Oral and Poster Abstracts
Oral and Poster Abstracts
Oral and Poster Abstracts
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
was immediately stopped <strong>and</strong> the heifers were treated, during 30 min,<br />
with 1 mL/kg BW of a calcium solution (ValléeCálcio ® ) with 2.44 g of<br />
calcium /100 mL, from three sources: Gluconate, Lactate <strong>and</strong> Sacarate,<br />
enriched with 5 g Glucose, 0.47 g phosphorus <strong>and</strong> 0.19 g magnesium<br />
per 100 mL. Venous blood samples were taken before infusion (T0),<br />
when the muscle tremors started (T1), at the end of the infusion (T2), at<br />
the end of the treatment (T3) <strong>and</strong> 24 h later (T4) for serum analysis of<br />
calcium, ionized calcium, phosphorus <strong>and</strong> magnesium, plasma glucose<br />
levels <strong>and</strong> blood activity (30 °C) of g-glutamyl transferase (gGT),<br />
aspartate aminotransferase (AST) <strong>and</strong> creatine kinase (CK). The<br />
induction generated a similar clinical picture as seen in the natural<br />
course of hypocalcemia <strong>and</strong> the treatment with the calcium solution<br />
promoted total recovery. The induction generated a significant decrease<br />
in calcium, ionized calcium, phosphorus <strong>and</strong> magnesium levels,<br />
principally at T2, but the treatment transiently increased the calcium<br />
<strong>and</strong> ionized calcium at T3 <strong>and</strong> all of the variables returned to normality<br />
24 h later. The plasma glucose levels increased only after the treatment,<br />
but returned to normal at T4. There was no change in the gGT activity<br />
throughout the trial, but a significant increase of AST <strong>and</strong> CK at T4,<br />
indicating that some muscle damage occurred during the process.<br />
Key words: hypocalcaemia, calcium, phosphorus, treatment<br />
503 Clinical Picture of Induced Hypocalcaemia in Holstein<br />
Heifers Subsequently Treated with an Enriched Calcium<br />
Solution<br />
R. Barreto júnior 1 , A. Minervino 2 , F. Rodrigues 2 , E. Meira júnior 2 ,<br />
R. Ferreira 2 , A. Lima 3 , C. Mori 2 , E. Ortolani 2<br />
1 Rural Federal University of Semi-Arid, Mossoró, Brazil<br />
2 College of Veterinary Medicine, University of Sao Paulo,<br />
Department of Clinical Sciences, Sao Paulo, Brazil<br />
3 Vallée S.A., Sao Paulo, Brazil<br />
Twelve two years-old Holstein heifers were used to study the clinical<br />
picture during the induction <strong>and</strong> recovery of hypocalcaemia. The<br />
picture was induced by continuous infusion of a EDTA solution (5%<br />
<strong>and</strong> pH 7.4) into the jugular vein at the speed of 220 mL/h until the<br />
animals presented definitive clinical signs of hypocalcaemia, such as<br />
sternal or lateral recumbency; then the infusion was immediately<br />
stopped <strong>and</strong> the heifers were treated, during 30 min, with 1 mL/kg BW<br />
of a calcium solution (ValléeCálcio ® ) with 2.44 g Ca (gluconate,<br />
lactate, <strong>and</strong> saharate), 5 g Glucose, 0.47g phosphorus <strong>and</strong> 0.19 g<br />
magnesium per 100 mL. A clinical examination was performed before<br />
infusion (T0), when the muscle tremors started (T1), at the end of the<br />
infusion (T2), at the end of the treatment (T3) <strong>and</strong> 24 h later (T4). The<br />
induction generated a similar clinical picture as seen in the natural<br />
course of hypocalcemia, but a constant <strong>and</strong> involuntary kinetic tongue<br />
movement cleaning the nostril <strong>and</strong> nose <strong>and</strong> causing a lip sound. Limb<br />
stiffness <strong>and</strong> uneasiness preceded the muscle tremor, <strong>and</strong> from this<br />
