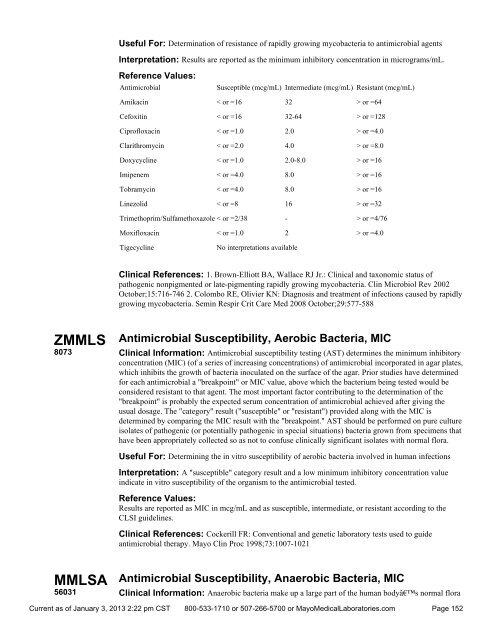
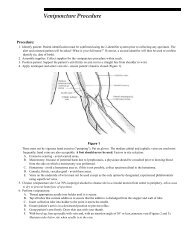
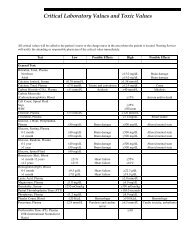
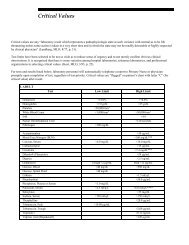
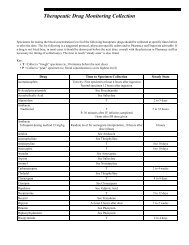
- Page 1 and 2:
Rochester 2013 Interpretive Handboo
- Page 3 and 4:
Policies - Mayo Medical Laboratorie
- Page 5 and 6:
Policies - Mayo Medical Laboratorie
- Page 7 and 8:
Policies - Mayo Medical Laboratorie
- Page 9 and 10:
Policies - Mayo Medical Laboratorie
- Page 11 and 12:
Policies - Mayo Medical Laboratorie
- Page 13 and 14:
TTIG 82506 DHVD 8822 Tetanus Toxoid
- Page 15 and 16:
DCRN 8847 not without risk, and is
- Page 17 and 18:
DOC 8547 defect has selectively aff
- Page 19 and 20:
FDSOX 91690 THCM 84284 11-Desoxycor
- Page 21 and 22:
FBP1 86208 these modified WHO crite
- Page 23 and 24:
17OHP 81151 exaggerated responses t
- Page 25 and 26:
OHPG 9231 mass spectrometry. Horm R
- Page 27 and 28:
FP73 88541 requiring differentiatio
- Page 29 and 30:
Useful For: As an adjunct to measur
- Page 31 and 32:
CYPKP 89082 challenge because most
- Page 33 and 34:
25HDN 83670 Clinical References: 1.
- Page 35 and 36:
FLUC 82741 F5HAR 57333 Salt Lake Ci
- Page 37 and 38:
6MAMM 89659 6MAMU 89605 6-Monoacety
- Page 39 and 40:
ACAC 82757 8-MOP blood levels. Beca
- Page 41 and 42:
ACM 8698 sensitization to particula
- Page 43 and 44:
ACHE_ 9287 ACHS 8522 Reference Valu
- Page 45 and 46:
SAFB 8213 ACT 8221 the era of enzym
- Page 47 and 48:
AHPS 9022 catalyzes APC inactivatio
- Page 49 and 50:
AHEPR 86137 hepatitis B virus infec
- Page 51 and 52:
FACY 90308 ACRN 82413 Acyclovir, Se
- Page 53 and 54:
1-7 days:
- Page 55 and 56:
demonstrate mild and intermittent b
- Page 57 and 58:
ADMIS 61213 ADA 80649 FADA 91554 Re
- Page 59 and 60:
FAAST 57116 FADE 91670 LADV 89074 A
- Page 61 and 62:
FAPG 91347 FADMK 91925 RACTH 82140
- Page 63 and 64:
FAERO 91865 AGXMS 89915 Clinical Re
- Page 65 and 66:
AGXKM 89916 E, Rumsby G: Selected e
- Page 67 and 68:
AGXT 83643 FALUF 57286 ALB Referenc
- Page 69 and 70:
FALCO 90084 ALS 8363 This specimen
- Page 71 and 72:
ALAV 6349 ARAV 6348 ALDS 8557 ALDU
- Page 73 and 74:
esponse to cholestatic liver diseas
- Page 75 and 76:
11 years: 185-507 U/L 12 years: 185
- Page 77 and 78:
FALMD 92001 ALM 82882 the dietary t
- Page 79 and 80:
FASU 91221 CD8 (double-negative T c
- Page 81 and 82:
A1ATR 83050 1981;81:777-780 2. Cros
- Page 83 and 84:
AAT 8161 A1M24 81036 1981;81:777-78
- Page 85 and 86:
A2M 9270 biological half-life of ap
- Page 87 and 88:
AFP 8162 might be found in chronic
- Page 89 and 90:
MAFP 81169 interpreted with caution
- Page 91 and 92:
FUCT 8815 Useful For: Screening for
- Page 93 and 94:
AGA 8785 from deficient activity of
- Page 95 and 96:
AGPB 9499 third decade with the dev
- Page 97 and 98:
IDSBS 60617 =1.0 nmol/h/mL) are not
- Page 99 and 100:
MANT 8773 Clinical Information: Cli
- Page 101 and 102: ANAS 8782 degraded GAG (also called
- Page 103 and 104: proportion of these cases, free alp
- Page 105 and 106: ALU 8828 and to define the allergen
- Page 107 and 108: Clinical Information: Under normal
- Page 109 and 110: TFE3 61013 alone, especially true w
- Page 111 and 112: AMIKR 81752 AMIKT 81593 Drugs.Clini
- Page 113 and 114: Clinical Information: Amino acids a
- Page 115 and 116: findings, and physical and cognitiv
- Page 117 and 118: Useful For: Evaluating patients wit
- Page 119 and 120: ALAUR 61547 Reference Values: GLUTA
- Page 121 and 122: ALAD 88924 Interpretation: In patie
- Page 123 and 124: AFC 80334 AMOBS 8325 correlate with
- Page 125 and 126: AMPCS 61518 clinical manifestations
- Page 127 and 128: AMPHM 84371 FAMPH 90113 Amphetamine
- Page 129 and 130: FAMPB 91994 AMPHB 80429 AMP 82664 P
- Page 131 and 132: AMLPC 60078 PAMYB 5079 12-17 months
- Page 133 and 134: AMSU 8356 Thus, conditions associat
- Page 135 and 136: FABP 91408 82091 Reference Values:
- Page 137 and 138: TTRX 83674 identified within the TT
- Page 139 and 140: FPGO 57160 ANCH 82345 Anaplasma pha
- Page 141 and 142: conjunction with measurement of oth
- Page 143 and 144: FACE 90447 ACE 8285 Interpretation:
- Page 145 and 146: ANSE 82487 Clinical Information: Cl
- Page 147 and 148: IGAAB 8154 FIGER 91788 Patients wit
- Page 149 and 150: ABID2 8988 ABSCM 8956 ABTIH 9000 Te
- Page 151: FASUQ 57517 FADS 91720 RIF 80430 MM
- Page 155 and 156: MTBV2 56032 MMLNS 82019 Med 2006;17
- Page 157 and 158: FANTU 91146 AMH 89711 Antimony, Uri
- Page 159 and 160: ANAH2 86038 (ANCA) and cANCA or pAN
- Page 161 and 162: deficiency are usually heterozygous
- Page 163 and 164: APO1S 60723 levels by 180 days post
- Page 165 and 166: APO2S 60725 APO2K 60726 Apolipoprot
- Page 167 and 168: APLB 80308 APOB 89097 Reference val
- Page 169 and 170: APPL 82712 populations are as follo
- Page 171 and 172: AWNS 87814 AWNC 87813 Arbovirus and
- Page 173 and 174: ABOPC 83897 may be influenced by ag
- Page 175 and 176: AVP 80344 ST. LOUIS ENCEPHALITIS AN
- Page 177 and 178: CGH 88898 Changes that are inherite
- Page 179 and 180: ARSAK 61260 ASFR 80375 Gieselmann V
- Page 181 and 182: ASU 8644 0-24 mcg/L Reference value
- Page 183 and 184: ASNA 89848 ASRU 89889 present in ha
- Page 185 and 186: ARST 8778 The gastrointestinal trac
- Page 187 and 188: ARSU 8777 Useful For: Detection of
- Page 189 and 190: VITC 60296 immune response to aller
- Page 191 and 192: lag, macrocephaly, and hypotonia. D
- Page 193 and 194: ASPAG 84356 Useful For: The determi
- Page 195 and 196: ASP 82911 Useful For: As an aid in
- Page 197 and 198: ADMA 83651 Useful For: Testing for
- Page 199 and 200: FAPPN 57142 AUPU 82855 crossreactiv
- Page 201 and 202: ADE 89904 Interpretation: Detection
- Page 203 and 204:
(GI) motility studies (eg, gastric,
- Page 205 and 206:
FADAE 91584 ARPKD 88911 MITOCHONDRI
- Page 207 and 208:
AVOC 82812 FAZAT This result must b
- Page 209 and 210:
CD40 89009 cytogenetics in hematolo
- Page 211 and 212:
IABCS 88800 Reference Values: An in
- Page 213 and 214:
Results Expressed as a Percentage o
- Page 215 and 216:
65 years: < or =59 pg/mL 66 years:
- Page 217 and 218:
PBAB 81147 may have hepatomegaly an
- Page 219 and 220:
SPUT 8095 UR 8105 ANAE 84292 Bacter
- Page 221 and 222:
EPRP 60235 PFGE 80349 chronically i
- Page 223 and 224:
BCYP 82722 0 Negative 1 0.35-0.69 E
- Page 225 and 226:
BARBU 80372 clinical manifestations
- Page 227 and 228:
BRLY 82687 20405 Clinical Reference
- Page 229 and 230:
BART 81575 BARRP 84440 Cypress, CA
- Page 231 and 232:
BASL 82489 FBBLK 91983 August;2(10)
- Page 233 and 234:
BA190 83336 fusion variants (e20/a2
- Page 235 and 236:
MBCR 80578 BAKDM 89609 BCR/ABL, Tra
- Page 237 and 238:
FBEAN 91646 FBLMA 91963 BWSRS 61010
