Tsunami - Beckman Institute Laser Resource Center
Tsunami - Beckman Institute Laser Resource Center
Tsunami - Beckman Institute Laser Resource Center
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Table of Contents<br />
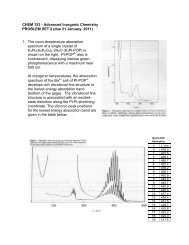
Figure 4-7: Typical MONITOR signal (DC offset: 0 V) .................... 4-10<br />
Figure 4-8: Typical SYNC signal (DC offset: .1.25 V) .................... 4-10<br />
Figure 4-9: Model 3910 RegulatorIFilter Purge Unit ...................... 4-12<br />
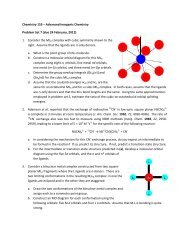
Figure 5-1 : Typical <strong>Tsunami</strong> Head and Pump <strong>Laser</strong> Head Layout .......... 5-2<br />
Figure 5-2: Routing Mirror Setup ...................................... 5-4<br />
Figure 5-3: Typical System Interconnect Diagram ........................ 5-8<br />
Figure 5-4: Gires-Tournois Interferometer (GTI). The input bezel<br />
and side rail are removed for clarity and the motorized mount<br />
shown is available only on Lok-to-Clock systems ...................... 5-12<br />
Figure 5-5: <strong>Tsunami</strong> <strong>Laser</strong> Head PC Board Connections (Cover Removed) . 5-13<br />
Figure 5-6: Photodiode PC Board ..................................... 5-14<br />
Figure 6-1 : Beam Path for <strong>Tsunami</strong> Model 3960C<br />
Femtosecond Configuration ......................................... 6-2<br />
Figure 6-2: Beam Path for <strong>Tsunami</strong> Model 3950C<br />
Picosecond Configuration ........................................... 6-3<br />
Figure 6-3: Birefringent Filter .......................................... 6-4<br />
Figure 6-4: The M3 Translation Stage .................................. 6-5<br />
Figure 6-5: Cavity Focus Mirrors M2 and M3 and the <strong>Laser</strong> Rod ........... 6-6<br />
Figure 6-6: Pump Mirrors PI and P2 ................................... 6-7<br />
Figure 6-7: MI and M3 Images Focused on the White Card ............... 6-8<br />
Figure 6-8: Locations of M4 and M5 for fs and ps operation ................ 6-9<br />
Figure 6-9: The Slit Control ........................................... 6-10<br />
Figure 6-1 0: Four PrismIFour Mirror Section of <strong>Laser</strong> Cavity .............. 6-11<br />
Figure 6-11 : Photodiode PC board ..................................... 6-14<br />
Figure 6-12: AOM. Output Coupler. Photodiode PC Board.<br />
and Beam Splitter ................................................. 6-17<br />
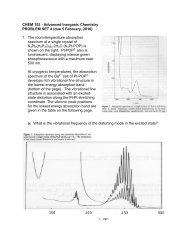
Figure 6-1 3: Precursor to mode locking a pulse (ps) as seen<br />
through an autocorrelator on an oscilloscope .......................... 6-19<br />
Figure 6-14: Beam Path for <strong>Tsunami</strong> Model 3960C<br />
Femtosecond Configuration ......................................... 6-22<br />
Figure 6-15: Beam Path for <strong>Tsunami</strong> Model 3950C<br />
Picosecond Configuration ........................................... 6-22<br />
Figure 6-1 6: Prl Prism Translation Adjust and Setscrew .................. 6-24<br />
Figure 6-1 7: Gires-Tournois Interferometer (GTI) . The input<br />
bezel and side rail are removed for clarity and the motorized<br />
mount shown is available only on Lok-to-Clock systems ................ 6-25<br />
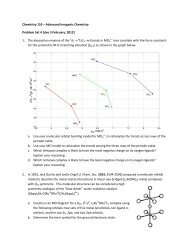
Figure 6-18: Prl/Pr4 prisms showing placement of beam . Refer to<br />
Table 6-3 for the value of x .......................................... 6-28