Reading Working Papers in Linguistics 4 (2000) - The University of ...
Reading Working Papers in Linguistics 4 (2000) - The University of ...
Reading Working Papers in Linguistics 4 (2000) - The University of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
P. KERSWILL & A. WILLIAMS<br />
naturalness. Restrict<strong>in</strong>g the discussion to just this factor is because, <strong>in</strong> this<br />
project, all the rema<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g factors are constant, even if their values are not<br />
always known. Where this fails, we look at the language-<strong>in</strong>ternal salience<br />
factors (phonological contrast and phonetic distance), and then at other<br />
language-external, sociol<strong>in</strong>guistic/social-psychological factors.<br />
Consonants<br />
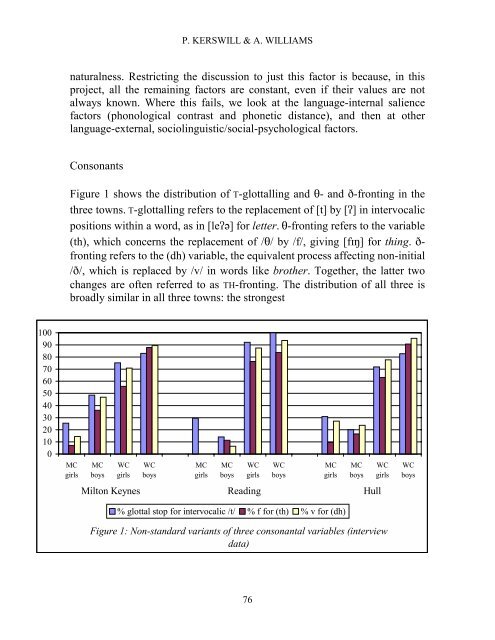
Figure 1 shows the distribution <strong>of</strong> T-glottall<strong>in</strong>g and ?- and 1-front<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> the<br />
three towns. T-glottall<strong>in</strong>g refers to the replacement <strong>of</strong> [t] by [C] <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong>tervocalic<br />
positions with<strong>in</strong> a word, as <strong>in</strong> [leCJ] for letter. ?-front<strong>in</strong>g refers to the variable<br />
(th), which concerns the replacement <strong>of</strong> /?/ by /f/, giv<strong>in</strong>g [fF@] for th<strong>in</strong>g. 1-<br />
front<strong>in</strong>g refers to the (dh) variable, the equivalent process affect<strong>in</strong>g non-<strong>in</strong>itial<br />
/1/, which is replaced by /v/ <strong>in</strong> words like brother. Together, the latter two<br />
changes are <strong>of</strong>ten referred to as TH-front<strong>in</strong>g. <strong>The</strong> distribution <strong>of</strong> all three is<br />
broadly similar <strong>in</strong> all three towns: the strongest<br />
100<br />
90<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
MC<br />
girls<br />
MC<br />
boys<br />
WC<br />
girls<br />
WC<br />
boys<br />
MC<br />
girls<br />
MC<br />
boys<br />
WC<br />
girls<br />
WC<br />
boys<br />
MC<br />
girls<br />
MC<br />
boys<br />
WC<br />
girls<br />
WC<br />
boys<br />
Milton Keynes<br />
<strong>Read<strong>in</strong>g</strong><br />
Hull<br />
% glottal stop for <strong>in</strong>tervocalic /t/ % f for (th) % v for (dh)<br />
Figure 1: Non-standard variants <strong>of</strong> three consonantal variables (<strong>in</strong>terview<br />
data)<br />
76