- Page 239 and 240:
BREG 82692 bronchospasm) in infants
- Page 241 and 242:
BEETS 82618 FQFKL 57294 6 > or =100
- Page 243 and 244:
BENZU 80370 Blood benzene concentra
- Page 245 and 246:
BERG 82892 3 3.50-17.4 Positive 4 1
- Page 247 and 248:
B2GP1 88894 manifestations, includi
- Page 249 and 250:
MB2GP 86181 systemic rheumatic dise
- Page 251 and 252:
B2OSH 300245 B2MC of CSF into the n
- Page 253 and 254:
B2M 9234 CTX 83175 and correction f
- Page 255 and 256:
BGABS 60986 presents at a later ons
- Page 257 and 258:
BGA 8486 (also known as mucopolysac
- Page 259 and 260:
BGL 8788 spots, and/or fibroblasts
- Page 261 and 262:
the beta subunit of LH and acts thr
- Page 263 and 264:
BLACT 8118 BLAC 82896 Beta-Lactamas
- Page 265 and 266:
FBIU 90357 9880 FBAF 91701 concentr
- Page 267 and 268:
19701 BILID 81787 (non-PSC vs. PSC
- Page 269 and 270:
BILI3 8452 permeability is increase
- Page 271 and 272:
BTDMS 89012 excretion are impaired
- Page 273 and 274:
BIOTS 88205 inherited in an autosom
- Page 275 and 276:
LCBKP 89982 DNA-containing viruses
- Page 277 and 278:
QBKU 87859 BLPEP 82814 polyomavirus
- Page 279 and 280:
SBLAS 86691 CBLAS 89986 responsible
- Page 281 and 282:
80326 BDIAL 83094 BTROP 82374 Washi
- Page 283 and 284:
UEBF 81834 BWOR 82840 to the nature
- Page 285 and 286:
BLUE 82359 of allergic reactions to
- Page 287 and 288:
BHINT 9027 BHQL osteomalacia, and o
- Page 289 and 290:
FBPTS 57290 for sensitive and rapid
- Page 291 and 292:
BOT 82715 BOV 82135 Botrytis cinere
- Page 293 and 294:
89045 BRAFM 83837 0 Negative 1 0.35
- Page 295 and 296:
BRAZ 82899 therapies directed to co
- Page 297 and 298:
FYSTB 91990 BROC 82817 Useful For:
- Page 299 and 300:
BRM 8608 BRUGM 89476 Clinical Refer
- Page 301 and 302:
BRUTA 8112 BSPR 82480 Reference Val
- Page 303 and 304:
affects the severity of the clinica
- Page 305 and 306:
in the mothers of 35 of the 41 pati
- Page 307 and 308:
BTKK 89306 mutations in female rela
- Page 309 and 310:
BUCW 82727 presentation. Females ar
- Page 311 and 312:
BFTH 82779 likelihood of allergic d
- Page 313 and 314:
BUPIS 89548 BUPM 500038 Bupivacaine
- Page 315 and 316:
FBUS 91115 BUAUC 83188 Buspirone (B
- Page 317 and 318:
FCPEP 91270 situations, insulin lev
- Page 319 and 320:
C1ES 8198 Useful For: Assessment of
- Page 321 and 322:
C1QFX 83374 Reference Values: C1Q B
- Page 323 and 324:
C2 81835 peptides that are chemotac
- Page 325 and 326:
FC3D 91725 C4U 88829 C4FX 83391 Adv
- Page 327 and 328:
C5FX 83392 C5DCU 88831 Clinical Ref
- Page 329 and 330:
C6FX 83393 C7FX 81064 C6 Complement
- Page 331 and 332:
C9FX 81066 CABB 33-58 U/mL Clinical
- Page 333 and 334:
CDOMB 89539 CDOM 80595 and to defin
- Page 335 and 336:
CDB 8682 CDRU 60156 Administration,
- Page 337 and 338:
2 9.2-13.7
- Page 339 and 340:
FCAH1 91275 5 12.8-17.3 24-175 Test
- Page 341 and 342:
17-Alpha-Hydroxyprogesterone, Serum
- Page 343 and 344:
4 10.7-15.6 47-208 5 11.8-18.6 50-2
- Page 345 and 346:
months to prepubertal levels. Prepu
- Page 347 and 348:
Note: Luteal progesterone peaked fr
- Page 349 and 350:
CATN 9160 Clinical References: 1. T
- Page 351 and 352:
CSRMS 83703 mildly-to-moderately el
- Page 353 and 354:
CAU 8594 apparent idiopathic hypopa
- Page 355 and 356:
IONCG 300235 CAUR 60157 > or =18 ye
- Page 357 and 358:
or =19 years: 8.9-10.1 mg/dL Refere
- Page 359 and 360:
CAVPC 83900 reabsorption in the pro
- Page 361 and 362:
FCALP 91597 FCAMP 91224 have been i
- Page 363 and 364:
CANW 81780 bronchospasm) in infants
- Page 365 and 366:
CDAB 82690 FCANA Reference Values:
- Page 367 and 368:
FFTH 90479 FCAPR 90062 CWAY 82493 I
- Page 369 and 370:
FCAR 81770 CAR 8654 Carbamazepine,
- Page 371 and 372:
HODGE 89676 199PC 89508 199PT 61530
- Page 373 and 374:
CA19 9288 CDG 89891 Interpretation:
- Page 375 and 376:
CDTA 82425 CHOU 9255 glycosylation
- Page 377 and 378:
CEAPT 61528 markers (ie, amylase an
- Page 379 and 380:
CEASF 8918 CARD 82491 tissue. Usefu
- Page 381 and 382:
FCRME 91660 CPTMS 61120 CPTKM 61121
- Page 383 and 384:
CARNS 60449 > or =18 years 34-78 25
- Page 385 and 386:
CACTS 61194 CACTK 61195 FREE 77-214
- Page 387 and 388:
CARO 8288 CROT 82742 Carotene, Seru
- Page 389 and 390:
CASH 82881 Class IgE kU/L Interpret
- Page 391 and 392:
CAT 82665 COMTO 60336 by Laboratory
- Page 393 and 394:
CATU 9276 action of MAO and COMT. P
- Page 395 and 396:
CATP 8532 Clinical References: 1. Y
- Page 397 and 398:
CALFL 82617 Not for clinical diagno
- Page 399 and 400:
2-5 months: 10.0-14.0 g/dL 6 months
- Page 401 and 402:
CD20B 89584 15 days-1 month: 2.50-1
- Page 403 and 404:
TCD4 84348 Sources of variability i
- Page 405 and 406:
CD4NY 28334 lymphocyte counts from
- Page 407 and 408:
long-lived in the periphery and thi
- Page 409 and 410:
may not necessarily correlate with
- Page 411 and 412:
55 years: 31-409 cells/mcL Natural
- Page 413 and 414:
CD8RT 89505 Reference Values: Inter
- Page 415 and 416:
CDKKM 60229 and KIP2; maternally ex
- Page 417 and 418:
CELY 82766 caused by the release of
- Page 419 and 420:
antibodies. The treatment for celia
- Page 421 and 422:
constipation.(2) Clinical symptoms
- Page 423 and 424:
CBPA 8937 Clinical Information: Bod
- Page 425 and 426:
CENTA 110006 CEAC 82387 Centromere
- Page 427 and 428:
SFIN 8009 metachromatic leukodystro
- Page 429 and 430:
80184 8032 disease and Menkes disea
- Page 431 and 432:
CFTRM 88876 increased risk for a cl
- Page 433 and 434:
FCCG 57274 CCHZ 82752 bronchospasm)
- Page 435 and 436:
CHER 82798 Interpretation: Detectio
- Page 437 and 438:
CNUT 82870 FCHIC 84308 Chestnut, Sw
- Page 439 and 440:
CDROP 82142 3 3.50-17.4 Positive 4
- Page 441 and 442:
CHIC 82703 sensitivity to inhalant
- Page 443 and 444:
CHIDB 83182 CHEP 84427 CHRGB 83186
- Page 445 and 446:
psittacosis, a disease characterize
- Page 447 and 448:
CTRNA 61551 clinical signs and symp
- Page 449 and 450:
MCRNA 61554 and in symptomatic male
- Page 451 and 452:
CDP 8610 Alpha-Chlordane Synonym(s)
- Page 453 and 454:
RCHLU 83747 CL 8460 Congenital chlo
- Page 455 and 456:
FCHO 91157 CHLBF 82945 determined t
- Page 457 and 458:
CHLE 8324 beta-LDL, alpha-1 HDL, al
- Page 459 and 460:
CROMU 89547 CRU 8593 Test Performed
- Page 461 and 462:
CGAK 34641 industry to make chromiu
- Page 463 and 464:
AF 8426 cancer diagnosis. However,
- Page 465 and 466:
CPG 89090 Useful For: Prenatal diag
- Page 467 and 468:
BM 8506 chromosomally abnormal clon
- Page 469 and 470:
CTI 8425 TUMOR 80258 exchange (SCE)
- Page 471 and 472:
FCSP 80602 PF 8912 Chromosome Anoma
- Page 473 and 474:
CHSUP 9025 hepatitis B virus infect
- Page 475 and 476:
CHUB 82822 lymphocytic leukemia. Br
- Page 477 and 478:
CINN 82624 FCIC 91497 Clinical Refe
