Attention! Your ePaper is waiting for publication!
By publishing your document, the content will be optimally indexed by Google via AI and sorted into the right category for over 500 million ePaper readers on YUMPU.
This will ensure high visibility and many readers!

Your ePaper is now published and live on YUMPU!
You can find your publication here:
Share your interactive ePaper on all platforms and on your website with our embed function

Handbook of air conditioning and refrigeration / Shan K
Handbook of air conditioning and refrigeration / Shan K
Handbook of air conditioning and refrigeration / Shan K
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
15.28 CHAPTER FIFTEEN<br />
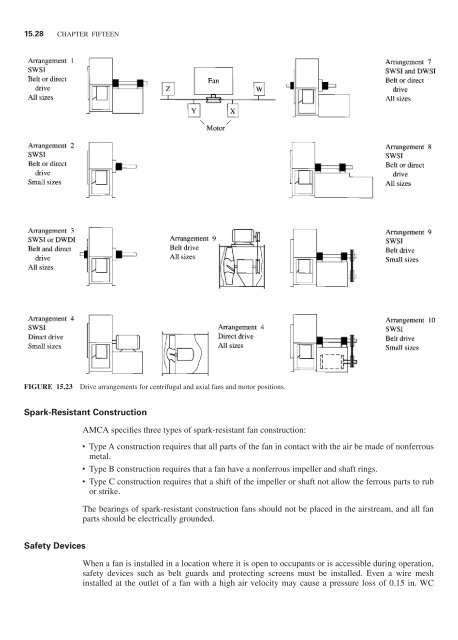
FIGURE 15.23 Drive arrangements for centrifugal <strong>and</strong> axial fans <strong>and</strong> motor positions.<br />
Spark-Resistant Construction<br />
Safety Devices<br />
AMCA specifies three types <strong>of</strong> spark-resistant fan construction:<br />
● Type A construction requires that all parts <strong>of</strong> the fan in contact with the <strong>air</strong> be made <strong>of</strong> nonferrous<br />
metal.<br />
● Type B construction requires that a fan have a nonferrous impeller <strong>and</strong> shaft rings.<br />
● Type C construction requires that a shift <strong>of</strong> the impeller or shaft not allow the ferrous parts to rub<br />
or strike.<br />
The bearings <strong>of</strong> spark-resistant construction fans should not be placed in the <strong>air</strong>stream, <strong>and</strong> all fan<br />
parts should be electrically grounded.<br />
When a fan is installed in a location where it is open to occupants or is accessible during operation,<br />
safety devices such as belt guards <strong>and</strong> protecting screens must be installed. Even a wire mesh<br />
installed at the outlet <strong>of</strong> a fan with a high <strong>air</strong> velocity may cause a pressure loss <strong>of</strong> 0.15 in. WC
15.28 CHAPTER FIFTEEN FIGURE 15.23 Drive arrangements for centrifugal <strong>and</strong> axial fans <strong>and</strong> motor positions. Spark-Resistant Construction Safety Devices AMCA specifies three types <strong>of</strong> spark-resistant fan construction: ● Type A construction requires that all parts <strong>of</strong> the fan in contact with the <strong>air</strong> be made <strong>of</strong> nonferrous metal. ● Type B construction requires that a fan have a nonferrous impeller <strong>and</strong> shaft rings. ● Type C construction requires that a shift <strong>of</strong> the impeller or shaft not allow the ferrous parts to rub or strike. The bearings <strong>of</strong> spark-resistant construction fans should not be placed in the <strong>air</strong>stream, <strong>and</strong> all fan parts should be electrically grounded. When a fan is installed in a location where it is open to occupants or is accessible during operation, safety devices such as belt guards <strong>and</strong> protecting screens must be installed. Even a wire mesh installed at the outlet <strong>of</strong> a fan with a high <strong>air</strong> velocity may cause a pressure loss <strong>of</strong> 0.15 in. WC
FIGURE 15.24 Direction <strong>of</strong> rotation <strong>and</strong> discharge position for centrifugal fans. 15.7 FAN SELECTION (37 Pa). Therefore, if the fan is covered by an enclosure or is accessible only when the fan is not in operation (during rep<strong>air</strong> or maintenance), a safety device is not required. Selection <strong>of</strong> a fan for a given type <strong>of</strong> <strong>air</strong> system or mechanical ventilating system actually is done in two stages: selection <strong>of</strong> fan type <strong>and</strong> determination <strong>of</strong> fan size. Conditions Clarified <strong>and</strong> Factors Considered Before the selection, the following conditions must be clarified: ● Setting (in a commercial building to h<strong>and</strong>le clean <strong>air</strong> at room temperature, or an industrial setting to h<strong>and</strong>le dirty <strong>air</strong>) ● Special requirements (such as high-temperature operation or spark-resistant construction) ● Function (supply fan or a return fan in an <strong>air</strong>-h<strong>and</strong>ling unit, or supply or exhaust fan in a ventilating system) ● Characteristics <strong>of</strong> the <strong>air</strong> system (constant volume or variable <strong>air</strong> volume) ● Room NC curve AIR SYSTEMS: COMPONENTS—FANS, COILS, FILTERS, AND HUMIDIFIERS 15.29 ● Approximate annual operating hours ● Unit cost <strong>of</strong> energy at the specific location During selection, the following factors should be considered: ● Pressure-volume flow operating characteristics. Selecting a fan to provide the required volume flow rate <strong>and</strong> total pressure loss for an <strong>air</strong> system or a ventilating system is <strong>of</strong> prime importance.
- Page 1 and 2:
HANDBOOK OF AIR CONDITIONING AND RE
- Page 3 and 4:
This book is dedicated to my dear w
- Page 5 and 6:
PREFACE TO SECOND EDITION Air condi
- Page 7 and 8:
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS PREFACE TO THE FIRS
- Page 9 and 10:
I.2 INDEX Air conditioning systems,
- Page 11 and 12:
I.4 INDEX Bernoulli equation, 17.2
- Page 13 and 14:
I.6 INDEX Chilled-water storage sys
- Page 15 and 16:
I.8 INDEX Constant-volume single-zo
- Page 17 and 18:
I.10 INDEX Discharge air temperatur
- Page 19 and 20:
I.12 INDEX Evaporative cooling syst
- Page 21 and 22:
I.14 INDEX Fault detection and diag
- Page 23 and 24:
I.16 INDEX Ice storage systems: com
- Page 25 and 26:
I.18 INDEX Packaged systems, fan-po
- Page 27 and 28:
I.20 INDEX Refrigerant flow control
- Page 29 and 30:
I.22 INDEX Silencers (Cont.) dissip
- Page 31 and 32:
I.24 INDEX Space pressurization or
- Page 33 and 34:
I.26 INDEX VAV systems, VAV cooling
- Page 35 and 36:
Preface to Second Edition xi Prefac
- Page 37 and 38:
Chapter 27. Air Conditioning System
- Page 39 and 40:
1.2 CHAPTER ONE limits for the comf
- Page 41 and 42:
1.4 CHAPTER ONE Individual Room Air
- Page 43 and 44:
1.6 CHAPTER ONE Unitary Packaged Ai
- Page 45 and 46:
1.8 CHAPTER ONE Water System Centra
- Page 47 and 48:
1.10 CHAPTER ONE fire protection sy
- Page 49 and 50:
1.12 CHAPTER ONE Unitary Packaged S
- Page 51 and 52:
1.14 CHAPTER ONE in the residential
- Page 53 and 54:
1.16 CHAPTER ONE shipments were 750
- Page 55 and 56:
1.18 CHAPTER ONE properly equipped
- Page 57 and 58:
1.20 CHAPTER ONE Engineer’s Quali
- Page 59 and 60:
1.22 CHAPTER ONE Drawings Specifica
- Page 61 and 62:
1.24 CHAPTER ONE criteria or system
- Page 63 and 64:
1.26 CHAPTER ONE ● Equipment sele
- Page 65 and 66:
1.28 CHAPTER ONE Rowland, F. S., Th
- Page 67 and 68:
2.2 CHAPTER TWO The amount of water
- Page 69 and 70:
2.4 CHAPTER TWO Dalton’s law is b
- Page 71 and 72:
2.6 CHAPTER TWO Temperature Measure
- Page 73 and 74:
2.8 CHAPTER TWO Degree of Saturatio
- Page 75 and 76:
2.10 CHAPTER TWO Density where pat
- Page 77 and 78:
2.12 CHAPTER TWO Thermodynamic Wet-
- Page 79 and 80:
2.14 CHAPTER TWO The term T � T
- Page 81 and 82:
2.16 CHAPTER TWO 2.8 HUMIDITY MEASU
- Page 83 and 84:
2.18 CHAPTER TWO FIGURE 2.7 Ion-exc
- Page 85 and 86:
2.20 CHAPTER TWO The last digit for
- Page 87 and 88:
2.22 CHAPTER TWO Cooling and Dehumi
- Page 89 and 90:
