xxiii Ïανελληνιο ÏÏ Î½ÎµÎ´Ïιο ÏÏ ÏÎ¹ÎºÎ·Ï ÏÏεÏÎµÎ±Ï ÎºÎ±ÏαÏÏαÏÎ·Ï & εÏιÏÏÎ·Î¼Î·Ï ...
xxiii Ïανελληνιο ÏÏ Î½ÎµÎ´Ïιο ÏÏ ÏÎ¹ÎºÎ·Ï ÏÏεÏÎµÎ±Ï ÎºÎ±ÏαÏÏαÏÎ·Ï & εÏιÏÏÎ·Î¼Î·Ï ...
xxiii Ïανελληνιο ÏÏ Î½ÎµÎ´Ïιο ÏÏ ÏÎ¹ÎºÎ·Ï ÏÏεÏÎµÎ±Ï ÎºÎ±ÏαÏÏαÏÎ·Ï & εÏιÏÏÎ·Î¼Î·Ï ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Structure and Dynamics of Branched Hexaalkyl and Functionalized Hexa-perihexabenzocoronenes<br />
M. M. Elmahdy 1* , G. Floudas 1 , X. Doo 2 and K. Müllen 2<br />
1 Department of Physics, University of Ioannina, P.O. Box. 1186, 451 10 Ioannina, Greece and Foundation for Research and<br />
Technology-Hellas, Biomedical Research Institute (FORTH-BRI)<br />
2 Max-Planck Institute for Polymer Research, 55128 Mainz, Germany<br />
* me01641@cc.uoi.gr<br />
In the past two decades, discotic liquid crystalline (LC) materials have attracted considerable interest because of their unique<br />
self-organization behaviour into columnar superstructures, leading to high charge carrier mobilities along the columnar stacks [1].<br />
This feature resulted in a successful application of such materials in field-effect transistors and photovoltaic devices [2]. Hexaperi-hexabenzocoronenes<br />
(HBCs) are particularly promising because their large aromatic core permits one of the highest values<br />
for the intrinsic charge carrier mobility for mesogenes [3,4].<br />
T=373 K T=383 K<br />
7<br />
6<br />
α<br />
T c<br />
(DSC)=344 K<br />
HBC-4Me<br />
5<br />
Col h<br />
-log(τ max<br />
/sec)<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
0<br />
<br />
μ α<br />
C r<br />
<br />
μ α<br />
-1<br />
T g<br />
=251K<br />
T g<br />
=235 K<br />
Cooling<br />
Heating<br />
-2<br />
2.4 2.8 3.2 3.6 4.0 4.4<br />
1000/T(K -1 )<br />
(a)<br />
(b)<br />
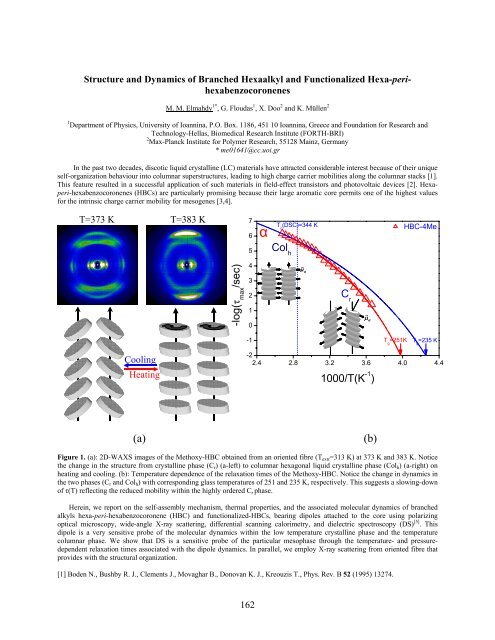
Figure 1. (a): 2D-WAXS images of the Methoxy-HBC obtained from an oriented fibre (T extr =313 K) at 373 K and 383 K. Notice<br />
the change in the structure from crystalline phase (C r ) (a-left) to columnar hexagonal liquid crystalline phase (Col h ) (a-right) on<br />
heating and cooling. (b): Temperature dependence of the relaxation times of the Methoxy-HBC. Notice the change in dynamics in<br />
the two phases (C r and Col h ) with corresponding glass temperatures of 251 and 235 K, respectively. This suggests a slowing-down<br />
of τ(T) reflecting the reduced mobility within the highly ordered C r phase.<br />
Herein, we report on the self-assembly mechanism, thermal properties, and the associated molecular dynamics of branched<br />
alkyls hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronene (HBC) and functionalized-HBCs, bearing dipoles attached to the core using polarizing<br />
optical microscopy, wide-angle X-ray scattering, differential scanning calorimetry, and dielectric spectroscopy (DS) [5] . This<br />
dipole is a very sensitive probe of the molecular dynamics within the low temperature crystalline phase and the temperature<br />
columnar phase. We show that DS is a sensitive probe of the particular mesophase through the temperature- and pressuredependent<br />
relaxation times associated with the dipole dynamics. In parallel, we employ X-ray scattering from oriented fibre that<br />
provides with the structural organization.<br />
[1] Boden N., Bushby R. J., Clements J., Movaghar B., Donovan K. J., Kreouzis T., Phys. Rev. B 52 (1995) 13274.<br />
162