- Page 479 and 480:
CTCP 60142 CITAL 83730 peripheral b
- Page 481 and 482:
CLAD 82912 Reference Values: 0-19 y
- Page 483 and 484:
FCLIN 80143 PCLLM 20437 responsible
- Page 485 and 486:
FCLOZ 57284 FCLOM 57276 CLONS 50010
- Page 487 and 488:
CLOV 82490 variability underlying t
- Page 489 and 490:
F_2 9121 F2IS 7805 250 to 500 copie
- Page 491 and 492:
F5IS 7807 activated partial thrombo
- Page 493 and 494:
F8A 9070 F_10 9066 Coagulation Fact
- Page 495 and 496:
F_11 9067 F11IS 7803 Useful For: De
- Page 497 and 498:
CORU 60354 Richards Company, Tricon
- Page 499 and 500:
COBCU 60353 FCOCB 90093 COKEM 84140
- Page 501 and 502:
FCOCC 57355 SCOC 8295 within the pa
- Page 503 and 504:
CIMRP 88804 rarely found in CSF. Ho
- Page 505 and 506:
CCNT 82739 testing often depend upo
- Page 507 and 508:
Q10 87853 5 50.0-99.9 Strongly posi
- Page 509 and 510:
CTF 80440 CMIL 82833 Colorado Tick
- Page 511 and 512:
C1Q 8851 activated T cells(2) -TACI
- Page 513 and 514:
AH50 88676 COM 8167 congenital C4 d
- Page 515 and 516:
FCMD 91452 CAHBS 84113 Test Perform
- Page 517 and 518:
low or undetectable. All 3 analytes
- Page 519 and 520:
CUU 8590 Reference Values: ANTINUCL
- Page 521 and 522:
CURU 60426 CUS 8612 test results, c
- Page 523 and 524:
CORI 82476 leakage through the kidn
- Page 525 and 526:
CORN 82705 FCRN4 91982 Clinical Ref
- Page 527 and 528:
17-Hydroxyprogesterone, Serum - DHE
- Page 529 and 530:
FCBGC 91673 hydrocortisone) increas
- Page 531 and 532:
CIVC 6347 CLAV 6346 CRAV 6345 SALCT
- Page 533 and 534:
CINP 9369 diagnosis of Cushing synd
- Page 535 and 536:
enzyme that converts cortisol to co
- Page 537 and 538:
CDIP 89860 COTT 82859 0-2 years: no
- Page 539 and 540:
CTWD 82748 Interpretation: Detectio
- Page 541 and 542:
FACX 91340 COXA 80248 FBCX 91341 Co
- Page 543 and 544:
CPOXK 61264 constipation, urinary r
- Page 545 and 546:
CRAY 82343 caused by the release of
- Page 547 and 548:
CKEL 80906 32 days-23 months 313-90
- Page 549 and 550:
CRC 8500 CK activity reaches a maxi
- Page 551 and 552:
listed in the following paragraphs:
- Page 553 and 554:
CTU 8513 FCDC clearance of creatini
- Page 555 and 556:
CRY_S 80988 FCRYP 90453 Reference V
- Page 557 and 558:
CRYPF 60320 SCRYR 28071 Interpretat
- Page 559 and 560:
CRYPS 80335 SFC 8719 Clinical Infor
- Page 561 and 562:
OATC 82916 sensitization to particu
- Page 563 and 564:
WHTC 82915 FUNID 8223 Cultivated Wh
- Page 565 and 566:
CURL 82852 testing often depend upo
- Page 567 and 568:
CIFS 8052 8041 rearrangement of the
- Page 569 and 570:
GRP 8771 CCP 84182 derived from veg
- Page 571 and 572:
CYCSP 8931 CSTC 82994 Reference Val
- Page 573 and 574:
CYSWB 81354 Exon 15: Q890X Exon 6b:
- Page 575 and 576:
CYSR 81067 CYSTINE 3-15 years: 11-5
- Page 577 and 578:
environmental factors. Useful For:
- Page 579 and 580:
2C19S 60439 to affect CYP1A2 activi
- Page 581 and 582:
2C19O 60335 Cytochrome P450 2C19 Ge
- Page 583 and 584:
2C9SO 60337 Useful For: Predicting
- Page 585 and 586:
elationship between the polymorphis
- Page 587 and 588:
2D6TO 60340 flashes that accompany
- Page 589 and 590:
2D6O 60334 Cytochrome P450 2D6 Geno
- Page 591 and 592:
3A4O 61242 Useful For: An aid to cl
- Page 593 and 594:
CMG 80750 may have primary CMV infe
- Page 595 and 596:
Clinical Information: Cytomegalovir
- Page 597 and 598:
determining over immunosuppression
- Page 599 and 600:
QCMV 82986 ANCA 9441 Rev 2000;13:83
- Page 601 and 602:
DLAC 8878 Useful For: Diagnosis of
- Page 603 and 604:
DAND 82694 Class IgE kU/L Interpret
- Page 605 and 606:
DATRE 82481 9803 6 > or =100 Strong
- Page 607 and 608:
DHEA/DHEAS and their 16-hydroxylate
- Page 609 and 610:
Interpretation: Elevated dehydroepi
- Page 611 and 612:
DRPLA 81801 FDOC 90134 the immune r
- Page 613 and 614:
DESIP 81854 clinical manifestations
- Page 615 and 616:
83365 FDXM 91956 1):167-170 2. Amag
- Page 617 and 618:
DIA 8629 type 1 diabetes. Only 2% t
- Page 619 and 620:
DIG 8674 free digoxin levels daily
- Page 621 and 622:
DHT remain normal with aging, despi
- Page 623 and 624:
FDILT 91118 FRVVT 91738 DIP 83262 6
- Page 625 and 626:
DLDL 200269 FDSAC 91414 FDISP 91595
- Page 627 and 628:
FDM1 91592 ADNA 8178 FDKYL DM1 DNA
- Page 629 and 630:
DRD3O There has been a strong assoc
- Page 631 and 632:
DRD4 89096 DRD4O 60344 Dopamine Rec
- Page 633 and 634:
DOXP 9301 FDOXY 90061 Class IgE kU/
- Page 635 and 636:
CDAU2 80918 intended to be used in
- Page 637 and 638:
CDAU 9446 confirmed by GC-MS or GC-
- Page 639 and 640:
DAAMP 505341 mass spectrometry (LC-
- Page 641 and 642:
DAUCO 505230 DMETH 505343 triazolam
- Page 643 and 644:
DPRP 505345 propoxyphene are >10,00
- Page 645 and 646:
CDAG 500755 DSS 8421 Propoxyphene 7
- Page 647 and 648:
PDSU 88760 FBDAS 91776 Molecular Di
- Page 649 and 650:
DAU9 505320 DASM4 60553 Results of
- Page 651 and 652:
DUCK 82708 DULOX 89305 Phencyclidin
- Page 653 and 654:
EEEP 83155 ESYC 82721 2. Donat JF,
- Page 655 and 656:
FECHC 91342 sensitization and clini
- Page 657 and 658:
FEGFR 91903 FEGGW 91976 EGG 82872 U
- Page 659 and 660:
EGGP 82477 wheat proteins) followed
- Page 661 and 662:
FECHA 91710 EHRL 84319 the prevalen
- Page 663 and 664:
ELDR 82392 Elastase has been implic
- Page 665 and 666:
EFP 81488 > or =16 years: 0-29 mEq/
- Page 667 and 668:
REPU 60068 PEL 80085 Electrophoresi
- Page 669 and 670:
ELM 82672 Interpretation: A charact
- Page 671 and 672:
or = 1:1 Antibody Detected Diagnosi
- Page 673 and 674:
FJAZ 61014 5362 FEMA Endometrial St
- Page 675 and 676:
SAM 9049 caused by the release of p
- Page 677 and 678:
FENT 91434 FENTQ 91312 Diagnosis of
- Page 679 and 680:
EOSU 8335 FEPHD 90109 EPUR 82854 In
- Page 681 and 682:
EPIP2 81881 3 3.50-17.4 Positive 4
- Page 683 and 684:
80786 several weeks to months after
- Page 685 and 686:
LEBV 81239 onset of the infection,
- Page 687 and 688:
REVP 84160 Useful For: A prospectiv
- Page 689 and 690:
EPOR 61679 Chronic renal failure pa
- Page 691 and 692:
EEST 81816 levels of
- Page 693 and 694:
well-nourished children. Inherited
- Page 695 and 696:
89213 ESTF 84230 information, in ad
- Page 697 and 698:
should be within the reference rang
- Page 699 and 700:
E1 81418 Stage IV 12.3 years 15-85
- Page 701 and 702:
Males may show delayed puberty and
- Page 703 and 704:
ETOHU 500323 ETX 8769 Interpretatio
- Page 705 and 706:
EOXD 82767 EUCL 82758 Ethylene Oxid
- Page 707 and 708:
EHOR 82662 Reference Values: Class
- Page 709 and 710:
83363 transcripts by reverse transc
- Page 711 and 712:
FABKM 88266 F9INH 83103 Fabry Disea
- Page 713 and 714:
F8INH 83102 FX13M 57302 anticoagula
- Page 715 and 716:
FAPKM 83001 clinical manifestations
- Page 717 and 718:
FD 85319 LDLRS 81013 clinical pheno
- Page 719 and 720:
LDLM 89073 19p13 and consists of 18
- Page 721 and 722:
FANCA 85318 or more mutations in in
- Page 723 and 724:
FAPCP 82042 progress to evaluate th
- Page 725 and 726:
Myristoleic Acid, C14:1 or =18 yea
- Page 727 and 728:
1-17 years: 50-130 nmol/mL > or =18
- Page 729 and 730:
Palmitic Acid, C16:0 or =18 years:
- Page 731 and 732:
FAPM 81939 > or =18 years: 0.2-0.5
- Page 733 and 734:
POX 81369 Stearic Acid, C18:0 or =
- Page 735 and 736:
FBN1 89308 prolapse. There is signi
- Page 737 and 738:
FETH2 81880 prenatal, and family co
- Page 739 and 740:
LEU 8046 FOBT 60693 Fecal Leukocyte
- Page 741 and 742:
FESE 82363 FENTU 89655 therapeutic
- Page 743 and 744:
FEEP 82143 FERR 8689 Clinical Refer
- Page 745 and 746:
FECHK 60372 by 50% can be identifie
- Page 747 and 748:
FMB 88841 FMBNY 30320 Fetomaternal
- Page 749 and 750:
FGAKM 60722 secondary to multiple m
- Page 751 and 752:
FIBR 8482 FBC 80333 number of acqui
- Page 753 and 754:
FFIL4 90068 Complete removal can be
- Page 755 and 756:
FANT 82698 0 Negative 1 0.35-0.69 E
- Page 757 and 758:
produced by the fetus and the place
- Page 759 and 760:
FLUCO 82522 FFLRO 91795 FL 8641 Flu
- Page 761 and 762:
PROLX 80458 FFLUR 90091 17BFP 89739
- Page 763 and 764:
FSH 8670 patients with neuropsychia
- Page 765 and 766:
9806 FOOD6 81874 FDP1 86207 Fontana
- Page 767 and 768:
FOOD4 81872 and to define the aller
- Page 769 and 770:
FOOD8 81876 FOOD1 81868 Company, 20
- Page 771 and 772:
FOOD3 81871 Reference Values: Class
- Page 773 and 774:
FFRM 90298 9881 60694 Normal: Avera
- Page 775 and 776:
FXPB 9569 6 > or =100 Strongly posi
- Page 777 and 778:
FRTIX 80315 FFRED 91819 Free Thyrox
- Page 779 and 780:
FRUCT 81610 FROS 81164 FA have repe
- Page 781 and 782:
FSS 83121 error of folate and histi
- Page 783 and 784:
FDERM 87283 FGEN 84389 FVAG If posi
- Page 785 and 786:
FFURO 91119 FUSM 82750 species such
- Page 787 and 788:
GABCC 61515 GABA 80826 Interpretati
- Page 789 and 790:
GDT 89302 GDUR 89316 gadobenate dim
- Page 791 and 792:
GDCRU 60428 after administration of
- Page 793 and 794:
GALU 8765 Interpretation: In patien
- Page 795 and 796:
GALT 8333 Galactose-1-Phosphate Uri
- Page 797 and 798:
GAL6 84366 galactose-a-1,3-galactos
- Page 799 and 800:
GCT 84360 Galactosemia Reflex, Bloo
- Page 801 and 802:
GAL3 86202 Interpretation: Values b
- Page 803 and 804:
GGT 8677 common in those of eastern
- Page 805 and 806:
GANC 80140 GM1B 83189 Ganciclovir,
- Page 807 and 808:
GARL 82760 FGIP 90171 Garlic, IgE C
- Page 809 and 810:
GBAMS 60711 gastrin levels (>400 pg
- Page 811 and 812:
GAUW 81235 GELA 86326 Interpretatio
- Page 813 and 814:
GSNKM 60718 GENPK 84695 Reference V
- Page 815 and 816:
GENTT 81591 GERB 82545 Gentamicin,
- Page 817 and 818:
GRAB 80628 Clinical Information: Cl
- Page 819 and 820:
DGLDN 89031 Clinical Information: C
- Page 821 and 822:
DAGL 89029 Clinical References: 1.
- Page 823 and 824:
FGLIP disease is associated with a
- Page 825 and 826:
GPI 9158 (insulin-dependent diabete
- Page 827 and 828:
RGLUR 89847 mellitus which is chara
- Page 829 and 830:
GD65S 81596 Clinical Information: H
- Page 831 and 832:
GLT 82894 Reference Values:
- Page 833 and 834:
GOAT 82783 Class IgE kU/L Interpret
- Page 835 and 836:
9810 9812 FGNRH 90165 immune respon
- Page 837 and 838:
GWEE 82378 GRAM 8078 6 > or =100 St
- Page 839 and 840:
GRFR 82836 clinical manifestations.
- Page 841 and 842:
GRAS2 81707 GRAS3 81708 5 50.0-99.9
- Page 843 and 844:
GCBN 82769 and to define the allerg
- Page 845 and 846:
GPEA 82887 GPEP 82623 Company, 2007
- Page 847 and 848:
ALDR 82671 Reference Values: Class
- Page 849 and 850:
GRHKM 50038 hyperoxalurias. Kidney
- Page 851 and 852:
FIRGH 90161 FGCU 57482 Reference Va
- Page 853 and 854:
GUAV 82357 GUIN 82706 Clinical Refe
- Page 855 and 856:
FHAD2 91965 HIBS 83261 likelihood o
- Page 857 and 858:
HALI 82633 HALO 80339 Halibut, IgE
- Page 859 and 860:
FHAN 90405 the concentration of IgE
- Page 861 and 862:
HAZ 82670 responsible for eliciting
- Page 863 and 864:
HMSBR 34506 Interpretation: The ref
- Page 865 and 866:
exposure. Absorbed arsenic is rapid
- Page 867 and 868:
HMHA 45479 HMNA 31070 SHELA 84409 H
- Page 869 and 870:
SHELI 80668 or =1.00 (positive) Ig
- Page 871 and 872:
UBT 81590 Useful For: As an aid in
- Page 873 and 874:
EXHB 60562 EXHBM 60558 HLLFH 34854
- Page 875 and 876:
9819 FHME 57485 HCASC 34626 anticip
- Page 877 and 878:
HBA1C 82080 H63D is insufficient to
- Page 879 and 880:
HBELC 81626 Hgb S/beta thalassemia
- Page 881 and 882:
HPFH 8270 SFMON 60205 3-5 months: 1
- Page 883 and 884:
UNHB 9095 HAEVP 84157 Interpretatio
- Page 885 and 886:
FIXMS 84209 Clinical Information: H
- Page 887 and 888:
UHSD 8582 HEPN 80609 *Alternative r
- Page 889 and 890:
of thrombocytopenia can be rapid (w
- Page 891 and 892:
HAV 83330 Useful For: Diagnosis of
- Page 893 and 894:
HBC 8347 CORAB 32111 are negative D
- Page 895 and 896:
HEPB 200905 Negative HEPATITIS Bs A
- Page 897 and 898:
HBAB 8254 Interpretation: Please re
- Page 899 and 900:
HBVQU 88634 (HBV) infection, or chr
- Page 901 and 902:
FHBGT 57478 FHBSA 57489 HEAB 80973
- Page 903 and 904:
HBGCD 83626 HCVPS 13009 Hepatitis B
- Page 905 and 906:
HCPCR 60707 Hepatitis C Antibody Sc
- Page 907 and 908:
FHFIB 91402 Reference Values: Negat
- Page 909 and 910:
HCCAD 87858 versus 24 weeks), patie
- Page 911 and 912:
QHCV 81130 Telaprevir-containing Co
- Page 913 and 914:
HEPP 200080 Reference Values: Refer
- Page 915 and 916:
FHER 91518 FHER2 81954 false-negati
- Page 917 and 918:
FH2MT 60655 In much the same way as
- Page 919 and 920:
HEMP 61337 Reference Values: Report
- Page 921 and 922:
HHTP 89394 Telangiectasia, ENG and
- Page 923 and 924:
ENGK 89391 that HHT1 has a more sev
- Page 925 and 926:
HPKM 88691 endometrium, and stomach
- Page 927 and 928:
FHRIN 91450 VDER 82048 Useful For:
- Page 929 and 930:
HSVG 84429 A negative result does n
- Page 931 and 932:
FHSAB 57434 FHERV 57305 cerebrospin
- Page 933 and 934:
HERR 82823 IgM 85% of the populatio
- Page 935 and 936:
MUGS 80350 2 0.70-3.49 Positive 3 3
- Page 937 and 938:
NAGW 8775 percent hexosaminidase A
- Page 939 and 940:
NAGS 8774 disease carrier identific
- Page 941 and 942:
HIPA 9756 FHISP 57275 FHISU 57207 p
- Page 943 and 944:
SHSTO 26692 CHIST 8230 HISTO 83853
- Page 945 and 946:
HBRPB 60751 HIV2F 80443 management
- Page 947 and 948:
HV1CD 83628 HIV antibody test resul
- Page 949 and 950:
HIVFA 81758 FHIVD 91901 Negative Se
- Page 951 and 952:
GHIVR 88782 Reference Values: Not a
- Page 953 and 954:
HIQGP 89402 indicated that detectio
- Page 955 and 956:
HIVQR 13035 Clinical References: 1.