2.24 CHAPTER TWO p ws � From Eq.
- Page 91 and 92:
2.26 CHAPTER TWO Aslam, S., Charmch
- Page 93 and 94:
3.2 CHAPTER THREE 3.1 BUILDING ENVE
- Page 95 and 96:
3.4 CHAPTER THREE Convective Heat T
- Page 97 and 98:
3.6 CHAPTER THREE Overall Heat Tran
- Page 99 and 100:
3.8 CHAPTER THREE Heat Capacity The
- Page 101 and 102:
3.10 CHAPTER THREE Coefficients for
- Page 103 and 104:
3.12 CHAPTER THREE Temperature also
- Page 105 and 106:
3.14 CHAPTER THREE FIGURE 3.3 Mass
- Page 107 and 108:
3.16 CHAPTER THREE Moisture Transfe
- Page 109 and 110:
3.18 CHAPTER THREE During summer, t
- Page 111 and 112:
3.20 CHAPTER THREE TABLE 3.3 Therma
- Page 113 and 114:
3.22 CHAPTER THREE 3.7 SOLAR ANGLES
- Page 115 and 116:
3.24 CHAPTER THREE ● Solar altitu
- Page 117 and 118:
3.26 CHAPTER THREE In Table 3.5, th
- Page 119 and 120:
3.28 CHAPTER THREE National Climati
- Page 121 and 122:
3.30 CHAPTER THREE silver coatings
- Page 123 and 124:
3.32 CHAPTER THREE 3.10 HEAT ADMITT
- Page 125 and 126:
3.34 CHAPTER THREE design condition
- Page 127 and 128:
3.36 CHAPTER THREE Shading Coeffici
- Page 129 and 130:
3.38 CHAPTER THREE 40° north latit
- Page 131 and 132:
3.40 CHAPTER THREE and fire protect
- Page 133 and 134:
3.42 CHAPTER THREE External Shading
- Page 135 and 136:
3.44 CHAPTER THREE FIGURE 3.16 Shad
- Page 137 and 138:
3.46 CHAPTER THREE 3.12 HEAT EXCHAN
- Page 139 and 140:
3.48 CHAPTER THREE Example 3.2. At
- Page 141 and 142:
3.50 CHAPTER THREE Fenestration, in
- Page 143 and 144:
3.52 CHAPTER THREE Donnelly, R. G.,
- Page 145 and 146:
4.2 CHAPTER FOUR 2. Indoor air qual
- Page 147 and 148:
4.4 CHAPTER FOUR 4.3 METABOLIC RATE
- Page 149 and 150:
4.6 CHAPTER FOUR When the air veloc
- Page 151 and 152:
4.8 CHAPTER FOUR calculated as TABL
- Page 153 and 154:
4.10 CHAPTER FOUR FIGURE 4.2 Mean v
- Page 155 and 156:
4.12 CHAPTER FOUR FIGURE 4.4 Dimens
- Page 157 and 158:
4.14 CHAPTER FOUR Effective Tempera
- Page 159 and 160:
FIGURE 4.5 Fanger’s comfort chart
- Page 161 and 162:
4.18 CHAPTER FOUR Dew-point tempera
- Page 163 and 164:
4.20 CHAPTER FOUR lower boundary in
- Page 165 and 166:
4.22 CHAPTER FOUR FIGURE 4.9 Relati
- Page 167 and 168:
4.24 CHAPTER FOUR levels are as fol
- Page 169 and 170:
4.26 CHAPTER FOUR In Eq. (4.24), 0.
- Page 171 and 172:
4.28 CHAPTER FOUR 1. Total particul
- Page 173 and 174:
4.30 CHAPTER FOUR Outdoor Air Requi
- Page 175 and 176:
4.32 CHAPTER FOUR 4.12 SOUND LEVEL
- Page 177 and 178:
4.34 CHAPTER FOUR Human Response an
- Page 179 and 180:
4.36 CHAPTER FOUR FIGURE 4.11 Room
- Page 181 and 182:
4.38 CHAPTER FOUR hazardous, contam
- Page 183 and 184:
4.40 TABLE 4.10 Climatic Conditions
- Page 185 and 186:
4.42 CHAPTER FOUR 3. Outdoor weathe
- Page 187 and 188:
CHAPTER 5 ENERGY MANAGEMENT AND CON
- Page 189 and 190:
The 1973 energy crisis greatly boos
- Page 191 and 192:
The later the building is construct
- Page 193 and 194:
Control Methods ENERGY MANAGEMENT A
- Page 195 and 196:
5.3 CONTROL MODES Two-Position Cont
- Page 197 and 198:
Floating Control Proportional Contr
- Page 199 and 200:
The set point is the desired value
- Page 201 and 202:
where K is the derivative gain. The
- Page 203 and 204:
ENERGY MANAGEMENT AND CONTROL SYSTE
- Page 205 and 206:
Pressure Sensors Flow Sensors ENERG
- Page 207 and 208:
An infrared occupancy sensor senses
- Page 209 and 210:
For a direct-acting pneumatic tempe
- Page 211 and 212:
attery backup. However, EEPROM cann
- Page 213 and 214:
Types of Control Valves to the elec
- Page 215 and 216:
Valve Selection ENERGY MANAGEMENT A
- Page 217 and 218:
design water flow rate V˙ , gpm (L
- Page 219 and 220:
The movement of the split damper fr
- Page 221 and 222:
damper is then fully opened. If the
- Page 223 and 224:
Damper Selection Damper Sizing wher
- Page 225 and 226:
BAC net SC BAC net UC UC UC UC SC A
- Page 227 and 228:
Future Development The development
- Page 229 and 230:
Network Layer Conformance Class, Fu
- Page 231 and 232:
5.10 CONTROL LOGIC AND ARTIFICIAL I
- Page 233 and 234:
Fuzzy Logic Controller. An FLC cons
- Page 235 and 236:
give a printout. A friendly dialog
- Page 237 and 238:
Artificial Neural Networks ENERGY M
- Page 239 and 240:
3. Evaluate the error � between t
- Page 241 and 242:
Graphical Programming for Mechanica
- Page 243 and 244:
System Capacity changes during off-
- Page 245 and 246:
Generic Controls ENERGY MANAGEMENT
- Page 247 and 248:
● Central plant control Multiple-
- Page 249 and 250:
The diagnostician used color coding
- Page 251 and 252:
Discharge air temperature T dis,
- Page 253 and 254:
REFERENCES ENERGY MANAGEMENT AND CO
- Page 255 and 256:
ENERGY MANAGEMENT AND CONTROL SYSTE
- Page 257 and 258:
6.2 CHAPTER SIX 6.1 SPACE LOAD CHAR
- Page 259 and 260:
6.4 CHAPTER SIX FIGURE 6.2 Solar he
- Page 261 and 262:
6.6 CHAPTER SIX Influence of Stored
- Page 263 and 264:
6.8 CHAPTER SIX leaving the coil, s
- Page 265 and 266:
6.10 CHAPTER SIX the maximum sum of
- Page 267 and 268:
6.12 CHAPTER SIX adoption of person
- Page 269 and 270:
6.14 CHAPTER SIX Characteristics of
- Page 271 and 272:
6.16 CHAPTER SIX where T sol, a �
- Page 273 and 274:
6.18 CHAPTER SIX Space latent heat
- Page 275 and 276:
6.20 CHAPTER SIX FIGURE 6.7 Relatio
- Page 277 and 278:
6.22 TABLE 6.2 CLTD for Calculating
- Page 279 and 280:
6.24 CHAPTER SIX Infiltration Infil
- Page 281 and 282:
6.26 CHAPTER SIX nighttime in summe
- Page 283 and 284:
6.28 CHAPTER SIX ● Outer surface
- Page 285 and 286:
6.30 TABLE 6.6 July Solar Cooling L
- Page 287 and 288:
6.32 CHAPTER SIX From Eqs. (6.19a)
- Page 289 and 290:
6.34 CHAPTER SIX thickness of the d
- Page 291 and 292:
6.36 CHAPTER SIX Simplifying Assump
- Page 293 and 294:
6.38 CHAPTER SIX where hci � conv
- Page 295 and 296:
6.40 CHAPTER SIX Adjacent Unheated
- Page 297 and 298:
6.42 CHAPTER SIX the next morning b
- Page 299 and 300:
6.44 CHAPTER SIX Trace 600 Input—
- Page 301 and 302:
6.46 CHAPTER SIX ● For the calcul
- Page 303 and 304:
6.48 CHAPTER SIX Area of perimeter
- Page 305 and 306:
6.50 CHAPTER SIX Komor, P., Space C
- Page 307 and 308:
7.2 CHAPTER SEVEN 7.1 FUNDAMENTALS
- Page 309 and 310:
7.4 CHAPTER SEVEN Open systems need
- Page 311 and 312:
7.6 CHAPTER SEVEN FIGURE 7.2 Fricti
- Page 313 and 314:
7.8 TABLE 7.1 Dimensions of Commonl
- Page 315 and 316:
TABLE 7.2 Dimensions of Copper Tube
- Page 317 and 318:
7.12 CHAPTER SEVEN Pipe Joints Copp
- Page 319 and 320:
7.14 CHAPTER SEVEN also be consider
- Page 321 and 322:
7.16 CHAPTER SEVEN Insulation expos
- Page 323 and 324:
7.18 CHAPTER SEVEN Valve Materials
- Page 325 and 326:
7.20 CHAPTER SEVEN Open Expansion T
- Page 327 and 328:
7.22 CHAPTER SEVEN FIGURE 7.8 Close
- Page 329 and 330:
7.24 CHAPTER SEVEN Penalties due to
- Page 331 and 332:
7.26 CHAPTER SEVEN TABLE 7.7 Analys
- Page 333 and 334:
7.28 CHAPTER SEVEN Changeover Two P
- Page 335 and 336:
7.30 CHAPTER SEVEN a semiautomatic
- Page 337 and 338:
7.32 CHAPTER SEVEN Performance Curv
- Page 339 and 340:
7.34 CHAPTER SEVEN remove. In most
- Page 341 and 342:
7.36 CHAPTER SEVEN FIGURE 7.15 Comb
- Page 343 and 344:
7.38 CHAPTER SEVEN The wire-to-wate
- Page 345 and 346:
7.40 CHAPTER SEVEN Variable Flow fo
- Page 347 and 348:
7.42 CHAPTER SEVEN Chiller VSD 2 VS
- Page 349 and 350:
7.44 5 2 6 Plant hot water pump Boi
- Page 351 and 352:
7.46 CHAPTER SEVEN Sequence of Oper
- Page 353 and 354:
7.48 CHAPTER SEVEN FIGURE 7.20 (Con
- Page 355 and 356:
7.50 CHAPTER SEVEN Use of Balancing
- Page 357 and 358:
7.52 CHAPTER SEVEN 2. For Qcs/Qcs,d
- Page 359 and 360:
7.54 CHAPTER SEVEN The following ar
- Page 361 and 362:
7.56 CHAPTER SEVEN loops. However,
- Page 363 and 364:
7.58 CHAPTER SEVEN DDC system contr
- Page 365 and 366:
7.60 CHAPTER SEVEN REFERENCES Input
- Page 367 and 368:
CHAPTER 8 HEATING SYSTEMS, FURNACES
- Page 369 and 370:
8.2 WARM AIR FURNACES Types of Warm
- Page 371 and 372:
Heat exchanger Warm air supply plen
- Page 373 and 374:
Saving Energy ● Annual fuel utili
- Page 375 and 376:
Nighttime Setback. ASHRAE research
- Page 377 and 378:
HEATING SYSTEMS, FURNACES, AND BOIL
- Page 379 and 380:
Gas and Oil Burners When natural ga
- Page 381 and 382:
Modern packaged boilers often inclu
- Page 383 and 384:
Electric Hot Water Boilers elements
- Page 385 and 386:
where volume flow rate of supply ai
- Page 387 and 388:
Thermal Stratification divided into
- Page 389 and 390:
15°F (8.3°C) is usually used. The
- Page 391 and 392:
Design Considerations FIGURE 8.8 Ba
- Page 393 and 394:
finned tube is 1190 Btu/h (350 W).
