Xilinx UG194 Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Tri-Mode Ethernet MAC ...
Xilinx UG194 Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Tri-Mode Ethernet MAC ...
Xilinx UG194 Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Tri-Mode Ethernet MAC ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chapter 2: <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> Overview<br />
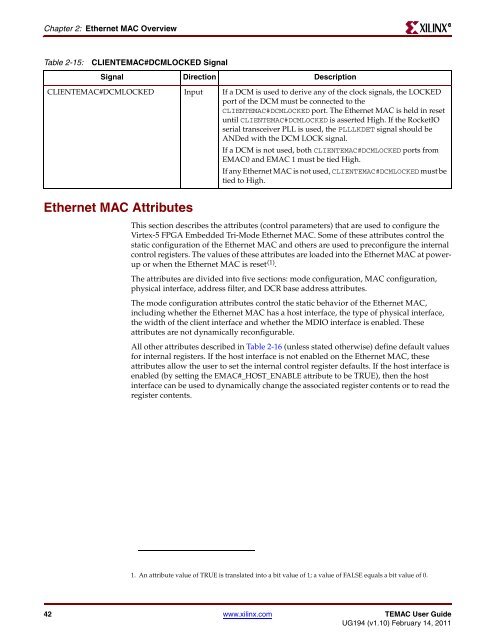
Table 2-15: CLIENTE<strong>MAC</strong>#DCMLOCKED Signal<br />
Signal Direction Description<br />
CLIENTE<strong>MAC</strong>#DCMLOCKED Input If a DCM is used to derive any of the clock signals, the LOCKED<br />
port of the DCM must be connected to the<br />
CLIENTE<strong>MAC</strong>#DCMLOCKED port. The <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> is held in reset<br />
until CLIENTE<strong>MAC</strong>#DCMLOCKED is asserted High. If the RocketIO<br />
serial transceiver PLL is used, the PLLLKDET signal should be<br />
ANDed with the DCM LOCK signal.<br />
If a DCM is not used, both CLIENTE<strong>MAC</strong>#DCMLOCKED ports from<br />
E<strong>MAC</strong>0 and E<strong>MAC</strong> 1 must be tied High.<br />
If any <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> is not used, CLIENTE<strong>MAC</strong>#DCMLOCKED must be<br />
tied to High.<br />
<strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> Attributes<br />
This section describes the attributes (control parameters) that are used to configure the<br />
<strong>Virtex</strong>-5 <strong>FPGA</strong> <strong>Embedded</strong> <strong>Tri</strong>-<strong>Mode</strong> <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong>. Some of these attributes control the<br />
static configuration of the <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> and others are used to preconfigure the internal<br />
control registers. The values of these attributes are loaded into the <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> at powerup<br />
or when the <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> is reset (1) .<br />
The attributes are divided into five sections: mode configuration, <strong>MAC</strong> configuration,<br />
physical interface, address filter, and DCR base address attributes.<br />
The mode configuration attributes control the static behavior of the <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong>,<br />
including whether the <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> has a host interface, the type of physical interface,<br />
the width of the client interface and whether the MDIO interface is enabled. These<br />
attributes are not dynamically reconfigurable.<br />
All other attributes described in Table 2-16 (unless stated otherwise) define default values<br />
for internal registers. If the host interface is not enabled on the <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong>, these<br />
attributes allow the user to set the internal control register defaults. If the host interface is<br />
enabled (by setting the E<strong>MAC</strong>#_HOST_ENABLE attribute to be TRUE), then the host<br />
interface can be used to dynamically change the associated register contents or to read the<br />
register contents.<br />
1. An attribute value of TRUE is translated into a bit value of 1; a value of FALSE equals a bit value of 0.<br />
42 www.xilinx.com TE<strong>MAC</strong> User Guide<br />
<strong>UG194</strong> (v1.10) February 14, 2011<br />
R