- Page 957 and 958:
WBANF 32466 low or undetectable HIV
- Page 959 and 960:
HIVE 9333 indicates infection with
- Page 961 and 962:
HIV2M 60356 FHV2Q 91490 Clinical Re
- Page 963 and 964:
DISII 32864 HLA15 89347 transplant
- Page 965 and 966:
HL57O 60347 Based on DNA sequence v
- Page 967 and 968:
HMBSK 61217 dominant disorder with
- Page 969 and 970:
HCYSU 80378 deficiency of B12 and f
- Page 971 and 972:
HVAR 60275 HUNY 82373 Medical. Edit
- Page 973 and 974:
HOP 82370 1 0.35-0.69 Equivocal 2 0
- Page 975 and 976:
HORM 82375 bronchospasm) in infants
- Page 977 and 978:
HFSF 82608 DF 82905 6 > or =100 Str
- Page 979 and 980:
HD1 81877 sensitization to particul
- Page 981 and 982:
HDHS 82903 FHPVG 57480 House Dust/H
- Page 983 and 984:
THCG 80678 HHV6 87532 Human Chorion
- Page 985 and 986:
FHMPV 91433 BHPV 83344 sequences ha
- Page 987 and 988:
60483 FHPL 91178 HTLVL 83277 along
- Page 989 and 990:
HTLVI 9539 Diagn Lab Immunol 1998;5
- Page 991 and 992:
FHISS 91370 > or =0.50 IU/mL Protec
- Page 993 and 994:
HD 61622 CORD BLOOD 510 - 1275 0 0
- Page 995 and 996:
FHYDC 90293 HYD18 80744 Performed B
- Page 997 and 998:
have demonstrated progressive incre
- Page 999 and 1000:
FHPEP 57369 oxalic and glyceric aci
- Page 1001 and 1002:
SAL 8768 HYPOG 82439 Hypersensitivi
- Page 1003 and 1004:
61207 IDNS 80945 Clinical Reference
- Page 1005 and 1006:
IGAS 87938 individuals with food al
- Page 1007 and 1008:
IGGS 9259 Adults 288-736 512 Test P
- Page 1009 and 1010:
FIG4F 91936 FIMRG 87995 synthesis o
- Page 1011 and 1012:
FICEP 91172 levels of imipramine an
- Page 1013 and 1014:
FISP 91624 IMFXO Immune Status Pane
- Page 1015 and 1016:
IGD 9272 Algorithm in Special Instr
- Page 1017 and 1018:
FLCP 84190 IGG 8160 Immunoglobulin
- Page 1019 and 1020:
BCGBM 31141 BCGRV 31142 lymphoproli
- Page 1021 and 1022:
TLCU 87934 Clinical Information: Th
- Page 1023 and 1024:
FIMMC 57370 FUIQL 57488 13-
- Page 1025 and 1026:
89067 IgA and IgG ASCA, PV of 90%.(
- Page 1027 and 1028:
PROD 60552 Interpretation: The pres
- Page 1029 and 1030:
800167 Influenza Virus Type A and T
- Page 1031 and 1032:
INHA 81049 Inhibin A, Tumor Marker,
- Page 1033 and 1034:
INHU 82789 Marker, Serum. For monit
- Page 1035 and 1036:
FINS 81728 INS 8664 Interpretation:
- Page 1037 and 1038:
(breast, colon, prostate, lung), an
- Page 1039 and 1040:
8 years 70-344 44 9 years 81-389 52
- Page 1041 and 1042:
IGF1 15867 antibodies: a problem fo
- Page 1043 and 1044:
36-40 years 106-277 41-45 years 98-
- Page 1045 and 1046:
emains controversial. Elevated seru
- Page 1047 and 1048:
FINTA 91708 FINTB 91719 BIL28 61702
- Page 1049 and 1050:
FIL10 91653 FIL2 90481 interpreted
- Page 1051 and 1052:
IMAX 5347 IFBA 9335 UIOD 9549 Inter
- Page 1053 and 1054:
FIPEC 91134 FEC 34624 Clinical Info
- Page 1055 and 1056:
absorption and progressive iron dep
- Page 1057 and 1058:
IA2 89588 FISLC 57306 Clinical Refe
- Page 1059 and 1060:
IMDI 82774 caused by the release of
- Page 1061 and 1062:
INHP 9768 IVD 83644 1 0.35-0.69 Equ
- Page 1063 and 1064:
ITCON 81247 JACK 82371 Itraconazole
- Page 1065 and 1066:
JAKXB 89189 JAKXM 4 17.5-49.9 Stron
- Page 1067 and 1068:
JAK2M 31155 thrombocythemia (25%-55
- Page 1069 and 1070:
JCEDR 82865 JMIL 82831 2005;106:120
- Page 1071 and 1072:
LCJC 88909 immunocompromised would
- Page 1073 and 1074:
9889 JUNE 82893 2 0.70-3.49 Positiv
- Page 1075 and 1076:
FKAN 90069 KETAU 89443 FKEBS 91887
- Page 1077 and 1078:
KIDBN 82619 CASA DeSilvio M, Khor L
- Page 1079 and 1080:
82266 89670 88956 in normal tissues
- Page 1081 and 1082:
88955 89669 Cancer 2004;40:689-695
- Page 1083 and 1084:
KPCRP 89675 Clinical Information: U
- Page 1085 and 1086:
GALCK 60695 KRAS 89378 Krabbe Disea
- Page 1087 and 1088:
specificity is derived from the fac
- Page 1089 and 1090:
LAA 8665 FLACT 91560 untreated pern
- Page 1091 and 1092:
LAMB 82699 0 Negative 1 0.35-0.69 E
- Page 1093 and 1094:
LAMO 80999 RDS is inversely related
- Page 1095 and 1096:
FLTX 57118 LATX 82787 5 50.0-99.9 S
- Page 1097 and 1098:
significantly since the introductio
- Page 1099 and 1100:
PBU 8600 LEADB 300098 blood lead re
- Page 1101 and 1102:
PBNA 89857 PBRU 60246 Clinical Info
- Page 1103 and 1104:
LEFLU 60292 Reference Values: CHOLE
- Page 1105 and 1106:
LEGI 8204 SLEG 8122 Fraser DW, Tsai
- Page 1107 and 1108:
LEIS 86219 LEM 82678 the Associatio
- Page 1109 and 1110:
LEPD 82849 FLEP 91339 5 50.0-99.9 S
- Page 1111 and 1112:
LEUC 9771 LCMS 3287 immune response
- Page 1113 and 1114:
LEVE 83140 Clinical Information: Le
- Page 1115 and 1116:
FLIMB 91635 LIME 82360 Therapeutic
- Page 1117 and 1118:
LINS 86311 Class IgE kU/L Interpret
- Page 1119 and 1120:
BFLAC 34622 LPSC 8053 > or =16 year
- Page 1121 and 1122:
LIPA 81558 available from multiple
- Page 1123 and 1124:
LMPP 83673 Lipoprotein Metabolism P
- Page 1125 and 1126:
FLIS 90717 FLIST 90048
- Page 1127 and 1128:
LOB 82744 LORAZ 80459 HA: Autoantib
- Page 1129 and 1130:
LUPN 82613 exhibiting ALK rearrange
- Page 1131 and 1132:
LH 8663 0.9-1.2 The INR is used onl
- Page 1133 and 1134:
9861 9956 PBORR 80574 syndrome. Pos
- Page 1135 and 1136:
FBBIA 91898 FBBAB 91309 LYWB 9535 b
- Page 1137 and 1138:
FBBC6 91899 inflammation around the
- Page 1139 and 1140:
CLYME 83856 FLASC 57281 LPMAF 60593
- Page 1141 and 1142:
LPAGF 60592 1-infected patients: to
- Page 1143 and 1144:
decrease in proliferation of only a
- Page 1145 and 1146:
LSDU 81743 LPC 83399 Lysergic Acid
- Page 1147 and 1148:
lipid component of myelin. The abse
- Page 1149 and 1150:
LYZKM 60720 MUR 8507 Edited by S Sa
- Page 1151 and 1152:
MACE 82492 Interpretation: ImmunoCA
- Page 1153 and 1154:
MGFT 60030 symptoms of hyperprolact
- Page 1155 and 1156:
MGRU 60245 likely source of such ex
- Page 1157 and 1158:
MGCRU 60244 FMASC 90054 Magnesium/C
- Page 1159 and 1160:
MAAN 82396 Clinical Information: Ma
- Page 1161 and 1162:
MAND 82352 MNU 8080 5 50.0-99.9 Str
- Page 1163 and 1164:
igidity, with increased scores on t
- Page 1165 and 1166:
MNCRU 60027 Clinical Information: M
- Page 1167 and 1168:
MBL 81051 FMPLE 57188 York, Chapter
- Page 1169 and 1170:
MARE 82141 constitutes tau-positive
- Page 1171 and 1172:
MCC 88636 9230 9829 Reference Value
- Page 1173 and 1174:
MFOX 82914 identify allergens which
- Page 1175 and 1176:
ME2KM 89285 are reported in males,
- Page 1177 and 1178:
MCADK 83934 patients, approximately
- Page 1179 and 1180:
FMELT 57120 MELN 82762 sensitizatio
- Page 1181 and 1182:
Reference Range: IgG
- Page 1183 and 1184:
FMCPC 57437 Diagnosis of central ne
- Page 1185 and 1186:
This test was developed and its per
- Page 1187 and 1188:
Reference Range:
- Page 1189 and 1190:
St. Louis encephalitis virus throug
- Page 1191 and 1192:
MEPHS 83778 FMERC 91120 HGOM 82755
- Page 1193 and 1194:
HGHAR 8498 eliciting a proliferatio
- Page 1195 and 1196:
METAF 83006 antibodies interact wit
- Page 1197 and 1198:
PMET 81609 60-69 years: 138-521 mcg
- Page 1199 and 1200:
patients from those with tumor-indu
- Page 1201 and 1202:
MTDNS 83131 Useful For: Monitoring
- Page 1203 and 1204:
METR 9322 MEVP 84159 other causes,
- Page 1205 and 1206:
FMMD 57307 MMAAF 81921 Test Perform
- Page 1207 and 1208:
MMAS 80289 Useful For: Evaluating c
- Page 1209 and 1210:
MAHKM 89135 Clinical Information: M
- Page 1211 and 1212:
MHDKM 61098 Carrier screening in ca
- Page 1213 and 1214:
FMI2 57186 RMA 81260 diminished or
- Page 1215 and 1216:
MPSF 82515 studies have shown that
- Page 1217 and 1218:
MTBS 81507 microsatellite instabili
- Page 1219 and 1220:
PMLK 82827 the concentration of IgE
- Page 1221 and 1222:
IHCO 29004 Mismatch Repair (MMR) Pr
- Page 1223 and 1224:
FMITO 91130 MLH1H 87978 Mitotane (L
- Page 1225 and 1226:
MLHKM 83002 mutation. In cases wher
- Page 1227 and 1228:
MLH12 83191 MLH1/MSH2 Mutation Scre
- Page 1229 and 1230:
MOLD1 81878 MINT 61696 Interpretati
- Page 1231 and 1232:
MOLUR 89473 MOLPS 89270 Molybdenum,
- Page 1233 and 1234:
FMNM 91829 inhibition of xanthine o
- Page 1235 and 1236:
found on protein electrophoresis (P
- Page 1237 and 1238:
Clinical Information: Serum protein
- Page 1239 and 1240:
MDCG 86880 MORP 83132 complement ca
- Page 1241 and 1242:
MOTH 82738 2 0.70-3.49 Positive 3 3
- Page 1243 and 1244:
MOUS 82707 4 17.5-49.9 Strongly pos
- Page 1245 and 1246:
9832 MPLB 89776 Useful For: Testing
- Page 1247 and 1248:
MSH2M 83016 dependent on the gene i
- Page 1249 and 1250:
MSH6M 83723 Useful For: Diagnostic
- Page 1251 and 1252:
9831 MCIV 85321 MPSSC 84464 disorde
- Page 1253 and 1254:
adaptive skills. Death generally oc
- Page 1255 and 1256:
MUG 82683 Clinical Information: Cli
- Page 1257 and 1258:
MENKM 81082 1 0.35-0.69 Equivocal 2
- Page 1259 and 1260:
FMUMM 91456 CMUMP Interpretation: O
- Page 1261 and 1262:
MMPG 82431 MMPM 80977 IgM Negative
- Page 1263 and 1264:
FMUSK 91445 MSTD 82801 sensitizatio
- Page 1265 and 1266:
FHST 91957 FHIST 90018 FHSAG 90017
- Page 1267 and 1268:
MGEP 83371 found in 13% of patients
- Page 1269 and 1270:
MGLES 83369 neurological complicati
- Page 1271 and 1272:
CTB 8205 CTBBL 82443 VA: Lambert-Ea
- Page 1273 and 1274:
MTBRP 88807 MTBPZ 56099 Mycobacteri
- Page 1275 and 1276:
MPA 81563 MGRP 60755 intermediate t
- Page 1277 and 1278:
FMPAB 90055 MPC 80422 that has been
- Page 1279 and 1280:
FMYEL 90476 FMDS 84387 Reference ra
- Page 1281 and 1282:
MYH 84304 May be useful to follow t
- Page 1283 and 1284:
MYOS 9035 REFERENCE RANGE: or = 1:
- Page 1285 and 1286:
FMY3P 57279 FMYO 91544 FCHOP Refere
- Page 1287 and 1288:
NAT2 83389 Useful For: Assisting in
- Page 1289 and 1290:
NMHIN 83011 Slow *14G 191G->A 282C-
- Page 1291 and 1292:
FNAD 80761 FNALO 91784 NARC 82026 N
- Page 1293 and 1294:
T- and B-CELL QN BY FLOW CYTOMETRY
- Page 1295 and 1296:
FNEFA 91135 MGRNA 61646 Clinical Re
- Page 1297 and 1298:
FNMEN 91669 Clinical Information: G
- Page 1299 and 1300:
NETT 82734 NEURF 88846 Reference Va
- Page 1301 and 1302:
PNEFS 84300 Bone Marrow Clinical In
- Page 1303 and 1304:
PNEFC 84299 Note: Titers lower than
- Page 1305 and 1306:
NMOER 60796 optic nerves and the sp
- Page 1307 and 1308:
NSESF 81796 reference range. Other
- Page 1309 and 1310:
FNEU 91688 FNTSM 91940 Reference Va
- Page 1311 and 1312:
NAD 81409 FNIAC 91379 that is unusu
- Page 1313 and 1314:
NIS 8622 essential for the catalyti
- Page 1315 and 1316:
NICOS 82509 toxic Ni compounds such
- Page 1317 and 1318:
NPDMS 61117 Reference Values: Non-t
- Page 1319 and 1320:
NIEM 9313 NPCKM 83118 Clinical Refe
- Page 1321 and 1322:
FNIFE 91747 NITF 8909 is a biochemi
- Page 1323 and 1324:
NMDCC 61513 stromal tumor, pseudopa
- Page 1325 and 1326:
SSF1 87294 NSIP 31769 Insulin Sensi
- Page 1327 and 1328:
FNORO 91893 FNLV 91366 NEREG 31767
- Page 1329 and 1330:
PBNP 84291 Toxic concentration: > o
- Page 1331 and 1332:
NTXPR 61656 diagnosis and short-ter
- Page 1333 and 1334:
NUTSP 31771 antibodies interact wit
- Page 1335 and 1336:
OATS 82688 3 3.50-17.4 Positive 4 1
- Page 1337 and 1338:
FLNZ 91129 OLIG 8017 sensitivity to
- Page 1339 and 1340:
FOLRU 91954 OLIV 82733 NY, Springer
- Page 1341 and 1342:
OPATM 84326 sensitivity to inhalant
- Page 1343 and 1344:
OPRM1 89612 morphine to codeine can
- Page 1345 and 1346:
9836 ORCH 82907 clinical manifestat
- Page 1347 and 1348:
OAU 80619 0 Negative 1 0.35-0.69 Eq
- Page 1349 and 1350:
OPTU 83190 metabolism of arginine.
- Page 1351 and 1352:
UOSMS 9340 UOSMU 9260 Clinical Refe
- Page 1353 and 1354:
FOVA1 57492 43 and 44. The N-MID-fr
- Page 1355 and 1356:
OXI 82679 testing often depend upon
- Page 1357 and 1358:
POXA 81408 deficiencies (primary hy
- Page 1359 and 1360:
FOXAZ 90108 OMHC 81030 FOXYC 91639
- Page 1361 and 1362:
OYST 82883 FPZ 91495 Oyster, IgE Cl
- Page 1363 and 1364:
NPAIN 200244 (GC-FID) the following
- Page 1365 and 1366:
FPANS 57129 FPANC 91415 HPP 8014 Pr
- Page 1367 and 1368:
PAPY 82356 PAPR 82810 Company, 2007
- Page 1369 and 1370:
and cellular immune responses to ca
- Page 1371 and 1372:
nonorgan-specific antibodies that a
- Page 1373 and 1374:
PTH (numbering, by universal conven
- Page 1375 and 1376:
parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels. T
- Page 1377 and 1378:
PTHRP 81774 from the needle for a s
- Page 1379 and 1380:
PJUD 82877 POFF Equivocal: 20.1-24.
- Page 1381 and 1382:
PSLY 82765 Interpretation: Steady-s
- Page 1383 and 1384:
FPB19 57483 86340 PARVO 83151 1983;
- Page 1385 and 1386:
FPCA3 57486 caused by the release o
- Page 1387 and 1388:
89671 Interpretation: An interpreta
- Page 1389 and 1390:
F512 84463 PECH 82816 imatinib resp
- Page 1391 and 1392:
PEAN 82888 PEAR 82807 Peanut, IgE C
- Page 1393 and 1394:
PAS38 83346 Reference Values: Class
- Page 1395 and 1396:
FPEMC 90120 PBPO 82660 immunoglobul
- Page 1397 and 1398:
PENIV 82656 PENL the specific organ
- Page 1399 and 1400:
FPCAY 91953 FPEPS 91638 FPERC 91631
- Page 1401 and 1402:
PNZN 9789 Clinical Information: Vit
- Page 1403 and 1404:
UPHB 9572 FPHFL 57309 PHU_ 9312 rel
- Page 1405 and 1406:
PCPU 80371 FPHNZ 90368 PBAR Referen
- Page 1407 and 1408:
PKU 8380 Test Performed By: Monogra
- Page 1409 and 1410:
PNYFR 9993 30 mcg/mL. Reference Val
- Page 1411 and 1412:
PHMA 82736 phenytoin, competes for
- Page 1413 and 1414:
natural autoantibodies.(2) Plasma f
- Page 1415 and 1416:
CLIPG 87987 an unexplained cutaneou
- Page 1417 and 1418:
MCLIP 81900 Interpretation: APL, GP
- Page 1419 and 1420:
PPL 8296 PMMIF 89657 Phospholipids,
- Page 1421 and 1422:
PHOS 8408 (CDG-Ia or PMM2-CDG) or p
- Page 1423 and 1424:
POU 8526 PAHD 82786 Phosphorus, Uri
- Page 1425 and 1426:
PIGE 82781 Reference Values: An int
- Page 1427 and 1428:
PIGF 82145 Class IgE kU/L Interpret
- Page 1429 and 1430:
PINW 9204 immune response to allerg
- Page 1431 and 1432:
PISTA 82808 Interpretation: Elevate
- Page 1433 and 1434:
PLAI 82837 PBLI 9302 characteristic
- Page 1435 and 1436:
newly diagnosed MM and also to dete
- Page 1437 and 1438:
PAI1 86083 OXYHEMOGLOBIN > or =12 m
- Page 1439 and 1440:
PLAB 8538 PTSE 61749 Interpretation
- Page 1441 and 1442:
FPM1 90192 PMLR 84114 3 3.50-17.4 P
- Page 1443 and 1444:
PMS2K 61174 Genetics and Genomics (
- Page 1445 and 1446:
SPN 8047 FPOLC 57265 sensitive (21%
- Page 1447 and 1448:
GAAKM 89897 involvement, and rate o
- Page 1449 and 1450:
FPORK 91935 PREGI 82691 5 50.0-99.9
- Page 1451 and 1452:
PBGDW 31894 PBGD_ 88925 Porphobilin
- Page 1453 and 1454:
PEWE 31893 has additional questions
- Page 1455 and 1456:
Clinical Information: The porphyria
- Page 1457 and 1458:
PFR 28117 Algorithm and Porphyria (
- Page 1459 and 1460:
PQNU 8562 porphyria and porphyria c
- Page 1461 and 1462:
PTP 8731 Males: < or =230 nmol/24 h
- Page 1463 and 1464:
POSV 9205 PMSBB 81931 range if the
- Page 1465 and 1466:
NAK 8468 KFT 60031 spectrometry for
- Page 1467 and 1468:
RKUR 84475 carbohydrates passing th
- Page 1469 and 1470:
FPOTW 92002 PWDNA 81153 Reference V
- Page 1471 and 1472:
17PRN 88646 taking recommended dail
- Page 1473 and 1474:
PREGN 88645 16-17 years:
- Page 1475 and 1476:
FPAP2 91198 Premature Adrenarche Pr
- Page 1477 and 1478:
PAD 81424 increase to 60-400 betwee
- Page 1479 and 1480:
PBPR blood and vaginal secretions;
- Page 1481 and 1482:
PA 8683 likelihood of allergic dise
- Page 1483 and 1484:
FPNTS 57311 PGSN 8141 levels in sep
- Page 1485 and 1486:
GRNMS 89188 GRNKM 89187 Progranulin
- Page 1487 and 1488:
PRLPM 84462 PRL cutoff results in a
- Page 1489 and 1490:
PHD2 61683 FPHEG 90101 deficiency(i
- Page 1491 and 1492:
FPRTG 91565 6-mercaptopurine. Metab
- Page 1493 and 1494:
FPPOX 57140 FPRSG 57149 FPGD2 90154
- Page 1495 and 1496:
SPSA 82023 previously diagnosed pro
- Page 1497 and 1498:
FPSAU 91817 PACP 8019 biopsy does n
- Page 1499 and 1500:
CFX 9339 2 0.70-3.49 Positive 3 3.5
- Page 1501 and 1502:
S_FX 80775 Clinical References: 1.
