QF0159 Marketing Release Record
QF0159 Marketing Release Record
QF0159 Marketing Release Record
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Novocastra Caspase-9<br />
Clone 2C9B11<br />
1 mL, 0.1 mL lyophilized NCL-CASP-9 P (HIER) W<br />
Caspase-9 is a member of the caspase family of cysteine proteases that has<br />
been implicated in apoptosis and cytokine processing. Caspases have been<br />
shown to be activated during normal human keratinocyte differentiation and<br />
this activation is required for the normal loss of the nucleus. In addition, this<br />
apoptotic pathway may be activated in cardiac myocytes under conditions<br />
of ischemia. In the presence of ATP, apoptotic stimuli induce proteolytic<br />
processing and activation of pro-caspase 9 by cytochrome c and Apaf-1.<br />
Activated caspase-9 cleaves downstream caspases such as caspase-3, 6<br />
and 7 initiating the caspase cascade. Caspase-9 is essential for apoptosis<br />
during the normal development of the central nervous system. Mutations or<br />
deficiencies in caspase-9 result in resistance to apoptotic stimuli that mimic<br />
conditions in developing tumors.<br />
Human rectal adenocarcinoma: immunohistochemical staining for caspase-9 protein using<br />
NCL-CASP-9. Note cytoplasmic staining of neoplastic epithelium. Paraffin section.<br />
Novocastra Cathepsin B<br />
Clone CB131<br />
1 mL lyophilized NCL-CATH-B P<br />
RUO*<br />
RUO*<br />
Cathepsin B is one member of a family of proteolytic enzymes and is<br />
expressed in cytoplasmic lysosomes in different types of normal and<br />
neoplastic tissues. It is a cysteine protease and like most cathepsins is<br />
involved in cellular metabolism such as protein degradation.<br />
Immunohistochemical studies have detected expression in bowel mucosa,<br />
skin, prostate and thyroid. Staining for cathepsin B, in common with other<br />
cathepsins, may be so intense that it appears to be nuclear in some cells. A<br />
proportion of endothelial cells are positive in many tissues. This has been<br />
reported previously where it has been described as sprouting endothelial<br />
cells. In tissues containing tumors this is thought to be related to tumor<br />
progression. Cathepsin B is an important matrix-degrading protease in<br />
several human cancers including lung adenocarcinomas, squamous cell<br />
carcinomas, rectal and breast carcinomas. Cathepsin B is reported to be<br />
overexpressed in squamous cell carcinoma where undifferentiated cells are<br />
strongly positive and the more differentiated cells in tumor islands are either<br />
weakly positive or negative. The expression of cathepsin B has also been<br />
reported in melanomas where the upregulation of this enzyme was found to<br />
be a characteristic of a more invasive tumor phenotype.<br />
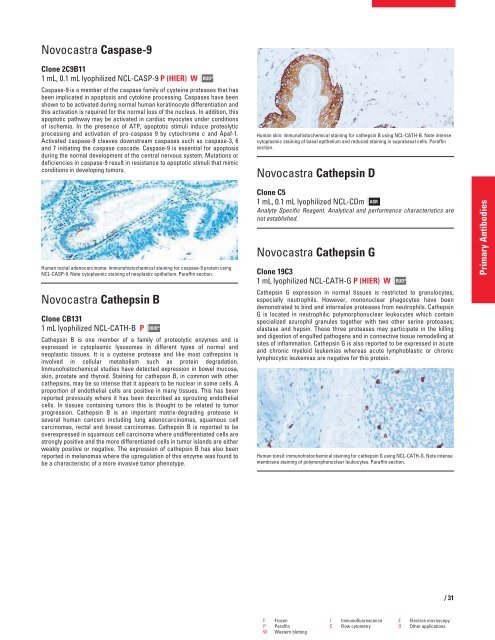
Human skin: immunohistochemical staining for cathepsin B using NCL-CATH-B. Note intense<br />
cytoplasmic staining of basal epithelium and reduced staining in suprabasal cells. Paraffin<br />
section.<br />
Novocastra Cathepsin D<br />
Clone C5<br />
1 mL, 0.1 mL lyophilized NCL-CDm ASR<br />
Analyte Specific Reagent. Analytical and performance characteristics are<br />
not established.<br />
Novocastra Cathepsin G<br />
Clone 19C3<br />
1 mL lyophilized NCL-CATH-G P (HIER) W<br />
RUO*<br />
Cathepsin G expression in normal tissues is restricted to granulocytes,<br />
especially neutrophils. However, mononuclear phagocytes have been<br />
demonstrated to bind and internalize proteases from neutrophils. Cathepsin<br />
G is located in neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes which contain<br />
specialized azurophil granules together with two other serine proteases;<br />
elastase and hepsin. These three proteases may participate in the killing<br />
and digestion of engulfed pathogens and in connective tissue remodelling at<br />
sites of inflammation. Cathepsin G is also reported to be expressed in acute<br />
and chronic myeloid leukemias whereas acute lymphoblastic or chronic<br />
lymphocytic leukemias are negative for this protein.<br />
Human tonsil: immunohistochemical staining for cathepsin G using NCL-CATH-G. Note intense<br />
membrane staining of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Paraffin section.<br />
F Frozen I Immunofluorescence E Electron microscopy<br />
P Paraffin C Flow cytometry O Other applications<br />
W Western blotting<br />
/31<br />
Primary Antibodies