moment on the animals refused food. Then apathy, staggering <strong>and</strong><br />
mydriasis became evident. These symptoms were followed by a rapid<br />
sternal <strong>and</strong> in most cases lateral recumbency. Even in this last position<br />
the heifers kept the head turned to the flank. At this moment the skin<br />
temperature at the lower limb <strong>and</strong> anal reflex were decreased; anuria<br />
<strong>and</strong> somnolence were evident. The heart rate <strong>and</strong> hypophonesis<br />
increased as higher was the EDTA infusion. Conversely, rumen stasis<br />
occurred in most cases at T1. Most animals had gas bloat. The<br />
treatment with calcium rapidly reversed the clinical picture, restored<br />
the heart rate <strong>and</strong> the rumen tonus <strong>and</strong> did not cause any adverse<br />
reaction within 48 hours after treatment.<br />
Key words: hypocalvaemia, symptoms, treatment, recovery<br />
504 Evaluation of Faecal Quality as a Diagnostic Tool in SARA<br />
Diagnosis in Dairy Cattle<br />
J. Tajik1, Mg. Nadalian1, A. Raoofi1, Gr. Mohamadi2, A. Bahonar1<br />
1 University of Tehran, Clinical Sciences, Internal Medicine, Tehran,<br />
Iran<br />
2 University of Tehran, Clinical Sciences, Tehran, Iran<br />
Objectives: Sub acute ruminal acidosis (SARA) is characterized by<br />
daily episodes of low ruminal pH between 5.5 <strong>and</strong> 5.0. This digestive<br />
disorder is the consequence of feeding high grain diets to dairy cows,<br />
which are adapted to digest predominantly forage diets. SARA may be<br />
a common <strong>and</strong> economically important problem in dairy herds. There<br />
is Limited knowledge of the symptomatology of SARA. Changes in<br />
faecal consistency <strong>and</strong> structure of SARA affected cows have been<br />
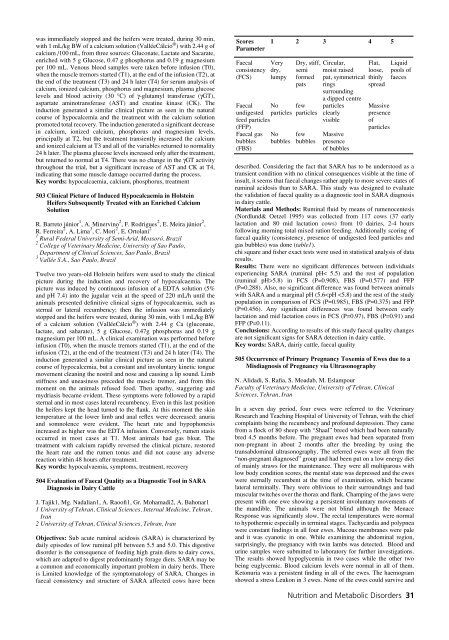
Scores 1 2 3 4 5<br />
Parameter<br />
Faecal Very Dry, stiff, Circular, Flat, Liquid<br />
consistency dry, semi moist raised loose, pools of<br />
(FCS) lumpy formed pat, symmetrical thinly faeces<br />
pats rings spread<br />
surrounding<br />
a dipped centre<br />
Faecal No few particles Massive<br />
undigested particles particles clearly presence<br />
feed particles visible of<br />
(FFP) particles<br />
Faecal gas No few Massive<br />
bubbles bubbles bubbles presence<br />
(FBS) of bubbles<br />
described. Considering the fact that SARA has to be understood as a<br />
transient condition with no clinical consequences visible at the time of<br />
insult, it seems that faecal changes rather apply to more severe states of<br />
ruminal acidosis than to SARA. This study was designed to evaluate<br />
the validation of faecal quality as a diagnostic tool in SARA diagnosis<br />
in dairy cattle.<br />
Materials <strong>and</strong> Methods: Ruminal fluid by means of rumenocentesis<br />
(Nordlund& Oetzel 1995) was collected from 117 cows (37 early<br />
lactation <strong>and</strong> 80 mid lactation cows) from 10 dairies, 2-4 hours<br />
following morning total mixed ration feeding. Additionally scoring of<br />
faecal quality (consistency, presence of undigested feed particles <strong>and</strong><br />
gas bubbles) was done (table1).<br />
chi square <strong>and</strong> fisher exact tests were used in statistical analysis of data<br />
results.<br />
Results: There were no significant differences between individuals<br />
experiencing SARA (ruminal pH< 5.5) <strong>and</strong> the rest of population<br />
(ruminal pH>5.8) in FCS (P=0.908), FBS (P=0.577) <strong>and</strong> FFP<br />
(P=0.288). Also, no significant difference was found between animals<br />
with SARA <strong>and</strong> a marginal pH (5.6