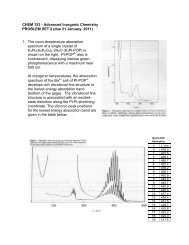
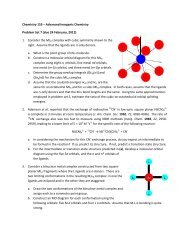
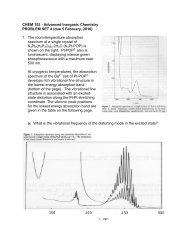
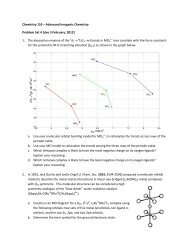
Tsunami - Beckman Institute Laser Resource Center
Tsunami - Beckman Institute Laser Resource Center
Tsunami - Beckman Institute Laser Resource Center
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
,, , , 8 , , , , , , , , , , , , , ., , , .," , ,- 1 1 . 1 , 1,1111 ,. I- -.<br />
I . .<br />
<strong>Tsunami</strong><br />
Typical Set-ups<br />
Example 1 : Synchronizing Pulses from<br />
Two LTC <strong>Tsunami</strong> <strong>Laser</strong>s<br />
A typical experiment set-up is shown in Figure 8-6. <strong>Tsunami</strong> "A" is the<br />
master oscillator, and the 80 MHz REF OUT from its Model 3930 Lok-to-<br />
Clock electronics module is used for the Model 3930 REF IN signal of<br />
<strong>Tsunami</strong> "B." The output beams of both lasers are combined and<br />
overlapped as shown in the figure.<br />
In an experiment using synchronized pulses from two LTC <strong>Tsunami</strong> lasers,<br />
the timing function (using either the manual TlMlNG controls or the sweep<br />
generator) facilitates locating your pulses by adjusting the timing of one<br />
pulse with respect to the other. Use the sweep to find the pulses, use the<br />
TlMlNG controls to overlap them. Note: modifying the laser frequency by<br />
50 Hz is equal to about 1 Fm of motion at mirror MI.<br />
1. Adjust each <strong>Tsunami</strong> laser for optimum performance at the desired<br />
wavelengths.<br />
2. With each Model 3930 unlocked (there are no illuminated segments<br />
in either STATUS display), place a photodiode (e.g., an ET2000) at the<br />
source of the experiment.<br />
3. Adjust the optical alignment so the pulse train for each <strong>Tsunami</strong> laser<br />
can be identified.<br />
4. Set up and lock <strong>Tsunami</strong> "A" as outlined in "Operation Notes" above.<br />
5. Repeat step 4 for <strong>Tsunami</strong> "B."<br />
The oscilloscope display should now show two pulse trains with a fixed<br />
delay. The pulse trains are now synchronized, but are probably not<br />
overlapped in time.<br />
6. Verify the time between the pulse trains can be varied by using the<br />
coarse TlMlNG control.<br />
The TlMlNG control on each system provides up to 2 ns of adjustment.<br />
If the pulses are more than 2 ns apart, change the length of the cable<br />
between the two Model 3930s (30 cm of cable corresponds to about 1<br />
ns of delay). Do not modify the cables between the laser head and the<br />
Model 3955! When the cable length is optimized, activate the sweep<br />
generator (by pressing the TlMlNG button) on the <strong>Tsunami</strong> "B" Model<br />
3930 and observe the pulses from <strong>Tsunami</strong> "B" sweeping back and<br />
forth over those from <strong>Tsunami</strong> "A."<br />
8-1 0