- Page 395 and 396:
Heating flux q u, Btu/h•ft 2 Floo
- Page 397 and 398:
● Pulse-width-modulated zone cont
- Page 399 and 400:
Design and Layout HEATING SYSTEMS,
- Page 401 and 402:
REFERENCES HEATING SYSTEMS, FURNACE
- Page 403 and 404:
CHAPTER 9 REFRIGERANTS, REFRIGERATI
- Page 405 and 406:
9.2 REFRIGERANTS Refrigerants, Cool
- Page 407 and 408:
9.3 PROPERTIES AND CHARACTERISTICS
- Page 409 and 410:
● Halide torch. This method is si
- Page 411 and 412:
9.9 Specific volume of Power Critic
- Page 413 and 414:
Action and Measures REFRIGERANTS, R
- Page 415 and 416:
Because of the worldwide effort to
- Page 417 and 418:
Zeotropic HFC HFC-410A is a blend o
- Page 419 and 420:
Refrigeration Cycles Unit of Refrig
- Page 421 and 422:
the diagram and temperature T, °R,
- Page 423 and 424:
The heat extracted from the source
- Page 425 and 426:
REFRIGERANTS, REFRIGERATION CYCLES,
- Page 427 and 428:
REFRIGERANTS, REFRIGERATION CYCLES,
- Page 429 and 430:
REFRIGERANTS, REFRIGERATION CYCLES,
- Page 431 and 432:
With subcooling, Savings in electri
- Page 433 and 434:
calculated as where p con � conde
- Page 435 and 436:
Coefficient of Performance REFRIGER
- Page 437 and 438:
Then, from Eq. (9.33), the total wo
- Page 439 and 440:
x 1 at interstage pressure p i1 can
- Page 441 and 442:
REFRIGERANTS, REFRIGERATION CYCLES,
- Page 443 and 444:
REFRIGERANTS, REFRIGERATION CYCLES,
- Page 445 and 446:
REFRIGERANTS, REFRIGERATION CYCLES,
- Page 447 and 448:
From Eq. (9.22), the enthalpy diffe
- Page 449 and 450:
FIGURE 9.13 (Continued) where p 1,
- Page 451 and 452:
If �c, �t, TR1� , TR3, and pr
- Page 453 and 454:
Recent Developments ASHRAE Standard
- Page 455 and 456:
The only type of non-positive displ
- Page 457 and 458:
Energy Use Index In Eq. (9.71), m˙
- Page 459 and 460:
For institutional or health care oc
- Page 461 and 462:
Storage of Refrigerants REFERENCES
- Page 463 and 464:
CHAPTER 10 REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS: C
- Page 465 and 466:
● Shell-and-tube liquid cooler wi
- Page 467 and 468:
at an oil concentration of 3 percen
- Page 469 and 470:
or h al � h ae � �(h ae � h
- Page 471 and 472:
FIGURE 10.3 Control of DX coils at
- Page 473 and 474:
Example 10.1. A DX coil in a packag
- Page 475 and 476:
REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS: COMPONENTS 1
- Page 477 and 478:
where U dirty, U clean � overall
- Page 479 and 480:
Temperature difference T ee � T e
- Page 481 and 482:
FIGURE 10.7 (Continued) (b) Schemat
- Page 483 and 484:
Total Heat Rejection Compared with
- Page 485 and 486:
FIGURE 10.9 Double-tube condenser.
- Page 487 and 488:
It is important to recognize that t
- Page 489 and 490:
REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS: COMPONENTS 1
- Page 491 and 492:
A refrigeration system with a lower
- Page 493 and 494:
REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS: COMPONENTS 1
- Page 495 and 496:
Selection and Installation REFRIGER
- Page 497 and 498:
Counterflow Forced-Draft Cooling To
- Page 499 and 500:
air film that surrounds the condens
- Page 501 and 502:
By using the numerical integration
- Page 503 and 504:
Tower Coefficient and Water-Air Rat
- Page 505 and 506:
Construction Materials cellular fil
- Page 507 and 508:
(T w2 � T w1)/(h s � h a), or t
- Page 509 and 510:
Blowdown Legionnaires’ Disease va
- Page 511 and 512:
REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS: COMPONENTS 1
- Page 513 and 514:
The rated conditions of air-cooled
- Page 515 and 516:
The corresponding saturated tempera
- Page 517 and 518:
Electric Expansion Valves slugs may
- Page 519 and 520:
Capillary Tube FIGURE 10.21 Float v
- Page 521 and 522:
REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS: COMPONENTS 1
- Page 523 and 524:
11.2 CHAPTER ELEVEN 11.1 RECIPROCAT
- Page 525 and 526:
11.4 CHAPTER ELEVEN refrigerants. A
- Page 527 and 528:
11.6 FIGURE 11.5 Schematic reciproc
- Page 529 and 530:
11.8 CHAPTER ELEVEN Accessories sys
- Page 531 and 532:
11.10 CHAPTER ELEVEN into the inner
- Page 533 and 534:
11.12 CHAPTER ELEVEN FIGURE 11.8 Se
- Page 535 and 536:
11.14 CHAPTER ELEVEN Size of Copper
- Page 537 and 538:
11.16 CHAPTER ELEVEN TABLE 11.3 Fit
- Page 539 and 540:
11.18 CHAPTER ELEVEN FIGURE 11.10 S
- Page 541 and 542:
11.20 CHAPTER ELEVEN 5. The minimum
- Page 543 and 544:
11.22 CHAPTER ELEVEN If a receiver
- Page 545 and 546:
11.24 CHAPTER ELEVEN 11.5 CAPACITY
- Page 547 and 548:
11.26 CHAPTER ELEVEN Safety Control
- Page 549 and 550:
11.28 CHAPTER ELEVEN FIGURE 11.16 L
- Page 551 and 552:
11.30 CHAPTER ELEVEN Refrigeration
- Page 553 and 554:
11.32 CHAPTER ELEVEN Performance of
- Page 555 and 556:
11.34 CHAPTER ELEVEN 11.7 SYSTEM BA
- Page 557 and 558:
11.36 CHAPTER ELEVEN compression ra
- Page 559 and 560:
11.38 CHAPTER ELEVEN is superheated
- Page 561 and 562:
11.40 CHAPTER ELEVEN in Fig. 11.22,
- Page 563 and 564:
11.42 CHAPTER ELEVEN (2048 kPa abs.
- Page 565 and 566:
11.44 CHAPTER ELEVEN Scroll Compres
- Page 567 and 568:
11.46 CHAPTER ELEVEN Compressor Per
- Page 569 and 570:
11.48 CHAPTER ELEVEN System Charact
- Page 571 and 572:
11.50 CHAPTER ELEVEN are specified
- Page 573 and 574:
11.52 CHAPTER ELEVEN FIGURE 11.29 T
- Page 575 and 576:
11.54 CHAPTER ELEVEN Variable Volum
- Page 577 and 578:
11.56 CHAPTER ELEVEN REFERENCES ASH
- Page 579 and 580:
CHAPTER 12 HEAT PUMPS, HEAT RECOVER
- Page 581 and 582:
where h 2� � enthalpy of hot ga
- Page 583 and 584:
climates, cold supply air may be re
- Page 585 and 586:
FIGURE 12.3 (Continued) HEAT PUMPS,
- Page 587 and 588:
Operating Modes System Performance
- Page 589 and 590:
load. When the outdoor temperature
- Page 591 and 592:
Controls Capacity and Selection HEA
- Page 593 and 594:
FIGURE 12.5 A typical groundwater h
- Page 595 and 596:
HEAT PUMPS, HEAT RECOVERY, GAS COOL
- Page 597 and 598:
A vertical ground coil is buried fr
- Page 599 and 600:
Exhaust airstream Runaround Coil Lo
- Page 601 and 602:
