How To Rebuild Your Ford V-8 351C-351M-400-429-460.pdf - Index of
How To Rebuild Your Ford V-8 351C-351M-400-429-460.pdf - Index of
How To Rebuild Your Ford V-8 351C-351M-400-429-460.pdf - Index of
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
When measuring piston diameter, do it level Scuff marks on piston skirt reveal engine<br />
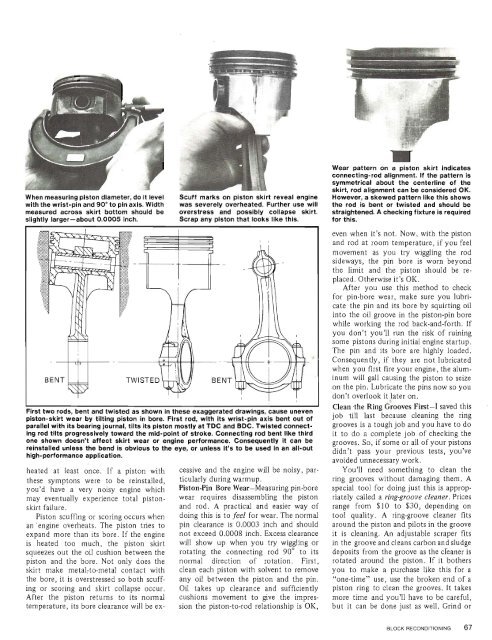
Wear pattern on a piston skirt indicates<br />
connecting-rod alignment. If the pattern is<br />
symmetrical about the centerline <strong>of</strong> the<br />
skirt, rod alignment can be considered OK.<br />
ow ever, a skewed pattern like this shows<br />
with the wrist-pin and 90" to pin axis. Width was severely overheated. Further use will the rod is bent or twisted and should be<br />
measured across skirt bottom should be overstress and possibly collapse skirt. straightened. A checking fixture is required<br />
slightly larger-about 0.0005 inch. Scrap any piston that looks like this. for this.<br />
I<br />
I<br />
First two rods, bent and twisted as shown in these exaggerated drawlngs, cause uneven<br />
piston-skirt wear by tilting piston in bore. First rod, with its wrist-pin axis bent out <strong>of</strong><br />
parallel with its bearing journal, tilts its piston mostly at T DC and BDC. Twisted connecting<br />
rod tilts progressively toward the mid-point <strong>of</strong> stroke. Connecting rod bent like third<br />
one shown doesn't affect skirt wear or engine performance. Consequently it can be<br />
reinstalled unless the bend is obvious to the eye, or unless it's to be used In an all-out<br />
high-performance application.<br />
heated at least once. If a piston with<br />
these symptons were to be reinstalled,<br />
you'd have a very noisy engine which<br />
may eventually experience total pistonskirt<br />
failure.<br />
Piston scuffing or scoring occurs when<br />
an 'engne overheats. The piston tries to<br />
expand more than its bore. If the engine<br />
is heated too much, the piston skirt<br />
squeezes out the oil cushion between the<br />
piston and the bore. Not only does the<br />
skirt make metalrto-metal contact with<br />
the bore, it is overstressed so both scuffing<br />
or scoring and skirt collapse occur.<br />
After the piston returns to its normal<br />
temperature, its bore clearance will be ex-<br />
cessive and the engine will be noisy, particularly<br />
during warmup.<br />
Piston-Pin Bore Wear-Measuring pin-bore<br />
wear requires disassembling the piston<br />
and rod. A practical and easier way <strong>of</strong><br />
doing this is to feel for wear. The normal<br />
pin clearance is 0.0003 inch and should<br />
not exceed 0.0008 inch. Excess clearance<br />
will show up when you try wiggling or<br />
rotating the connecting rod 90' to its<br />
normal direction <strong>of</strong> rotation. First,<br />
clean each piston with solvent to remove<br />
any oil between the piston and the pin.<br />
Oil takes up clearance and sufficiently<br />
cushions movement to give the impression<br />
the piston-to-rod relationship is OK,<br />
even when it's not. Now, with the piston<br />
and rod at room temperature, if you feel<br />
movement as you try wiggling the rod<br />
sideways, the pin bore is worn beyond<br />
the limit and the piston should be replaced.<br />
Otherwise it's OK.<br />
After you use this method to check<br />
for pin-bore wear, make sure you lubricate<br />
the pin and its bore by squirting oil<br />
into the oil groove in the piston-pin bore<br />
while working the rod back-and-forth. If<br />
you don't you'll run the risk <strong>of</strong> ruining<br />
some pistons during initial engine startup.<br />
The pin and its bore are highly loaded.<br />
Consequently, if they are not lubricated<br />
when you first fire your engine, the aluminum<br />
will gall causing the piston to seize<br />
.on the pin. Lubricate the pins now so you<br />
don't overlook itJater on.<br />
Clean the Ring G~OOV~S First-l saved this<br />
job till last because cleaning the ring<br />
grooves is a tough job and you have to do<br />
it to do a complete job <strong>of</strong> checking the<br />
grooves. So, if some or all <strong>of</strong> your pistons<br />
didn't pass your previous tests, you've<br />
avoided unnecessary work.<br />
You'll need something to clean the<br />
ring grooves without damaging them. A<br />
special tool for doing just this is appropriately<br />
called a ring-groove cleaner. Prices<br />
range from $10 to $30, depending on<br />
tool quality. A ring-groove cleaner fits<br />
around the piston and pilots in the groove<br />
it is cleaning. An adjustable scraper fits<br />
in the groove and cleans carbon and sludge<br />
deposits from the groove as the cl'eaner is<br />
rotated around the piston. If it bothers<br />
you to make a purchase like this for a<br />
"one-time" use, use the broken end <strong>of</strong> a<br />
piston ring to clean the grooves. It takes<br />
more time and you'll have to be careful,<br />
but it can be done just as well. Grind or