. 14 have recently reported distinctive<br />
miRNA signatures in MM and MGUS characterized mainly by<br />
the overexpression of miRNAs. Moreover, the <strong>de</strong>regulated<br />
miRNAs are not the same in the two studies. There are some<br />
miRBD b<br />
Pictar b<br />
miRanda b<br />
No. of sites (predicted<br />
by TargetScan)<br />
hsa-miR-486-5p (MIMAT0002177)<br />
PIM1 NM_002648 0.33 74 - 146 2<br />
hsa-miR-320a (MIMAT0000510)<br />
MLLT3 NM_004529 0.49 87 5.56 295 2<br />
hsa-miR-20a(MIMAT0000075)<br />
CDKN1A NM_078467 0.3 78 5.27 144 2<br />
ADAM9 NM_003816 0.38 67 1.68 159 1<br />
FURIN NM_002569 0.33 50 6.23 153 2<br />
YES1 NM_005433 0.32 0 4.28 152 2<br />
hsa-miR-214 (MIMAT0000271)<br />
RASSF5 NM_182663 0.44 61 4.98 291 3<br />
PLAGL2 NM_002657 0.32 60 6.28 443 3<br />
hsa-miR-19b (MIMAT0000074)<br />
SGK1 NM_005627 0.56 79 6.83 153 2<br />
IGF1 NM_001111283 0.48 71 - 314 2<br />
hsa-miR-15a (MIMAT0000068)<br />
CCND2 NM_001759 0.33 - 3.43 155 3<br />
hsa-miR-10b (MIMAT0000254)<br />
KLF11 NM_003597 0.4 75 2.21 140 1<br />
hsa-miR-186 (MIAMT0000456)<br />
BTBD3 NM_014962 0.78 87 0 582 3<br />
UBE2B NM_003337 0.45 71 0.31 292 1<br />
FBXO33 NM_203301 0.51 88 1.28 289 2<br />
hsa-miR-19a (MIMAT0000073)<br />
KRAS NM_0033360 0.35 0 3.72 152 2<br />
IGF1 NM_001111283 0.48 71 - 314 2<br />
CCND2 NM_001759 0.46 70 2.99 151 2<br />
MAPK6 NM_002748 0.43 77 - 296 1<br />
hsa-miR-let-7b (MIMAT0000063)<br />
MAPK6 NM_002748 0.4 72 - 158 1<br />
LRIG3 NM_153377 0.51 93 4.4 166 1<br />
hsa-miR-125a-5p (MIMAT0000443)<br />
ARID3B NM_006465 0.49 82 20.42 291 3<br />
hsa-miR-223 (MIMAT0000280)<br />
DUSP10 NM_007207 0.57 80 6.99 308 2<br />
STIM1 NM_003156 0.3 52 2.57 159 1<br />
hsa-miR-374a (MIMAT0000727)<br />
GADD45A NM_001924 0.54 78 0.92 162 1<br />
PELI1 NM_020651 0.86 99 3.18 462 3<br />
MAPK6 NM_002748 0.68 92 - 286 2<br />
hsa-miR-let-7c (MIMAT0000064)<br />
LRIG3 NM_153377 0.51 92 4.4 163 1<br />
hsa-miR-130a (MIMAT0000425)<br />
CFL2 NM_138638 0.46 77 9.9 281 2<br />
a All the target genes were upregulated in the gene expression analysis.<br />
b Prediction score.<br />
microRNAs in myeloma<br />
NC Gutiérrez et al<br />
plausible explanations for these discrepancies. First, the<br />
platforms used for miRNA analysis were different and there<br />
are around 110 miRNAs only explored by one of the two<br />
approaches; second, the number of primary myelomas analysed<br />
in this study is higher and the samples are selected according to<br />
the genetic abnormalities, whereas the genetic status of MM<br />
samples from Pichiorri’s study is unknown; and at last, the<br />
statistical <strong>de</strong>sign in terms of class comparisons and significance<br />
level is also different.<br />
miRNA target prediction remains a major bioinformatic<br />
challenge, particularly because of false-positive predictions. In<br />
this study, we combined several strategies to i<strong>de</strong>ntify miRNA–<br />
mRNA interactions more susceptible to a <strong>de</strong>gradation process.<br />
Using these stringent criteria, we found that the miR-135b and<br />
miR-146a (Table 3), both downregulated in MM with t(4;14),<br />
targeted two genes (PELI2 and IRAK1) involved in IL-1 signalling<br />
635<br />
Leukemia