Xilinx UG194 Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Tri-Mode Ethernet MAC ...
Xilinx UG194 Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Tri-Mode Ethernet MAC ...
Xilinx UG194 Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Tri-Mode Ethernet MAC ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
R<br />
Gigabit Media Independent Interface (GMII)<br />
Due to the timing relationship between the MII transmit clock and the internal client clock<br />
signals, the TX_ACK signal (CLIENTE<strong>MAC</strong>#TXACK) is registered at the output of the<br />
<strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong>.<br />
Gigabit Media Independent Interface (GMII)<br />
The Media Independent Interface (MII), defined in IEEE 802.3, clause 22, is a parallel<br />
interface that connects a 10-Mb/s and/or 100-Mb/s capable <strong>MAC</strong> to the physical<br />
sublayers. The Gigabit Media Independent Interface (GMII), defined in IEEE 802.3, clause<br />
35, is an extension of the MII used to connect a 1-Gb/s capable <strong>MAC</strong> to the physical<br />
sublayers. MII can be considered a subset of GMII, and as a result, GMII/MII can carry<br />
<strong>Ethernet</strong> traffic at 10 Mb/s, 100 Mb/s, and 1 Gb/s.<br />
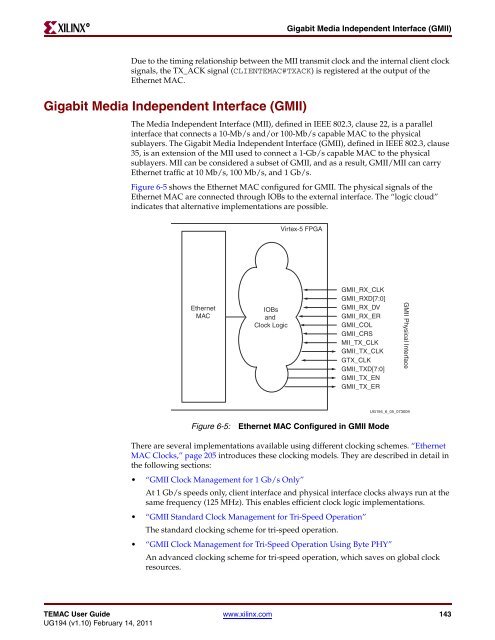
Figure 6-5 shows the <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> configured for GMII. The physical signals of the<br />
<strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> are connected through IOBs to the external interface. The “logic cloud”<br />
indicates that alternative implementations are possible.<br />
<strong>Ethernet</strong><br />
<strong>MAC</strong><br />
IOBs<br />
and<br />
Clock Logic<br />
<strong>Virtex</strong>-5 <strong>FPGA</strong><br />
GMII_RX_CLK<br />
GMII_RXD[7:0]<br />
GMII_RX_DV<br />
GMII_RX_ER<br />
GMII_COL<br />
GMII_CRS<br />
MII_TX_CLK<br />
GMII_TX_CLK<br />
GTX_CLK<br />
GMII_TXD[7:0]<br />
GMII_TX_EN<br />
GMII_TX_ER<br />
Figure 6-5: <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> Configured in GMII <strong>Mode</strong><br />
There are several implementations available using different clocking schemes. “<strong>Ethernet</strong><br />
<strong>MAC</strong> Clocks,” page 205 introduces these clocking models. They are described in detail in<br />
the following sections:<br />
“GMII Clock Management for 1 Gb/s Only”<br />
At 1 Gb/s speeds only, client interface and physical interface clocks always run at the<br />
same frequency (125 MHz). This enables efficient clock logic implementations.<br />
“GMII Standard Clock Management for <strong>Tri</strong>-Speed Operation”<br />
The standard clocking scheme for tri-speed operation.<br />
“GMII Clock Management for <strong>Tri</strong>-Speed Operation Using Byte PHY”<br />
An advanced clocking scheme for tri-speed operation, which saves on global clock<br />
resources.<br />
TE<strong>MAC</strong> User Guide www.xilinx.com 143<br />
<strong>UG194</strong> (v1.10) February 14, 2011<br />
GMII Physical Interface<br />
<strong>UG194</strong>_6_05_073009