Intel® 865G/865GV Chipset Datasheet - download.intel.nl - Intel
Intel® 865G/865GV Chipset Datasheet - download.intel.nl - Intel
Intel® 865G/865GV Chipset Datasheet - download.intel.nl - Intel
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
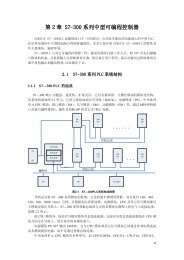
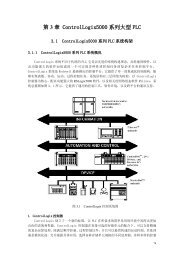
Functional Description5.2.2.1 Dynamic Addressing ModeWhen the GMCH is configured to operate in this mode, FSB-to-memory bus address mappingundergoes a significant change compared to that of in a Linear Operating mode (normal operatingmode). In non-dynamic mode, the row selection (row indicates the side of a DIMM) via chip selectsignals is accomplished based on the size of the row. For example, for a 512-Mb, 16Mx8x4b has arow size of 512 MB selected by CS0# and o<strong>nl</strong>y four open pages can be maintained for the full512 MB. This lowers the memory performance (increases read latencies) if most of the memorycycles are targeted to that single row, resulting in opening and closing of accessed pages in thatrow.Dynamic Addressing mode minimizes the overhead of opening/closing pages in memory banksallowing for row switching to be done less often.5.2.3 Single-Channel (SC) ModeIf either o<strong>nl</strong>y channel A or o<strong>nl</strong>y channel B is populated, the GMCH is set to operate in singlechannelmode. Data is accessed in chunks of 64 bits (8 B) from the memory channels. If bothchannels are populated with uneven memory (DIMMs), the GMCH defaults to virtual singlechannel(VSC) mode. Even with similar memory configuration on both the channels, it is possibleto force the GMCH to operate in single-channel mode, which by default is configured as Lock Stepmode. The GMCH behaves identical in both single-channel and virtual single-channel modes(hereafter referred to as single-channel (SC) mode).In this mode of operation, the populated DIMMs configuration can be identical or completelydifferent. In addition, for SC mode, not all the slots need to be populated. For example, populatingo<strong>nl</strong>y one DIMM in channel A is a valid configuration for SC mode. Likewise, in VSC mode oddnumber of slots can be populated. For Dynamic Mode operation, the requirement is to have an evennumber of rows (side of the DIMM) populated. In SC, dynamic mode operation can be enabledwith one single-sided (SS), two SS or two double-sided (DS). For VSC mode, both the channelsneed to have an identical row structure.5.2.3.1 Linear Mode5.2.3.2 Tiled ModeThis mode is the normal mode of operation for the GMCH with internal graphics device disabled.This mode was specifically aimed at improving the performance of the Integrated Graphics Device.5.2.4 Memory Address Translation and DecodingThe address translation and decoding for the GMCH is provided in Table 19 through Table 24. Thesupported DIMM configurations are listed in the following bullets. Refer to Section 5.2.5 fordetails about the configurations being double-sided versus single-sided.• Technology 128 Mbit – 16Mx8 – page size of 8 KB – row size of 128 MB• Technology 128 Mbit – 8Mx16 – page size of 4 KB – row size of 64 MB• Technology 256 Mbit – 32Mx8 – page size of 8 KB – row size of 256 MB• Technology 256 Mbit – 16Mx16 – page size of 4 KB – row size of 128 MB• Technology 512 Mbit – 32Mx16 – page size of 8 KB – row size of 256 MB• Technology 512 Mbit – 64Mx8 – page size of 16 KB – row size of 512 MBNote:In Table 19 through Table 24 A0, A1, … refers to memory address MA0, MA1, ….The table cell contents refers to host address signals HAx.<strong>Intel</strong> ® 82<strong>865G</strong>/82<strong>865G</strong>V GMCH <strong>Datasheet</strong> 151