HEAT PUMPS, HEAT RECOVERY, GAS COOL
- Page 603 and 604:
Comparison between Various Air-to-A
- Page 605 and 606:
Gas-Engine Chiller Gas Engines HEAT
- Page 607 and 608:
When the engine jacket water is rou
- Page 609 and 610:
CHAPTER 13 REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS: C
- Page 611 and 612:
Compressor REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS: C
- Page 613 and 614:
Purge Unit FIGURE 13.3 Orifice plat
- Page 615 and 616:
Types of Centrifugal Chiller match
- Page 617 and 618:
For water-cooled centrifugal chille
- Page 619 and 620:
FIGURE 13.5 (Continued ) REFRIGERAT
- Page 621 and 622:
(5.6 to 6.7°C) in temperature diff
- Page 623 and 624:
● The maintenance cost can be red
- Page 625 and 626:
FIGURE 13.10 (Continued ) where Q r
- Page 627 and 628:
13.6 CAPACITY CONTROL OF CENTRIFUGA
- Page 629 and 630:
Comparison between Inlet Vanes and
- Page 631 and 632:
Condenser Water Temperature Control
- Page 633 and 634:
7. After the oil pressure has been
- Page 635 and 636:
The log-mean temperature difference
- Page 637 and 638:
Therefore, from Eq. (13.12) the eva
- Page 639 and 640:
The actual percentage of design pow
- Page 641 and 642:
water enters the condenser T en, c
- Page 643 and 644:
Chiller Minimum Performance Design
- Page 645 and 646:
REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS: CENTRIFUGAL
- Page 647 and 648:
14.2 CHAPTER FOURTEEN Historical De
- Page 649 and 650: 14.4 CHAPTER FOURTEEN Equilibrium C
- Page 651 and 652: 14.6 CHAPTER FOURTEEN If an aqueous
- Page 653 and 654: 14.8 CHAPTER FOURTEEN Air Purge Uni
- Page 655 and 656: 14.10 CHAPTER FOURTEEN 10 5 20 40 1
- Page 657 and 658: 14.12 CHAPTER FOURTEEN Also, Therma
- Page 659 and 660: 14.14 CHAPTER FOURTEEN Coefficient
- Page 661 and 662: 14.16 CHAPTER FOURTEEN From the psy
- Page 663 and 664: 14.18 CHAPTER FOURTEEN bypass recir
- Page 665 and 666: 14.20 CHAPTER FOURTEEN Corrosion Co
- Page 667 and 668: 14.22 CHAPTER FOURTEEN Actual Perfo
- Page 669 and 670: 14.24 CHAPTER FOURTEEN absorber and
- Page 671 and 672: 14.26 CHAPTER FOURTEEN Coefficient
- Page 673 and 674: CHAPTER 15 AIR SYSTEMS: COMPONENTS
- Page 675 and 676: FIGURE 15.1 Types of fans: (a) cent
- Page 677 and 678: The fan power input on the fan shaf
- Page 679 and 680: where �p t,s � fan total pressu
- Page 681 and 682: The total pressure developed is AIR
- Page 683 and 684: Forward-Curved Fans AIR SYSTEMS: CO
- Page 685 and 686: AIR SYSTEMS: COMPONENTS—FANS, COI
- Page 687 and 688: AIR SYSTEMS: COMPONENTS—FANS, COI
- Page 689 and 690: AIR SYSTEMS: COMPONENTS—FANS, COI
- Page 691 and 692: AIR SYSTEMS: COMPONENTS—FANS, COI
- Page 693 and 694: Inlet Vanes Modulation AIR SYSTEMS:
- Page 695 and 696: Inlet Cone Modulation AIR SYSTEMS:
- Page 697 and 698: the smooth airflow suddenly breaks
- Page 699: High-Temperature Fans AIR SYSTEMS:
- Page 703 and 704: octave bands for axial fans are far
- Page 705 and 706: Types of Coils Fins AIR SYSTEMS: CO
- Page 707 and 708: AIR SYSTEMS: COMPONENTS—FANS, COI
- Page 709 and 710: Contact Conductance AIR SYSTEMS: CO
- Page 711 and 712: Water Circuits Contact conductance
- Page 713 and 714: If the thermal resistance of copper
- Page 715 and 716: AIR SYSTEMS: COMPONENTS—FANS, COI
- Page 717 and 718: Coil Construction Parameters AIR SY
- Page 719 and 720: And from Eq. (15.34), Assume � f
- Page 721 and 722: Dry Part airstream and water stream
- Page 723 and 724: FIGURE 15.32 Psychrometric analysis
- Page 725 and 726: cooling and dehumidifying capacity
- Page 727 and 728: From Eq. (15.27), Then the outer su
- Page 729 and 730: Coil Cleanliness Drain and Isolatin
- Page 731 and 732: AIR SYSTEMS: COMPONENTS—FANS, COI
- Page 733 and 734: particles may range from � 1�m
- Page 735 and 736: AIR SYSTEMS: COMPONENTS—FANS, COI
- Page 737 and 738: 15.14 AIR FILTERS Filtration Mechan
- Page 739 and 740: ● Most low-efficiency filters hav
- Page 741 and 742: 15.15 ELECTRONIC AIR CLEANERS AIR S
- Page 743 and 744: usually decreases the adsorption ca
- Page 745 and 746: FIGURE 15.41 Humidifying load for a
- Page 747 and 748: Heating Element Humidifiers AIR SYS
- Page 749 and 750: Ultrasonic Humidifiers An ultrasoni
- Page 751 and 752:
15.21 AIR WASHERS The air washer wa
- Page 753 and 754:
Bypass Control For a cooling and de
- Page 755 and 756:
industrial manufacturing processes
- Page 757 and 758:
REFERENCES AIR SYSTEMS: COMPONENTS
- Page 759 and 760:
CHAPTER 16 AIR SYSTEMS: EQUIPMENT
- Page 761 and 762:
FIGURE 16.1 Type of air-handling un
- Page 763 and 764:
Coils Filters Humidifiers AIR SYSTE
- Page 765 and 766:
AIR SYSTEMS: EQUIPMENT—AIR-HANDLI
- Page 767 and 768:
15.10, the cooling coil face veloci
- Page 769 and 770:
16.11 TABLE 16.2 Volume Flow and Fa
- Page 771 and 772:
AIR SYSTEMS: EQUIPMENT—AIR-HANDLI
- Page 773 and 774:
Indoor Packaged Units AIR SYSTEMS:
- Page 775 and 776:
Reciprocating and scroll compressor
- Page 777 and 778:
Minimum Performance 9. Compressor l
- Page 779 and 780:
16.21 TABLE 16.4 Supply Fan Perform
- Page 781 and 782:
There will be no carryover of conde
- Page 783 and 784:
AIR SYSTEMS: EQUIPMENT—AIR-HANDLI
- Page 785 and 786:
FIGURE 16.9 Interior core fan room:
- Page 787 and 788:
CHAPTER 17 AIR SYSTEMS: AIR DUCT DE
- Page 789 and 790:
p� 1 � � 1v 1 2 (17.4) If bot
- Page 791 and 792:
Stack Effect where � � air dens
- Page 793 and 794:
Velocity Distribution Equation of C
- Page 795 and 796:
FIGURE 17.3 Pressure characteristic
- Page 797 and 798:
where Psy � each air system total
- Page 799 and 800:
Rectangular Ducts AIR SYSTEMS: AIR
- Page 801 and 802:
17.15 TABLE 17.2 Rectangular Ferrou
- Page 803 and 804:
TABLE 17.4 Round Ferrous Metal Duct
- Page 805 and 806:
17.4 DUCT HEAT GAIN, HEAT LOSS, AND
- Page 807 and 808:
Temperature Rise Curves If the temp
- Page 809 and 810:
In an ideal smooth tube or duct, th
- Page 811 and 812:
loss per unit length �p f, in in.
- Page 813 and 814:
Circular Equivalents Example 17.1.
