QF0159 Marketing Release Record
QF0159 Marketing Release Record
QF0159 Marketing Release Record
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
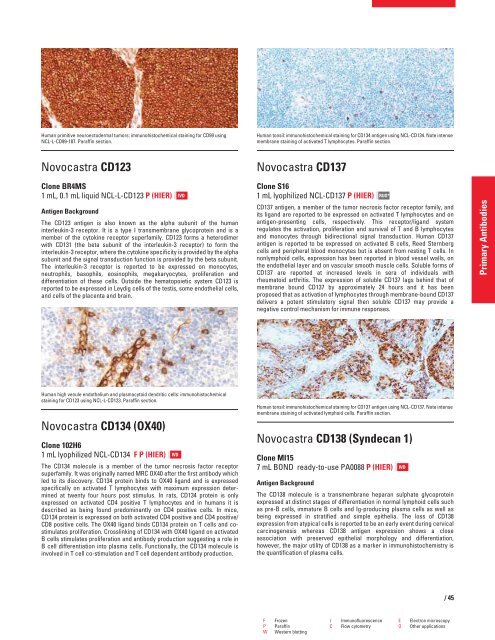
Human primitive neuroectodermal tumors: immunohistochemical staining for CD99 using<br />
NCL-L-CD99-187. Paraffin section.<br />
Novocastra CD123<br />
Clone BR4MS<br />
1 mL, 0.1 mL liquid NCL-L-CD123 P (HIER)<br />
Antigen Background<br />
The CD123 antigen is also known as the alpha subunit of the human<br />
interleukin-3 receptor. It is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein and is a<br />
member of the cytokine receptor superfamily. CD123 forms a heterodimer<br />
with CD131 (the beta subunit of the interleukin-3 receptor) to form the<br />
interleukin-3 receptor, where the cytokine specificity is provided by the alpha<br />
subunit and the signal transduction function is provided by the beta subunit.<br />
The interleukin-3 receptor is reported to be expressed on monocytes,<br />
neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, megakaryocytes, proliferation and<br />
differentiation of these cells. Outside the hematopoietic system CD123 is<br />
reported to be expressed in Leydig cells of the testis, some endothelial cells,<br />
and cells of the placenta and brain.<br />
Human high venule endothelium and plasmacytoid dendritic cells: immunohistochemical<br />
staining for CD123 using NCL-L-CD123. Paraffin section.<br />
Novocastra CD134 (OX40)<br />
Clone 102H6<br />
1 mL lyophilized NCL-CD134 F P (HIER)<br />
The CD134 molecule is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor<br />
superfamily. It was originally named MRC OX40 after the first antibody which<br />
led to its discovery. CD134 protein binds to OX40 ligand and is expressed<br />
specifically on activated T lymphocytes with maximum expression determined<br />
at twenty four hours post stimulus. In rats, CD134 protein is only<br />
expressed on activated CD4 positive T lymphocytes and in humans it is<br />
described as being found predominantly on CD4 positive cells. In mice,<br />
CD134 protein is expressed on both activated CD4 positive and CD4 positive/<br />
CD8 positive cells. The OX40 ligand binds CD134 protein on T cells and costimulates<br />
proliferation. Crosslinking of CD134 with OX40 ligand on activated<br />
B cells stimulates proliferation and antibody production suggesting a role in<br />
B cell differentiation into plasma cells. Functionally, the CD134 molecule is<br />
involved in T cell co-stimulation and T cell dependent antibody production.<br />
IVD<br />
IVD<br />
Human tonsil: immunohistochemical staining for CD134 antigen using NCL-CD134. Note intense<br />
membrane staining of activated T lymphocytes. Paraffin section.<br />
Novocastra CD137<br />
Clone S16<br />
1 mL lyophilized NCL-CD137 P (HIER)<br />
CD137 antigen, a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family, and<br />
its ligand are reported to be expressed on activated T lymphocytes and on<br />
antigen-presenting cells, respectively. This receptor/ligand system<br />
regulates the activation, proliferation and survival of T and B lymphocytes<br />
and monocytes through bidirectional signal transduction. Human CD137<br />
antigen is reported to be expressed on activated B cells, Reed Sternberg<br />
cells and peripheral blood monocytes but is absent from resting T cells. In<br />
nonlymphoid cells, expression has been reported in blood vessel walls, on<br />
the endothelial layer and on vascular smooth muscle cells. Soluble forms of<br />
CD137 are reported at increased levels in sera of individuals with<br />
rheumatoid arthritis. The expression of soluble CD137 lags behind that of<br />
membrane bound CD137 by approximately 24 hours and it has been<br />
proposed that as activation of lymphocytes through membrane-bound CD137<br />
delivers a potent stimulatory signal then soluble CD137 may provide a<br />
negative control mechanism for immune responses.<br />
Human tonsil: immunohistochemical staining for CD137 antigen using NCL-CD137. Note intense<br />
membrane staining of activated lymphoid cells. Paraffin section.<br />
Novocastra CD138 (Syndecan 1)<br />
Clone MI15<br />
7 mL BOND ready-to-use PA0088 P (HIER)<br />
Antigen Background<br />
RUO*<br />
The CD138 molecule is a transmembrane heparan sulphate glycoprotein<br />
expressed at distinct stages of differentiation in normal lymphoid cells such<br />
as pre-B cells, immature B cells and Ig-producing plasma cells as well as<br />
being expressed in stratified and simple epithelia. The loss of CD138<br />
expression from atypical cells is reported to be an early event during cervical<br />
carcinogenesis whereas CD138 antigen expression shows a close<br />
association with preserved epithelial morphology and differentiation,<br />
however, the major utility of CD138 as a marker in immunohistochemistry is<br />
the quantification of plasma cells.<br />
IVD<br />
F Frozen I Immunofluorescence E Electron microscopy<br />
P Paraffin C Flow cytometry O Other applications<br />
W Western blotting<br />
/45<br />
Primary Antibodies