- Page 1503 and 1504:
12PTU 89043 S and C4bBP are coordin
- Page 1505 and 1506:
TP 8520 by increased plasma concent
- Page 1507 and 1508:
PR3 82965 FPFRG 91503 exercise. Low
- Page 1509 and 1510:
PT 9236 Prothrombin Time, Plasma Cl
- Page 1511 and 1512:
PPFE 8739 PROTR 9797 CHED The Metab
- Page 1513 and 1514:
PCHES 8518 FPTHC 91504 Nelson TC, B
- Page 1515 and 1516:
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (20%-30
- Page 1517 and 1518:
PTP22 89315 9901 Tartaglia M, Kalid
- Page 1519 and 1520:
PUPY 81420 Useful For: Testing for
- Page 1521 and 1522:
PLP 60295 B6PA 61065 30-125 ng/mL p
- Page 1523 and 1524:
PK 8659 PYRC 83356 dehydrogenase co
- Page 1525 and 1526:
QUAD 81149 of the infection, the ou
- Page 1527 and 1528:
QPALM 82863 risk depends on the lev
- Page 1529 and 1530:
REPII 82782 ventricular arrhythmia.
- Page 1531 and 1532:
RUPR 82148 immunoglobulin E (IgE)-s
- Page 1533 and 1534:
RWEED 82616 testing often depend up
- Page 1535 and 1536:
RAT 82725 testing often depend upon
- Page 1537 and 1538:
RTUP 82794 FRECM 91892 5 50.0-99.9
- Page 1539 and 1540:
SORR 82737 Class IgE kU/L Interpret
- Page 1541 and 1542:
4986 8104 osmotic and nonosmotic di
- Page 1543 and 1544:
PRA 8060 the transplanted kidney (a
- Page 1545 and 1546:
RSVAN 110300 RSVP 60550 IgG:
- Page 1547 and 1548:
FREB 90331 RBP24 81783 such as vita
- Page 1549 and 1550:
RHNI 82856 of polystyrene latex par
- Page 1551 and 1552:
VITB2 61637 RIB 87837 virological r
- Page 1553 and 1554:
FRCBP 57342 3 3.50-17.4 Positive 4
- Page 1555 and 1556:
RNAP 83397 RNP 81357 RNA Polymerase
- Page 1557 and 1558:
MARS 82701 sometimes been called "w
- Page 1559 and 1560:
ROSC 80262 Clinical Information: Pr
- Page 1561 and 1562:
ROC 5194 ROM 80979 Rubeola (Measles
- Page 1563 and 1564:
RYEG 82908 2 0.70-3.49 Positive 3 3
- Page 1565 and 1566:
AASCA 83022 GASCA 83023 Saccharomyc
- Page 1567 and 1568:
SALM 82754 FSMLA 91889 Reference Va
- Page 1569 and 1570:
SARD 82818 SCLE 82716 Clinical Refe
- Page 1571 and 1572:
SHUR 60451 FSCHC 91781 Interpretati
- Page 1573 and 1574:
OXK 8148 SEAFP 31770 Immunology Pri
- Page 1575 and 1576:
SECOS 8243 FSEC 90173 FSED 91811 Cl
- Page 1577 and 1578:
SEUR 60077 SES 9765 Jun;27(6):662-6
- Page 1579 and 1580:
FER 81641 SEMA 9206 Interpretation:
- Page 1581 and 1582:
FSMN 91449 SEPTK 61101 1 0.35-0.69
- Page 1583 and 1584:
information from both trimesters is
- Page 1585 and 1586:
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH),
- Page 1587 and 1588:
HTR2O 60338 pharmacogenetic finding
- Page 1589 and 1590:
HTTO 60339 SERU 87834 Clinical Refe
- Page 1591 and 1592:
SERWB 84373 Reference values apply
- Page 1593 and 1594:
develop. In advanced tumors, morbid
- Page 1595 and 1596:
SHBG 9285 and to define the allerge
- Page 1597 and 1598:
FSRY 88537 Stage III 13.6 5.8-182 S
- Page 1599 and 1600:
Clinical References: Homburger HA:
- Page 1601 and 1602:
SCADK 83947 Reference Values: Class
- Page 1603 and 1604:
FSHOX 57127 FSHRP 91650 SHRI 82677
- Page 1605 and 1606:
BIR 82674 1 0.35-0.69 Equivocal 2 0
- Page 1607 and 1608:
SIRO 81768 SM 81358 Sirolimus, Bloo
- Page 1609 and 1610:
SMA 6284 Deletion/Duplication, FISH
- Page 1611 and 1612:
NABF 8039 NAF 8374 osmolality, and
- Page 1613 and 1614:
NAU 8525 sodium) is a predictable c
- Page 1615 and 1616:
STFR 84283 SLC1B 61736 autoimmune h
- Page 1617 and 1618:
FSOMA 90172 substrates of OATP1B1,
- Page 1619 and 1620:
SPAG 8980 SGBF 8275 antibodies inte
- Page 1621 and 1622:
SAAS 89882 SAAI 89883 Useful For: D
- Page 1623 and 1624:
SPIN 86312 FSMAC 57189 Clinical Ref
- Page 1625 and 1626:
FSCA2 91586 FSCA3 91587 FSCA6 91588
- Page 1627 and 1628:
SFGP 83679 SPRU 82394 FSCC 57312 fo
- Page 1629 and 1630:
SQUID 82631 FSRP 57187 Squid, IgE C
- Page 1631 and 1632:
SSB 81359 adenopathy. SS-A/Ro is 1
- Page 1633 and 1634:
ST2S 61723 frequency of encephaliti
- Page 1635 and 1636:
FSTS 88539 Clinical Information: Cl
- Page 1637 and 1638:
INSEC 31765 STBY 82676 Clinical Ref
- Page 1639 and 1640:
SPNC 89971 SPNEU 83150 Although the
- Page 1641 and 1642:
espond to immunization with unconju
- Page 1643 and 1644:
FSTRP 90440 FSTSC 91984 STR 8746 de
- Page 1645 and 1646:
FSAI 57313 STCH 9928 FSTYR 91094 Re
- Page 1647 and 1648:
SDHSP 89550 involving the telomeres
- Page 1649 and 1650:
SDHKM 89554 heterozygous germline m
- Page 1651 and 1652:
SDHSB 89551 will probably not resul
- Page 1653 and 1654:
SDHSD 89553 corresponding figures a
- Page 1655 and 1656:
SUAC 83635 FSUCC 57460 9849 9850 FS
- Page 1657 and 1658:
SFZ 8238 testing often depend upon
- Page 1659 and 1660:
SUNFS 82813 Reference Values: Inter
- Page 1661 and 1662:
poorly understood. Urine supersatur
- Page 1663 and 1664:
normal or increased citrate value s
- Page 1665 and 1666:
SNS 82594 15-25 mg/kg of body weigh
- Page 1667 and 1668:
5581 SGUM 82483 verbal and written
- Page 1669 and 1670:
VERG 82909 3 3.50-17.4 Positive 4 1
- Page 1671 and 1672:
83361 cell tumors (Ewing sarcoma, a
- Page 1673 and 1674:
SGSU 81035 Flunisolide: 0.10 mcg/dL
- Page 1675 and 1676:
SYPGN 32184 antibodies, RPR titers
- Page 1677 and 1678:
TBNY 82589 may actually represent e
- Page 1679 and 1680:
12-17 years: 1,000-2,200 cells/mcL*
- Page 1681 and 1682:
6-11 years: 31-47%* 12-17 years: 31
- Page 1683 and 1684:
Reference Values: T- AND B-CELL QUA
- Page 1685 and 1686:
TCMPF 60588 LYMPHOCYTE RATIO H/S ra
- Page 1687 and 1688:
TBBS 9336 0-2 months: 170-1,100 cel
- Page 1689 and 1690:
12-17 years: 31-52%* 18-55 years: 3
- Page 1691 and 1692:
FRTLP 89040 and trisomy 8 in hepato
- Page 1693 and 1694:
TREC 87959 2004;36:1084-1089 T-Cell
- Page 1695 and 1696:
TCGR 83122 12-23 months: 620-2,000
- Page 1697 and 1698:
TCGRV 31140 TCP 89319 malignancies
- Page 1699 and 1700:
CD4+CD62L+CD27+ naive T cells 15-71
- Page 1701 and 1702:
TREGS 89318 volunteers: relationshi
- Page 1703 and 1704:
FRT3P 600915 et al: CD127 expressio
- Page 1705 and 1706:
T3 8613 TUP 81792 Clinical Referenc
- Page 1707 and 1708:
FRT4 8725 T4TF 8684 hypothalamic-pi
- Page 1709 and 1710:
FFTAP 57299 TARR 82486 immunosuppre
