Reading Working Papers in Linguistics 4 (2000) - The University of ...
Reading Working Papers in Linguistics 4 (2000) - The University of ...
Reading Working Papers in Linguistics 4 (2000) - The University of ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
J. MARSHALL<br />
case that these people are passive recipients <strong>of</strong> this <strong>in</strong>fluence. Many<br />
commuters take a job <strong>in</strong> an urban centre <strong>in</strong> order to ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> a rural lifestyle.<br />
This is when their life modes become complex and composite, even if they are<br />
still ideologically determ<strong>in</strong>ed by the rural life mode (Pedersen 1994: 90).<br />
<strong>The</strong>se people are more reliable at work and less supportive <strong>of</strong> pay disputes;<br />
they are farmers and rema<strong>in</strong> so. This may be a transitional stage <strong>in</strong> which<br />
more and more <strong>of</strong> the rural life mode will be displaced by the urban one, but<br />
Pedersen suspects that it is a reasonably stable situation which can last the<br />
lifetime <strong>of</strong> the <strong>in</strong>dividual and even be passed on to the next generation. She<br />
believes that life modes are not specifiable to the po<strong>in</strong>t where one can measure<br />
them directly, but they can illum<strong>in</strong>ate l<strong>in</strong>guistic and other behavioural patterns<br />
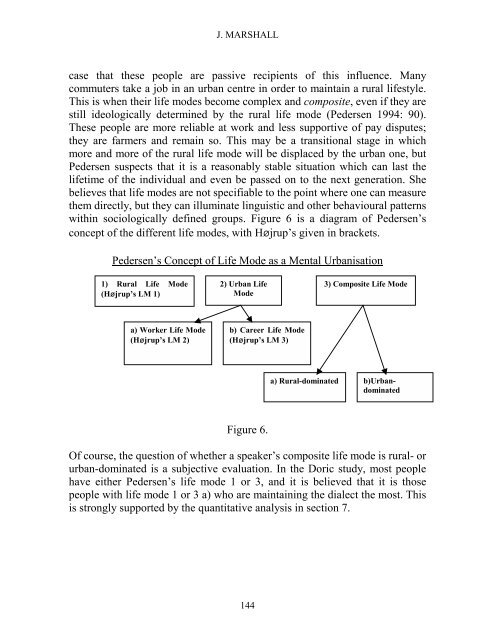
with<strong>in</strong> sociologically def<strong>in</strong>ed groups. Figure 6 is a diagram <strong>of</strong> Pedersen’s<br />
concept <strong>of</strong> the different life modes, with Højrup’s given <strong>in</strong> brackets.<br />
Pedersen’s Concept <strong>of</strong> Life Mode as a Mental Urbanisation<br />
1) Rural Life Mode<br />
(Højrup’s LM 1)<br />
2) Urban Life<br />
Mode<br />
3) Composite Life Mode<br />
a) Worker Life Mode<br />
(Højrup’s LM 2)<br />
b) Career Life Mode<br />
(Højrup’s LM 3)<br />
a) Rural-dom<strong>in</strong>ated b)Urbandom<strong>in</strong>ated<br />
Figure 6.<br />
Of course, the question <strong>of</strong> whether a speaker’s composite life mode is rural- or<br />
urban-dom<strong>in</strong>ated is a subjective evaluation. In the Doric study, most people<br />
have either Pedersen’s life mode 1 or 3, and it is believed that it is those<br />
people with life mode 1 or 3 a) who are ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g the dialect the most. This<br />
is strongly supported by the quantitative analysis <strong>in</strong> section 7.<br />
144