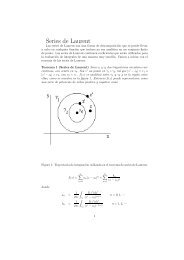
- Page 1 and 2:
INSTITUTO POLITÉCNICO NACIONALESCU
- Page 3 and 4:
INSTITUTO POLITECNICO NACIONALSECRE
- Page 5 and 6:
RESUMENUsando el método de mapeos
- Page 7 and 8:
ContenidoINTRODUCCIÓNiiiCAPÍTULO
- Page 9 and 10:
INTRODUCCIÓNMuchos son los misteri
- Page 11 and 12:
INTRODUCCIÓNvEn este trabajo, pres
- Page 13 and 14:
CAPÍTULO 1RELATIVIDAD GENERAL Y ES
- Page 15 and 16:
1.1. RELATIVIDAD GENERAL Y ESPECIAL
- Page 17 and 18:
1.1. RELATIVIDAD GENERAL Y ESPECIAL
- Page 19 and 20:
1.1. RELATIVIDAD GENERAL Y ESPECIAL
- Page 21 and 22:
1.1. RELATIVIDAD GENERAL Y ESPECIAL
- Page 23 and 24:
1.1. RELATIVIDAD GENERAL Y ESPECIAL
- Page 25 and 26:
1.1. RELATIVIDAD GENERAL Y ESPECIAL
- Page 27 and 28:
1.1. RELATIVIDAD GENERAL Y ESPECIAL
- Page 29 and 30:
1.2. TEORíA DE CUERDAS 17donde es
- Page 31 and 32:
1.2. TEORíA DE CUERDAS 19Si elegim
- Page 33 and 34:
1.2. TEORíA DE CUERDAS 21La Teorí
- Page 35 and 36:
CAPÍTULO 2GEOMETRÍA DIFERENCIAL Y
- Page 37 and 38:
2.2. RELACIONES DE EQUIVALENCIA Y E
- Page 39 and 40:
2.2. RELACIONES DE EQUIVALENCIA Y E
- Page 41 and 42:
2.2. RELACIONES DE EQUIVALENCIA Y E
- Page 43 and 44:
2.3. ESPACIOS VECTORIALES 31De…ni
- Page 45 and 46:
2.4. TENSORES Y P-FORMAS 33La acci
- Page 47 and 48:
2.4. TENSORES Y P-FORMAS 35Los tens
- Page 49 and 50:
2.5. ESPACIOS TOPOLÓGICOS Y VARIED
- Page 51 and 52:
2.5. ESPACIOS TOPOLÓGICOS Y VARIED
- Page 53 and 54:
2.5. ESPACIOS TOPOLÓGICOS Y VARIED
- Page 55 and 56:
2.5. ESPACIOS TOPOLÓGICOS Y VARIED
- Page 57 and 58: 2.5. ESPACIOS TOPOLÓGICOS Y VARIED
- Page 59 and 60: 2.5. ESPACIOS TOPOLÓGICOS Y VARIED
- Page 61 and 62: 2.5. ESPACIOS TOPOLÓGICOS Y VARIED
- Page 63 and 64: 2.6. HACES FIBRADOS 512.6. Haces Fi
- Page 65 and 66: 2.6. HACES FIBRADOS 53Grá…cament
- Page 67 and 68: 2.6. HACES FIBRADOS 55Según, la de
- Page 69 and 70: 2.6. HACES FIBRADOS 57Proposición
- Page 71 and 72: 2.6. HACES FIBRADOS 59lo que en un
- Page 73 and 74: CAPÍTULO 3ÁLGEBRAS Y GRUPOS DE LI
- Page 75 and 76: 3.1. GRUPOS DE LIE 63los elementos
- Page 77 and 78: 3.1. GRUPOS DE LIE 65(4) LorentzO(1
- Page 79 and 80: 3.2. ÁLGEBRAS DE LIE 67De…nició
- Page 81 and 82: 3.2. ÁLGEBRAS DE LIE 69independien
- Page 83 and 84: 3.2. ÁLGEBRAS DE LIE 71Demostraci
- Page 85 and 86: 3.2. ÁLGEBRAS DE LIE 73siendo A un
- Page 87 and 88: 3.3. GRUPO SIMPLÉCTICO 75matrix an
- Page 89 and 90: 4.1. ACCIÓN EFECTIVA PARA EMDA 774
- Page 91 and 92: 4.1. ACCIÓN EFECTIVA PARA EMDA 79L
- Page 93 and 94: 4.1. ACCIÓN EFECTIVA PARA EMDA 81D
- Page 95 and 96: 4.2. MODELO- NO-LINEAL PARA EMDA 83
- Page 97 and 98: CAPÍTULO 5MAPEOS ARMÓNICOSAhora q
- Page 99 and 100: 5.1. ECUACIONES QUIRALES 87Nota 1.
- Page 101 and 102: 5.2. HERRAMIENTA MATEMÁTICA 89que
- Page 103 and 104: 5.2. HERRAMIENTA MATEMÁTICA 91dond
- Page 105 and 106: 5.3. MAPEOS ARMÓNICOS 93además, c
- Page 107: 5.3. MAPEOS ARMÓNICOS 95donde A i
- Page 111 and 112: CAPÍTULO 6SOLUCIÓN PARA LA TEORÍ
- Page 113 and 114: 6. SOLUCIÓN PARA LA TEORÍA EMDA P
- Page 115 and 116: 6. SOLUCIÓN PARA LA TEORÍA EMDA P
- Page 117 and 118: 6. SOLUCIÓN PARA LA TEORÍA EMDA P
- Page 119 and 120: 6. SOLUCIÓN PARA LA TEORÍA EMDA P
- Page 121 and 122: 6. SOLUCIÓN PARA LA TEORÍA EMDA P
- Page 123 and 124: 6. SOLUCIÓN PARA LA TEORÍA EMDA P
- Page 125 and 126: 6. SOLUCIÓN PARA LA TEORÍA EMDA P
- Page 127 and 128: 6. SOLUCIÓN PARA LA TEORÍA EMDA P
- Page 129 and 130: 6. SOLUCIÓN PARA LA TEORÍA EMDA P
- Page 131 and 132: CONCLUSIONES 119de esta manera tant
- Page 133 and 134: BIBLIOGRAFÍA 121[11] Nakahara, Mik
- Page 135: BIBLIOGRAFÍA 123[36] Chiang-Mei Ch