- Page 1711 and 1712:
TSD 82588 gangliosides in cells of
- Page 1713 and 1714:
FFTEI 91284 FFTEM 80763 TTBS 80065
- Page 1715 and 1716:
serum testosterone should still be
- Page 1717 and 1718:
pituitary-gonadal feedback involvin
- Page 1719 and 1720:
TTFB 83686 > or =19 years: 240-950
- Page 1721 and 1722:
kept within the normal female range
- Page 1723 and 1724:
symptoms. These may include some de
- Page 1725 and 1726:
TTOX 82138 FFTEN 57102 critical iss
- Page 1727 and 1728:
skeletal anomalies (chest abnormali
- Page 1729 and 1730:
TGFK2 89462 factor-beta receptor ge
- Page 1731 and 1732:
THEVP 84158 others. Approximately 2
- Page 1733 and 1734:
TLRU 60324 TLCRU 60325 FFTHC 90094
- Page 1735 and 1736:
TAMV 82514 TDP 85753 the therapeuti
- Page 1737 and 1738:
83343 HPV have been shown to be at
- Page 1739 and 1740:
89118 cervical/vaginal cytologic di
- Page 1741 and 1742:
FCYNS 57491 FFTHM 90354 Useful For:
- Page 1743 and 1744:
FFTHI 91126 TT 9059 g/L) Thiosulfat
- Page 1745 and 1746:
THYM 82606 normal function. Acquire
- Page 1747 and 1748:
Excision Circles [TREC] Analysis fo
- Page 1749 and 1750:
first year and every 6 months in th
- Page 1751 and 1752:
TGAB 84382 36-55 years: 142-844 cel
- Page 1753 and 1754:
TGFNA 89379 HTG1 83069 Thyroglobuli
- Page 1755 and 1756:
THSCM 83633 Clinical Information: S
- Page 1757 and 1758:
and Tg autoantibodies in either aut
- Page 1759 and 1760:
Clinical Information: Autoimmune th
- Page 1761 and 1762:
TIAG 82524 mcg/dL) -Normal TBG of 2
- Page 1763 and 1764:
PTICK 83266 FFTIC 91273
- Page 1765 and 1766:
FFTIN 91101 TSTGP 83671 Reference V
- Page 1767 and 1768:
TTGG 83660 should be referred for s
- Page 1769 and 1770:
TIRU 89529 evidence that titanium i
- Page 1771 and 1772:
TICRU 89530 independently predict p
- Page 1773 and 1774:
TOBR 81751 TOBT 81594 Useful For: M
- Page 1775 and 1776:
FFTOL 91122 TOMA 82695 St. Paul, MN
- Page 1777 and 1778:
incidence of congenital toxoplasmos
- Page 1779 and 1780:
shed oocysts in feces that rapidly
- Page 1781 and 1782:
TOXGM 81647 serology assays, antibo
- Page 1783 and 1784:
FFTGI 91419 in feces that rapidly m
- Page 1785 and 1786:
TRAG 82495 FFTRA 91693 Tragacanth,
- Page 1787 and 1788:
TRSF 34623 TACIF 84388 170-340 mg/d
- Page 1789 and 1790:
TACIG 89122 Clinical References: 1.
- Page 1791 and 1792:
TREE2 81703 sensitization and clini
- Page 1793 and 1794:
TREE4 81705 FFTPG 57315 6 > or =100
- Page 1795 and 1796:
FFTRE 90306 Trichloroethylene Expos
- Page 1797 and 1798:
TRPU 82386 clinical manifestations.
- Page 1799 and 1800:
3 weeks of treatment are required b
- Page 1801 and 1802:
FFTHE 91109 TMA 82867 Lipids, Lipop
- Page 1803 and 1804:
TPPTL 89494 Clinical Information: T
- Page 1805 and 1806:
FFTRO 57159 TWRP 80909 345 Oyster P
- Page 1807 and 1808:
TROT 82788 Clinical Information: Tr
- Page 1809 and 1810:
FFTRF 57317 FFTLI 57318 TRYPA 32283
- Page 1811 and 1812:
TRYPU 83823 from 0 to 5 years of ag
- Page 1813 and 1814:
FFTUM 91729 TUNA 82547 Reference va
- Page 1815 and 1816:
TURK 82702 2 0.70-3.49 Positive 3 3
- Page 1817 and 1818:
FFTYS 91855 UBEMS 89919 Tysabri Ant
- Page 1819 and 1820:
UGTKO 60351 may cause reduced or ab
- Page 1821 and 1822:
UGT2O 60350 UGTI 89397 Clinical Ref
- Page 1823 and 1824:
U1A1 83949 transcriptional activity
- Page 1825 and 1826:
UEA1 80180 ULCH 82546 UPD 82970 ins
- Page 1827 and 1828:
RURAU 89845 URAU 8330 URRP 60758 Ur
- Page 1829 and 1830:
URIC 8440 Interpretation: Uric acid
- Page 1831 and 1832:
thought to be formed from partially
- Page 1833 and 1834:
UPGDW 31892 obstruction. Hemoglobin
- Page 1835 and 1836:
UPGC 80288 FURO 81975 0.80-0.99 Rel
- Page 1837 and 1838:
USNU 82388 89219 in aneurysmal bone
- Page 1839 and 1840:
VPA 8707 VU 83395 Clinical Referenc
- Page 1841 and 1842:
VCRU 60575 which most is excreted i
- Page 1843 and 1844:
VANCT 81592 recommended for therape
- Page 1845 and 1846:
VH 9254 sensitization and clinical
- Page 1847 and 1848:
VMAR 60274 FVAP 91277 FVZD 91752 VZ
- Page 1849 and 1850:
VZM 80964 are at risk of suffering
- Page 1851 and 1852:
VIP 8150 VDRL 80632 VDSF 9028 Vasoa
- Page 1853 and 1854:
9945 VLCMS 60036 Venlafaxine is sig
- Page 1855 and 1856:
VIGA 91089 VIRNR 87266 Clinical Inf
- Page 1857 and 1858:
function of the retina (adaptation
- Page 1859 and 1860:
FB12 9156 Vitamin B12 and Folate, S
- Page 1861 and 1862:
FB12V 90431 FPAB 57394 800-2600 pg/
- Page 1863 and 1864:
FBIOT 91902 VITE 60297 FVIK1 Vitami
- Page 1865 and 1866:
VLTB 89190 VLTS 8632 Volatile Scree
- Page 1867 and 1868:
VHLD 89211 Cutoff concentration: 10
- Page 1869 and 1870:
VHLKP 89084 erythrocytosis or polyc
- Page 1871 and 1872:
VWFX 89792 X-linked recessive disor
- Page 1873 and 1874:
serves as a carrier protein for coa
- Page 1875 and 1876:
VWF serves as an adhesive protein i
- Page 1877 and 1878:
FPIKE 91662 WALN 82732 monitoring:
- Page 1879 and 1880:
Clinical Information: Warfarin is a
- Page 1881 and 1882:
polymorphism in order to maintain t
- Page 1883 and 1884:
WMEL 86304 responsible for elicitin
- Page 1885 and 1886:
WEED3 81884 Clinical Information: C
- Page 1887 and 1888:
WNV 84186 1 0.35-0.69 Equivocal 2 0
- Page 1889 and 1890:
WNVP 87802 LCWNV 86197 Clinical Ref
- Page 1891 and 1892:
WEEP 83156 IgM: or =1:10 indicates
- Page 1893 and 1894:
FWHT4 91978 WHT 82686 Wheat IgG4 Re
- Page 1895 and 1896:
BENW 82726 immunoglobulin E (IgE)-s
- Page 1897 and 1898:
WHIC 82719 2 0.70-3.49 Positive 3 3
- Page 1899 and 1900:
FWHFS 91961 FER2 8893 wheat protein
- Page 1901 and 1902:
WSCR 81163 testing often depend upo
- Page 1903 and 1904:
WDKM 83698 WDMS 83697 Company, 2007
- Page 1905 and 1906:
FBUCC 8668 Clinical Information: Cl
- Page 1907 and 1908:
XAN 80313 protein expression, albei
- Page 1909 and 1910:
FXAB 57321 Reference Values: Report
- Page 1911 and 1912:
FYSTG 92000 YFHV 82657 Italy. J Cli
- Page 1913 and 1914:
ZAP70 83727 9864 NEZPP Immunoblot R
- Page 1915 and 1916:
ZNRU 60526 FZRBC 91949 Reference va
- Page 1917 and 1918:
FZIP 57107 ZONI 83685 minor, second
- Page 1919:
one marrow transplantation compatib