- Page 815 and 816:
17.29 42 15.6 17.1 18.5 19.9 21.1 2
- Page 817 and 818:
For galvanized steel flat oval duct
- Page 819 and 820:
AIR SYSTEMS: AIR DUCT DESIGN 17.33
- Page 821 and 822:
FIGURE 17.12 Round and flat oval te
- Page 823 and 824:
FIGURE 17.14 Openings mounted on a
- Page 825 and 826:
FIGURE 17.16 Total pressure loss
- Page 827 and 828:
FIGURE 17.17 Combination of flow re
- Page 829 and 830:
Fig. 17.19a, are given as and (17.6
- Page 831 and 832:
● An optimal duct system layout w
- Page 833 and 834:
● From node 1, the total pressure
- Page 835 and 836:
TABLE 17.10 Duct Leakage Classifica
- Page 837 and 838:
each fire damper. Many regulatory a
- Page 839 and 840:
The designer then compares various
- Page 841 and 842:
T Method planes 1 and 2, and the vo
- Page 843 and 844:
h, or in I-P units For SI units, FI
- Page 845 and 846:
When the total pressure loss of the
- Page 847 and 848:
TABLE 17.11 Local Loss Coefficients
- Page 849 and 850:
Return or Exhaust Duct Systems AIR
- Page 851 and 852:
and the sized diameter 0.0147 � 2
- Page 853 and 854:
FIGURE 17.25 Rectangular supply duc
- Page 855 and 856:
If the height of the rectangular du
- Page 857 and 858:
FIGURE 17.28 A return duct system w
- Page 859 and 860:
Design Interface AIR SYSTEMS: AIR D
- Page 861 and 862:
vacuum used in duct cleaning is oft
- Page 863 and 864:
accurate measurement, an inclined m
- Page 865 and 866:
AIR SYSTEMS: AIR DUCT DESIGN 17.79
- Page 867 and 868:
18.2 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN Design Consid
- Page 869 and 870:
18.4 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN cooling load
- Page 871 and 872:
18.6 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN FIGURE 18.2 F
- Page 873 and 874:
18.8 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN Confined Air
- Page 875 and 876:
18.10 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN Free Nonisot
- Page 877 and 878:
18.12 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN Ceiling Diff
- Page 879 and 880:
18.14 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN Slot Diffuse
- Page 881 and 882:
18.16 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN TABLE 18.1 P
- Page 883 and 884:
18.18 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN FIGURE 18.12
- Page 885 and 886:
18.20 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN 18.4 MIXING
- Page 887 and 888:
18.22 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN FIGURE 18.15
- Page 889 and 890:
18.24 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN FIGURE 18.17
- Page 891 and 892:
18.26 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN FIGURE 18.19
- Page 893 and 894:
18.28 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN ● The loca
- Page 895 and 896:
18.30 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN ● The aver
- Page 897 and 898:
18.32 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN ● Cost. In
- Page 899 and 900:
18.34 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN ● A termin
- Page 901 and 902:
18.36 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN FIGURE 18.22
- Page 903 and 904:
18.38 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN The return s
- Page 905 and 906:
18.40 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN Ventilating
- Page 907 and 908:
18.42 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN 18.8 STRATIF
- Page 909 and 910:
18.44 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN 18.9 PROJECT
- Page 911 and 912:
18.46 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN Target Veloc
- Page 913 and 914:
18.48 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN Application
- Page 915 and 916:
18.50 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN Heat Unneutr
- Page 917 and 918:
18.52 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN CFD Becomes
- Page 919 and 920:
18.54 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN Conducting C
- Page 921 and 922:
18.56 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN Wendes, H.,
- Page 923 and 924:
19.2 CHAPTER NINETEEN Sound Paths T
- Page 925 and 926:
19.4 CHAPTER NINETEEN 9. Check this
- Page 927 and 928:
19.6 CHAPTER NINETEEN Branch ducts
- Page 929 and 930:
19.8 CHAPTER NINETEEN TABLE 19.3 So
- Page 931 and 932:
19.10 CHAPTER NINETEEN End Reflecti
- Page 933 and 934:
19.12 CHAPTER NINETEEN 19.4 SILENCE
- Page 935 and 936:
19.14 CHAPTER NINETEEN facing. A so
- Page 937 and 938:
19.16 CHAPTER NINETEEN Active Silen
- Page 939 and 940:
19.18 CHAPTER NINETEEN Recommendati
- Page 941 and 942:
19.20 CHAPTER NINETEEN FIGURE 19.6
- Page 943 and 944:
19.22 CHAPTER NINETEEN TABLE 19.11
- Page 945 and 946:
19.24 CHAPTER NINETEEN Array of Cei
- Page 947 and 948:
19.26 CHAPTER NINETEEN Environmenta
- Page 949 and 950:
19.28 CHAPTER NINETEEN Octave band
- Page 951 and 952:
19.30 CHAPTER NINETEEN Sound Source
- Page 953 and 954:
19.32 CHAPTER NINETEEN Structure-Bo
- Page 955 and 956:
CHAPTER 20 AIR SYSTEMS: BASICS AND
- Page 957 and 958:
Air Distribution Systems Ventilatio
- Page 959 and 960:
20.2 BUILDING LEAKAGE AREA AND BUIL
- Page 961 and 962:
20.3 SPACE PRESSURIZATION Space Pre
- Page 963 and 964:
doors and windows are closed. When
- Page 965 and 966:
Wind speed from a meteorological st
- Page 967 and 968:
In Eq. (20.8), m˙ inf indicates th
- Page 969 and 970:
System Operating Point FIGURE 20.4
- Page 971 and 972:
20.6 SYSTEM EFFECT ● Condition 1.
- Page 973 and 974:
Inlet System Effect Loss fan inlet
- Page 975 and 976:
FIGURE 20.7 Outlet system effect: (
- Page 977 and 978:
For a SWSI centrifugal fan with A b
- Page 979 and 980:
Two Fan-Duct Systems Connected in S
- Page 981 and 982:
volume flow and fan total pressure.
- Page 983 and 984:
FIGURE 20.12 Two parallel fan-duct
- Page 985 and 986:
Similarly, the residual pressure of
- Page 987 and 988:
Modulation of Fan-Duct Systems AIR
- Page 989 and 990:
FIGURE 20.14 (Continued) AIR SYSTEM
- Page 991 and 992:
Plot the fan performance curve Ft a
- Page 993 and 994:
20.9 CLASSIFICATION OF AIR SYSTEMS
- Page 995 and 996:
To save energy, most AHU and PU man
- Page 997 and 998:
where ws,wr � humidity ratio at t
- Page 999 and 1000:
exchanger is called the sensible co
- Page 1001 and 1002:
compressed air, or ultrasonic force
- Page 1003 and 1004:
AIR SYSTEMS: BASICS AND CONSTANT-VO
- Page 1005 and 1006:
FIGURE 20.21 Adiabatic mixing and b
- Page 1007 and 1008:
and the heating coil load is 20.16
- Page 1009 and 1010:
Cooling mode operation in summer co
- Page 1011 and 1012:
ecirculating air m is usually lower
- Page 1013 and 1014:
● Outdoor damper activates with s
- Page 1015 and 1016:
3. To provide a desirable air veloc
- Page 1017 and 1018:
Air Conditioning Rules Graphical Me
- Page 1019 and 1020:
FIGURE 20.25 Effect of sensible hea
- Page 1021 and 1022:
2. Because the air temperature at t
- Page 1023 and 1024:
At a temperature of 72°F (22.2°C)
- Page 1025 and 1026:
Because w m � w s, Therefore, Fro
- Page 1027 and 1028:
Part-Load Operation 7. Draw a verti
- Page 1029 and 1030:
Reheating is a simple and effective
- Page 1031 and 1032:
Operating Parameters and Calculatio
- Page 1033 and 1034:
REFERENCES AIR SYSTEMS: BASICS AND
- Page 1035 and 1036:
21.2 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE 21.1 SYSTEM
- Page 1037 and 1038:
FIGURE 21.1 A single-zone VAV syste
- Page 1039 and 1040:
21.6 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE FIGURE 21.2
- Page 1041 and 1042:
21.8 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE Region IV:
- Page 1043 and 1044:
21.10 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE dry-bulb e
- Page 1045 and 1046:
21.12 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE Consider a
- Page 1047 and 1048:
21.14 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE ● The ou
- Page 1049 and 1050:
21.16 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE outdoor ve
- Page 1051 and 1052:
21.18 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE 7. When T
- Page 1053 and 1054:
21.20 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE VAV Reheat
- Page 1055 and 1056:
21.22 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE FIGURE 21.
