Acute boekje - REP-Online
Acute boekje - REP-Online
Acute boekje - REP-Online
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
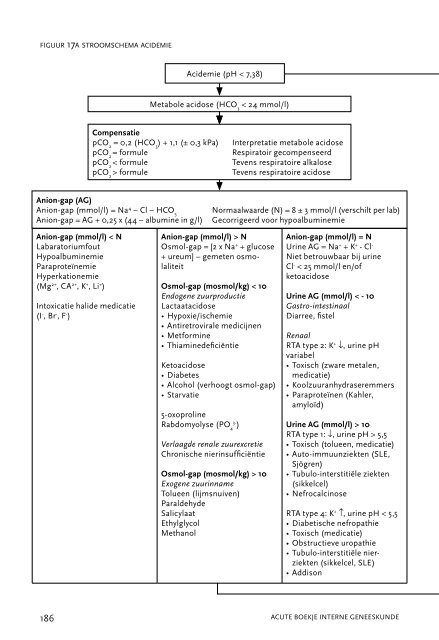
f i g u u r 17a s t r o o m s c h e m a ac id emie<br />
Acidemie (pH < 7,38)<br />
Metabole acidose (HCo 3 < 24 mmol/l)<br />
Compensatie<br />
pCo 2 = 0,2 (HCo 3 ) + 1,1 (± 0,3 kPa) Interpretatie metabole acidose<br />
pCo 2 = formule respiratoir gecompenseerd<br />
pCo 2 < formule Tevens respiratoire alkalose<br />
pCo 2 > formule Tevens respiratoire acidose<br />
Anion-gap (AG)<br />
Anion-gap (mmol/l) = Na4 – Cl – HCo3 Normaalwaarde (N) = 8 ± 3 mmol/l (verschilt per lab)<br />
Anion-gap = AG + 0,25 x (44 – albumine in g/l) Gecorrigeerd voor hypoalbuminemie<br />
Anion-gap (mmol/l) < N<br />
Labaratoriumfout<br />
Hypoalbuminemie<br />
Paraproteïnemie<br />
Hyperkationemie<br />
(Mg 2+ , CA 2+ , k + , Li + )<br />
Intoxicatie halide medicatie<br />
(I - , Br - , F - )<br />
Anion-gap (mmol/l) > N<br />
osmol-gap = [2 x Na + + glucose<br />
+ ureum] – gemeten osmolaliteit<br />
Osmol-gap (mosmol/kg) < 10<br />
Endogene zuurproductie<br />
Lactaatacidose<br />
• Hypoxie/ischemie<br />
• Antiretrovirale medicijnen<br />
• Metformine<br />
• Thiaminedeficiëntie<br />
ketoacidose<br />
• Diabetes<br />
• Alcohol (verhoogt osmol-gap)<br />
• Starvatie<br />
5-oxoproline<br />
3- rabdomyolyse (Po ) 4<br />
Verlaagde renale zuurexcretie<br />
Chronische nierinsufficiëntie<br />
Osmol-gap (mosmol/kg) > 10<br />
Exogene zuurinname<br />
Tolueen (lijmsnuiven)<br />
Paraldehyde<br />
Salicylaat<br />
ethylglycol<br />
Methanol<br />
Anion-gap (mmol/l) = N<br />
urine AG = Na + + k + - Cl -<br />
Niet betrouwbaar bij urine<br />
Cl - < 25 mmol/l en/of<br />
ketoacidose<br />
Urine AG (mmol/l) < - 10<br />
Gastro-intestinaal<br />
Diarree, fistel<br />
Renaal<br />
rTA type 2: k + ↓, urine pH<br />
variabel<br />
• Toxisch (zware metalen,<br />
medicatie)<br />
• koolzuuranhydraseremmers<br />
• Paraproteïnen (kahler,<br />
amyloïd)<br />
Urine AG (mmol/l) > 10<br />
rTA type 1: ↓, urine pH > 5,5<br />
• Toxisch (tolueen, medicatie)<br />
• Auto-immuunziekten (SLe,<br />
Sjögren)<br />
• Tubulo-interstitiële ziekten<br />
(sikkelcel)<br />
• Nefrocalcinose<br />
rTA type 4: k + ↑, urine pH < 5,5<br />
• Diabetische nefropathie<br />
• Toxisch (medicatie)<br />
• obstructieve uropathie<br />
• Tubulo-interstitiële nierziekten<br />
(sikkelcel, SLe)<br />
• Addison<br />
respiratoire acidose (pCo 2 > 5,3 kPa)<br />
Compensatie<br />
HCo 3 – (mmol/l) Interpretatie respiratoire acidose<br />
1 ↑ per 1,3 kPa pCo 2 ↑ <strong>Acute</strong> respiratoire acidose<br />
< 1 ↑ per 1,3 kPa pCo 2 ↑ Tevens metabole acidose<br />
3,5 ↑ per 1,3 kPa pCo 2 ↑ Chronische respiratoire acidose<br />
> 3,5 ↑ per 1,3 kPa pCo 2 ↑ Tevens metabole alkalose<br />
A-a gradiënt<br />
A-a gradient = P a o 2 - P a o 2 = (20 – pCo 2 x 1,25) – po 2 (kPa)<br />
0,7 – 2,0 kPa > 2,6 kPa<br />
Neurologisch/neuromusculair<br />
Sedativa/opiaten<br />
CVA<br />
Pickwick-syndroom<br />
uitputting<br />
Myasthenia<br />
Guillain-Barré<br />
Neurotoxinen (botulisme,<br />
tetanus, curare)<br />
ernstige hypokaliëmie<br />
ernstige hypofosfatemie<br />
Delta/delta<br />
- -<br />
Delta AG (mmol/l)/Delta HCo = (AG – N)/(24 – HCo3<br />
3<br />
1/1 ketoacidose<br />
1,5/1 Lactaatacidose<br />
> 1,5/1 Tevens metabole alkalose<br />
< 1,5/1 Tevens normaal AG metabole acidose<br />
V/P-mismatch<br />
CoPD-exacerbatie<br />
Atelectase<br />
Pneumonie<br />
Pneumothorax<br />
Longembolie<br />
Intrinsieke longziekten<br />
Linkszijdig hartfalen<br />
Methemoglobulinemie<br />
186 ACuTe Boekje INTerNe GeNeeSkuNDe Zuur-BASeNSToorNISSeN<br />
187