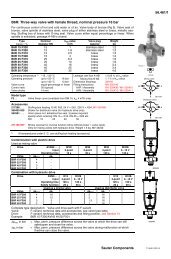
OMRON Sysdrive 3G3HV - Detector Cooling Section
OMRON Sysdrive 3G3HV - Detector Cooling Section
OMRON Sysdrive 3G3HV - Detector Cooling Section
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
PID Control<br />
PID (proportional, integral, and differential) control is a method to control a mechanical<br />
system by making the feedback values obtained from the mechanical<br />
system agree with the set point that has been preset.<br />
This method makes it possible to control a mechanical system that has dead<br />
time.<br />
The Inverter is not suitable for PID control that requires a response time of 50 ms<br />
or less.<br />
Refer to the following for examples of PID control that can be performed by the<br />
Inverter as well as the operation of PID control in detail and the settings and adjustments<br />
of the parameters.<br />
Examples of PID Control<br />
Refer to the following for examples of PID control that can be performed<br />
by the Inverter.<br />
Application Control Required sensor<br />
Speed control The Inverter uses the feedback of speed data of the Tachometric generator<br />
mechanical system and makes the operation speed<br />
of the mechanical system agree with the set point.<br />
The Inverter controls the mechanical system in<br />
synchronization with another mechanical system that<br />
inputs its speed data as the set point to the Inverter.<br />
Pressure control The Inverter performs constant pressure control with Pressure sensor<br />
the feedback of pressure data.<br />
Flow control The Inverter performs flow control with the feedback Flow sensor<br />
of flow data.<br />
Temperature<br />
control<br />
The Inverter performs temperature control using fans<br />
with the feedback of temperature data.<br />
Thermocouple<br />
Thermistor<br />
PID Control Operation<br />
The following graph shows control output (output frequency) changes<br />
with a constant deviation (i.e., the difference between the set point and<br />
feedback is constant).<br />
Deviation<br />
Time<br />
Control<br />
output<br />
Differential<br />
control<br />
PID control<br />
Integral control<br />
Proportional control<br />
Time<br />
Proportional Control<br />
Control output in proportion to the deviation is obtained through proportional control. Proportional<br />
control alone cannot make the deviation zero.