- Page 1057 and 1058:
21.24 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE FIGURE 21.
- Page 1059 and 1060:
21.26 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE In dead-ba
- Page 1061 and 1062:
21.28 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE For the pe
- Page 1063 and 1064:
21.30 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE calculated
- Page 1065 and 1066:
21.32 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE For the wi
- Page 1067 and 1068:
21.34
- Page 1069 and 1070:
21.36 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE Number of
- Page 1071 and 1072:
21.38 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE Mixing Mod
- Page 1073 and 1074:
21.40 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE ● Modula
- Page 1075 and 1076:
21.42 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE where Q rs
- Page 1077 and 1078:
21.44 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE From Eq. (
- Page 1079 and 1080:
FIGURE 21.13 (Continued) 21.46
- Page 1081 and 1082:
21.48 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE Fan-Powere
- Page 1083 and 1084:
21.50 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE The drawba
- Page 1085 and 1086:
21.52 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE Zone Contr
- Page 1087 and 1088:
21.54 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE Percentage
- Page 1089 and 1090:
21.56 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE ● During
- Page 1091 and 1092:
21.58 CHAPTER TWENTY-ONE Wendes, H.
- Page 1093 and 1094:
22.2 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO 22.1 RETURN
- Page 1095 and 1096:
22.4 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO 22.2 FAN CO
- Page 1097 and 1098:
22.6 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO Recirculati
- Page 1099 and 1100:
22.8 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO flow rate o
- Page 1101 and 1102:
22.10 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO FIGURE 22.
- Page 1103 and 1104:
22.12 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO The system
- Page 1105 and 1106:
22.14 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO to balance
- Page 1107 and 1108:
22.16 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO The fixed
- Page 1109 and 1110:
22.18 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO air is ext
- Page 1111 and 1112:
22.20 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO Air Econom
- Page 1113 and 1114:
22.22 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO (2) The re
- Page 1115 and 1116:
22.24 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO FIGURE 22.
- Page 1117 and 1118:
22.26 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO FIGURE 22.
- Page 1119 and 1120:
22.28 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO ● The as
- Page 1121 and 1122:
22.30 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO FIGURE 22.
- Page 1123 and 1124:
22.32 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO Design Con
- Page 1125 and 1126:
22.34 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO �a � a
- Page 1127 and 1128:
22.36 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO The pressu
- Page 1129 and 1130:
22.38 CHAPTER TWENTY-TWO REFERENCES
- Page 1131 and 1132:
CHAPTER 23 AIR SYSTEMS: MINIMUM VEN
- Page 1133 and 1134:
ASHRAE Standard 62-1999 control, a
- Page 1135 and 1136:
The system outdoor air volume flow
- Page 1137 and 1138:
CO 2 Sensor or Mixed-Gases Sensor L
- Page 1139 and 1140:
supplied to a control zone in a VAV
- Page 1141 and 1142:
Economizer damper Exhaust damper Mi
- Page 1143 and 1144:
AIR SYSTEMS: MINIMUM VENTILATION AN
- Page 1145 and 1146:
● The maximum supply volume flow
- Page 1147 and 1148:
where m˙ ex,r, m˙ eu � mass flo
- Page 1149 and 1150:
System Description AIR SYSTEMS: MIN
- Page 1151 and 1152:
AIR SYSTEMS: MINIMUM VENTILATION AN
- Page 1153 and 1154:
● It lowers the duct heat gain or
- Page 1155 and 1156:
AIR SYSTEMS: MINIMUM VENTILATION AN
- Page 1157 and 1158:
Steam Humidifier Control Dew Point
- Page 1159 and 1160:
consumption than proportional contr
- Page 1161 and 1162:
AIR SYSTEMS: MINIMUM VENTILATION AN
- Page 1163 and 1164:
AIR SYSTEMS: MINIMUM VENTILATION AN
- Page 1165 and 1166:
REFERENCES AIR SYSTEMS: MINIMUM VEN
- Page 1167 and 1168:
24.1 IAQ PROBLEMS CHAPTER 24 IMPROV
- Page 1169 and 1170:
air economizer cycle and mixed air
- Page 1171 and 1172:
Sundell (1996) noted that many stud
- Page 1173 and 1174:
Service Life of Air Filters Filter
- Page 1175 and 1176:
● To eliminate or to reduce indoo
- Page 1177 and 1178:
Chemisorption Fig. 24.1, the sharp
- Page 1179 and 1180:
and final filter in air systems wit
- Page 1181 and 1182:
REFERENCES IMPROVING INDOOR AIR QUA
- Page 1183 and 1184:
25.2 CHAPTER TWENTY-FIVE energy res
- Page 1185 and 1186:
25.4 CHAPTER TWENTY-FIVE Mitigating
- Page 1187 and 1188:
25.6 CHAPTER TWENTY-FIVE Energy Aud
- Page 1189 and 1190:
25.8 CHAPTER TWENTY-FIVE Green Buil
- Page 1191 and 1192:
25.10 CHAPTER TWENTY-FIVE Energy St
- Page 1193 and 1194:
25.12 CHAPTER TWENTY-FIVE 25.5 CASE
- Page 1195 and 1196:
25.14 CHAPTER TWENTY-FIVE For both
- Page 1197 and 1198:
25.16 CHAPTER TWENTY-FIVE Unit elec
- Page 1199 and 1200:
25.18 CHAPTER TWENTY-FIVE Physical
- Page 1201 and 1202:
25.20 CHAPTER TWENTY-FIVE condensin
- Page 1203 and 1204:
25.22 CHAPTER TWENTY-FIVE Condenser
- Page 1205 and 1206:
25.24 CHAPTER TWENTY-FIVE The polyn
- Page 1207 and 1208:
25.26 CHAPTER TWENTY-FIVE Loads Sys
- Page 1209 and 1210:
25.28 CHAPTER TWENTY-FIVE ● Recip
- Page 1211 and 1212:
25.30 CHAPTER TWENTY-FIVE Scientifi
- Page 1213 and 1214:
26.2 CHAPTER TWENTY-SIX The purpose
- Page 1215 and 1216:
26.4 CHAPTER TWENTY-SIX requiring l
- Page 1217 and 1218:
26.6 CHAPTER TWENTY-SIX the nutriti
- Page 1219 and 1220:
26.8 CHAPTER TWENTY-SIX Space Limit
- Page 1221 and 1222:
26.10 CHAPTER TWENTY-SIX and throug
- Page 1223 and 1224:
26.12 CHAPTER TWENTY-SIX Controls F
- Page 1225 and 1226:
26.14 CHAPTER TWENTY-SIX Exterior l
- Page 1227 and 1228:
