- Page 3 and 4:
Science, Strategy and WarThe Strate
- Page 5 and 6:
We are survival machines.Richard Da
- Page 7 and 8:
CONTENTS1. INTRODUCTION............
- Page 9 and 10:
Introduction.......................
- Page 11 and 12:
1. INTRODUCTIONTo flourish and grow
- Page 13 and 14:
testing of the decision selected by
- Page 15 and 16:
momentum and tempo, which in combin
- Page 17 and 18:
tracing the history of war Boyd saw
- Page 19 and 20:
in general. Referring to Karl Poppe
- Page 21 and 22:
constitute an argument about strate
- Page 23:
2. ON STRATEGY AND STRATEGIC THEORY
- Page 26 and 27:
its internal make up and the dynami
- Page 28 and 29:
strategist’s task is not to creat
- Page 30 and 31:
must be holistic, paying due respec
- Page 32 and 33:
Such a division can also be discern
- Page 34 and 35:
sensibility that would be capable o
- Page 36 and 37:
Why strategic theorizing is difficu
- Page 38 and 39:
truth is independent of human belie
- Page 40 and 41:
policy, is policy’ 107 . Subseque
- Page 42 and 43:
of systems of thought which will gu
- Page 44 and 45:
Science and Strategic TheoryDominan
- Page 46 and 47:
the major intellectual currents tha
- Page 48 and 49:
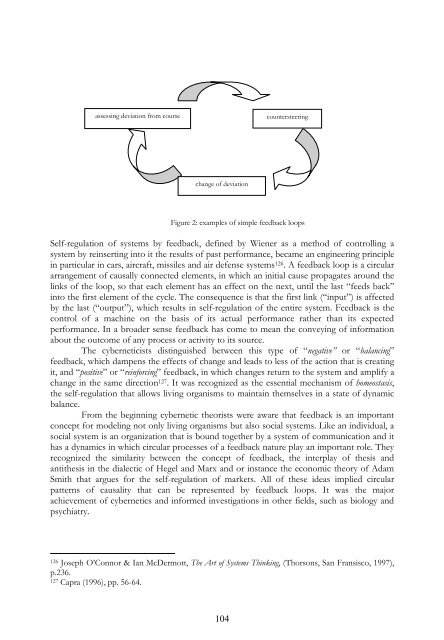
friction, which is infused with the
- Page 50 and 51:
3. THE SEEDS OF A THEORY AND THE FE
- Page 52 and 53:
Slowly his writings matured. In 196
- Page 54 and 55:
This situation also reflected the d
- Page 56 and 57:
at the cost of airspeed depletion)
- Page 58 and 59:
and air power theorists are notably
- Page 60 and 61:
Lawrence wrote Liddell Hart that fo
- Page 62 and 63:
The Indirect ApproachThe foregoing
- Page 64 and 65: in weakening the opponent’s will
- Page 66 and 67: standing in a direct theoretical li
- Page 68 and 69: perfect information, so Chapter 9 r
- Page 70 and 71: According with the enemy is the ass
- Page 72 and 73: preconceived battle plan depends up
- Page 74 and 75: mental or moral, instead they aim t
- Page 76 and 77: calculation, based on the assumptio
- Page 78 and 79: Turbulent environmentThis convictio
- Page 80 and 81: the introduction of the M1 Abrams t
- Page 82 and 83: campaign with which it was most com
- Page 84 and 85: The debates resulted via the improv
- Page 86 and 87: emphasized being more responsive, a
- Page 88 and 89: 4. SCIENCE: BOYD’S FOUNTAINKnowle
- Page 90 and 91: The list exceeds 20 pages. Indeed,
- Page 92 and 93: counter-culture. He had read severa
- Page 94 and 95: Popper’s Evolutionary Epistemolog
- Page 96 and 97: species. Finally, theories, unlike
- Page 98 and 99: discovery’ 39 . ‘We have here t
- Page 100 and 101: for failure and an encouragement fo
- Page 102 and 103: investigated and a change of the ru
- Page 104 and 105: Paradigm shiftBeyond NewtonIn the p
- Page 106 and 107: philosophical aspects, Prigogine an
- Page 108 and 109: uncertainty in another “conjugate
- Page 110 and 111: The link between thermodynamics and
- Page 112 and 113: As Ludwig Bertalanffy noted, the gr
- Page 116 and 117: the system by the environment or ot
- Page 118 and 119: A slightly more complex model from
- Page 120 and 121: implementation of the right program
- Page 122 and 123: The model below shows this process
- Page 124 and 125: The process of learning, and the pr
- Page 126 and 127: Positive indicatorsNegative indicat
- Page 128 and 129: In Patterns of Conflict he also emp
- Page 130 and 131: progressed and developed a new lang
- Page 132 and 133: advances in knowledge, adaptation,
- Page 134 and 135: TraditionalReductionismLinear causa
- Page 136 and 137: exist only because they are open. T
- Page 138 and 139: Concentration of chemical ANew stab
- Page 140 and 141: It preserves the web-like pattern o
- Page 142 and 143: Orientation shapes the character of
- Page 144 and 145: either. The edge of chaos is where
- Page 146 and 147: The final region is the boundary be
- Page 148 and 149: Levels of adaptationThis naturally
- Page 150 and 151: Operate inside adversary’s OODA l
- Page 152 and 153: Organisms which are internally cons
- Page 154 and 155: The last mentioned feature implies
- Page 156 and 157: mathematics, in short chaos and com
- Page 158 and 159: Such efforts have lead to suggestio
- Page 160 and 161: processes are maintained simultaneo
- Page 162 and 163: Boyd’s views on command and contr
- Page 164 and 165:
Several of these ideas surface in B
- Page 166 and 167:
problems they seek to comprehend or
- Page 168 and 169:
ehavior in reaction to what the oth
- Page 170 and 171:
sciences, which he termed a new int
- Page 172 and 173:
egulations, orders, and other means
- Page 174 and 175:
as focus for military planning on t
- Page 176 and 177:
A Discourse and the scientific Zeit
- Page 178 and 179:
Sharpening our mental capabilities
- Page 180 and 181:
perceive it’ 184 . By trying to c
- Page 182 and 183:
Ensure a large variety of conceptua
- Page 184 and 185:
The main intent of the effort is to
- Page 186 and 187:
e true. Thus tested and refined, it
- Page 188 and 189:
particulars or we can start with th
- Page 190 and 191:
inconsistencies may emerge to stifl
- Page 192 and 193:
although not exact1y -- since the u
- Page 194 and 195:
eality 29 . As indicated earlier, t
- Page 196 and 197:
He then incorporates a section of t
- Page 198 and 199:
Attack enemy’s plans as best poli
- Page 200 and 201:
planning process which included var
- Page 202 and 203:
Boyd does not find fault with these
- Page 204 and 205:
oth methods the same processes seem
- Page 206 and 207:
strategic planning in light of the
- Page 208 and 209:
gauged all the conditions indicated
- Page 210 and 211:
Blitzkrieg disrupts the connections
- Page 212 and 213:
- a medium to realize superior inte
- Page 214 and 215:
Only the fourth condition relates t
- Page 216 and 217:
Shape and exploit crises environmen
- Page 218 and 219:
penetrate an adversary to subvert,
- Page 220 and 221:
Maneuver Conflict - as practices by
- Page 222 and 223:
In light of his previous observatio
- Page 224 and 225:
difficult) subordinates that accept
- Page 226 and 227:
This then leads to the second wrap-
- Page 228 and 229:
mask one’s own system against any
- Page 230 and 231:
dimension on the behavior of a stra
- Page 232 and 233:
Theme for Disintegration and Collap
- Page 234 and 235:
Strategic AimDiminish adversary’s
- Page 236 and 237:
ApplicationRevisiting Sun Tzu, rein
- Page 238 and 239:
The general underlying idea of Coun
- Page 240 and 241:
to victory by connecting them to th
- Page 242 and 243:
destruction and creation to his inv
- Page 244 and 245:
Boyd’s inspiration also came in p
- Page 246 and 247:
The Big O: Orientation.The ensuing
- Page 248 and 249:
implicit cross-referencing process
- Page 250 and 251:
Magnify adversary’s friction and
- Page 252 and 253:
This differs from traditional views
- Page 254 and 255:
patterns that produced success in m
- Page 256 and 257:
General SurveyIn this section his i
- Page 258 and 259:
city, however, the situation is qui
- Page 260 and 261:
“Destruction and Creation”, by
- Page 262 and 263:
So Boyd discerns within the adversa
- Page 264 and 265:
On isolation and interactionPhysica
- Page 266 and 267:
The Art of Success:Shape or influen
- Page 268 and 269:
The meaning of strategy and the art
- Page 270 and 271:
however is not much different, but
- Page 272 and 273:
Examples from EngineeringSome Outst
- Page 274 and 275:
words, in order to gain a richer im
- Page 276 and 277:
what applies to science and enginee
- Page 278 and 279:
technology, is connected to the gam
- Page 280 and 281:
The real OODA loop270
- Page 282 and 283:
This relates the OODA loop clearly
- Page 284 and 285:
for a process of learning, of evolv
- Page 286 and 287:
thing any system is constantly faci
- Page 288 and 289:
communication and explicit directio
- Page 290 and 291:
8. CONCLUSIONThe history of science
- Page 292 and 293:
found himself in. To Sun Tzu Boyd a
- Page 294 and 295:
strategy. He elaborates on several
- Page 296 and 297:
ehavior, demonstrating the value of
- Page 298 and 299:
film, sociology, geography, literar
- Page 300 and 301:
That social scientific knowledge, o
- Page 302 and 303:
undertakes to improve its own perfo
- Page 304 and 305:
The reflexive nature of modern soci
- Page 306 and 307:
the context within which the situat
- Page 308 and 309:
“road maps for action”, but rat
- Page 310 and 311:
all point at the changes the techno
- Page 312 and 313:
central sign of post-modernity. In
- Page 314 and 315:
a revolution in military affairs oc
- Page 316 and 317:
This will affect war and warfare:
- Page 318 and 319:
Athena’s Camp. They see swarming
- Page 320 and 321:
commanders to improve their decisio
- Page 322 and 323:
Military War Beyond Military War No
- Page 324 and 325:
schemas. Gell-Mann developed the id
- Page 326 and 327:
extent in the novel approach for th
- Page 328 and 329:
ANNEX B: BIBLIOGRAPHY OF PATTERNS O
- Page 330 and 331:
LeBoeuf, Michael, “GMP, The Great
- Page 332 and 333:
Wolf, Eric R., “Peasant Wars of t
- Page 334 and 335:
Bartolomasi, Paolo: ‘The Realitie
- Page 336 and 337:
Cohen, William S.: Report of the Qu
- Page 338 and 339:
Fukuyama, Francis: The Great Disrup
- Page 340 and 341:
Hughes, Daniel: ‘Abuses of German
- Page 342 and 343:
Lewin, Roger, and Birute Regine:
- Page 344 and 345:
Murdock, Paul, ‘Principles of War
- Page 346 and 347:
Rosenau, James, N.: ‘Many Damn Th
- Page 348 and 349:
Walt, Stephen M.: ‘Rigor or Rigor