26.16 CHAPTER TWENTY-SIX Harold, R.
- Page 1229 and 1230:
27.2 CHAPTER TWENTY-SEVEN condition
- Page 1231 and 1232:
27.4 CHAPTER TWENTY-SEVEN 2. Water-
- Page 1233 and 1234:
27.6 CHAPTER TWENTY-SEVEN TABLE 27.
- Page 1235 and 1236:
27.8 CHAPTER TWENTY-SEVEN FIGURE 27
- Page 1237 and 1238:
27.10 CHAPTER TWENTY-SEVEN Effectiv
- Page 1239 and 1240:
27.12 CHAPTER TWENTY-SEVEN consumpt
- Page 1241 and 1242:
50 50 13.0 27.14 40 40 60 60 50 50
- Page 1243 and 1244:
27.16 CHAPTER TWENTY-SEVEN Assume t
- Page 1245 and 1246:
27.18 CHAPTER TWENTY-SEVEN System C
- Page 1247 and 1248:
27.20 CHAPTER TWENTY-SEVEN If the e
- Page 1249 and 1250:
27.22 CHAPTER TWENTY-SEVEN coil and
- Page 1251 and 1252:
27.24 CHAPTER TWENTY-SEVEN warm and
- Page 1253 and 1254:
27.26 CHAPTER TWENTY-SEVEN REFERENC
- Page 1255 and 1256:
CHAPTER 28 AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEMS
- Page 1257 and 1258:
Induction Systems annoying. A recei
- Page 1259 and 1260:
Fan-Coil Units AIR CONDITIONING SYS
- Page 1261 and 1262:
Volume Flow Rate Fan Motor. Permane
- Page 1263 and 1264:
Heating Capacity If the sensible he
- Page 1265 and 1266:
where � ps � air density of out
- Page 1267 and 1268:
Part-Load Operation At cooling mode
- Page 1269 and 1270:
TABLE 28.1 System Characteristics o
- Page 1271 and 1272:
AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEMS: SPACE CON
- Page 1273 and 1274:
where w s � humidity ratio of fan
- Page 1275 and 1276:
In a typical nonchangeover two-pipe
- Page 1277 and 1278:
For all the rooms in the perimeter
- Page 1279 and 1280:
Loop Temperatures AIR CONDITIONING
- Page 1281 and 1282:
leaving condition of 60°F (15.6°C
- Page 1283 and 1284:
Water Heater Storage Tanks heat pum
- Page 1285 and 1286:
System Characteristics starts the f
- Page 1287 and 1288:
● If ceiling units are used, good
- Page 1289 and 1290:
CHAPTER 29 AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEMS
- Page 1291 and 1292:
Applications AC SYSTEMS: PACKAGED A
- Page 1293 and 1294:
Controls Energy Use Intensities Sys
- Page 1295 and 1296:
29.3 SINGLE-ZONE VAV PACKAGED SYSTE
- Page 1297 and 1298:
d. That is capable of being set bac
- Page 1299 and 1300:
volume flow rate when the total pre
- Page 1301 and 1302:
FIGURE 29.2 A VAV reheat packaged s
- Page 1303 and 1304:
liquid slugging. Liquid slugging ma
- Page 1305 and 1306:
A VAV packaged system is shut off d
- Page 1307 and 1308:
more widely used. Fan-powered VAV p
- Page 1309 and 1310:
AC SYSTEMS: PACKAGED AND DESICCANT-
- Page 1311 and 1312:
AC SYSTEMS: PACKAGED AND DESICCANT-
- Page 1313 and 1314:
FIGURE 29.4 A desiccant-based air c
- Page 1315 and 1316:
As defined in Sec. 3.4, a sorption
- Page 1317 and 1318:
flow rate of the mixture of the pro
- Page 1319 and 1320:
Part-Load Operation and Controls Wh
- Page 1321 and 1322:
System Description AC SYSTEMS: PACK
- Page 1323 and 1324:
System Characteristics REFERENCES A
- Page 1325 and 1326:
CHAPTER 30 AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEMS
- Page 1327 and 1328:
● Special process temperature and
- Page 1329 and 1330:
Air and Water Temperature Different
- Page 1331 and 1332:
of a VAV system using inlet vane mo
- Page 1333 and 1334:
System Characterisics System charac
- Page 1335 and 1336:
System Characteristics the supply a
- Page 1337 and 1338:
System Characteristics AC SYSTEMS:
- Page 1339 and 1340:
FIGURE 30.1 A clean-room system for
- Page 1341 and 1342:
Manufacturing an integrated circuit
- Page 1343 and 1344:
Summer Mode Operation Room temperat
- Page 1345 and 1346:
System Pressure AC SYSTEMS: CENTRAL
- Page 1347 and 1348:
FIGURE 30.2 (Continued) Effect of F
- Page 1349 and 1350:
AC SYSTEMS: CENTRAL SYSTEMS AND CLE
- Page 1351 and 1352:
31.2 CHAPTER THIRTY-ONE mechanical
- Page 1353 and 1354:
31.4 CHAPTER THIRTY-ONE Refrigerati
- Page 1355 and 1356:
31.6 CHAPTER THIRTY-ONE 31.2 ICE-ON
- Page 1357 and 1358:
31.8 CHAPTER THIRTY-ONE FIGURE 31.3
- Page 1359 and 1360:
31.10 CHAPTER THIRTY-ONE TABLE 31.1
- Page 1361 and 1362:
31.12 CHAPTER THIRTY-ONE Water leve
- Page 1363 and 1364:
31.14 CHAPTER THIRTY-ONE Location o
- Page 1365 and 1366:
31.16 CHAPTER THIRTY-ONE FIGURE 31.
- Page 1367 and 1368:
31.18 CHAPTER THIRTY-ONE In additio
- Page 1369 and 1370:
31.20 CHAPTER THIRTY-ONE Temperatur
- Page 1371 and 1372:
31.22 CHAPTER THIRTY-ONE volume flo
- Page 1373 and 1374:
31.24 CHAPTER THIRTY-ONE Storage co
- Page 1375 and 1376:
31.26 CHAPTER THIRTY-ONE Charging P
- Page 1377 and 1378:
31.28 CHAPTER THIRTY-ONE System Per
- Page 1379 and 1380:
CHAPTER 32 COMMISSIONING AND MAINTE
- Page 1381 and 1382:
● Clarifly owner priorities and d
- Page 1383 and 1384:
intent. The CC also makes sure that
- Page 1385 and 1386:
APPENDIX A NOMENCLATURE AND ABBREVI
- Page 1387 and 1388:
I DN i m I a I rad I ref I t solar
- Page 1389 and 1390:
SC shadding coefficient Sc Schmidt
- Page 1391 and 1392:
2g second-stage generator go satura
- Page 1393 and 1394:
� relative humidity, percent; sol
- Page 1395 and 1396:
APPENDIX B PSYCHROMETRIC CHART, TAB
- Page 1397 and 1398:
B.3 TABLE B.1 Thermodynamic Propert
- Page 1399 and 1400:
TABLE B.2 Physical Properties of Ai
- Page 1401:
PSYCHROMETRIC CHART, TABLES OF PROP
Inappropriate
Loading...
Inappropriate
You have already flagged this document.
Thank you, for helping us keep this platform clean.
The editors will have a look at it as soon as possible.
Mail this publication
Loading...
Embed
Loading...
Delete template?
Are you sure you want to delete your template?
DOWNLOAD ePAPER
This ePaper is currently not available for download.
You can find similar magazines on this topic below under ‘Recommendations’.