Xilinx UG194 Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Tri-Mode Ethernet MAC ...
Xilinx UG194 Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Tri-Mode Ethernet MAC ...
Xilinx UG194 Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Tri-Mode Ethernet MAC ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Chapter 3: Client Interface<br />
Requirement for Flow Control<br />
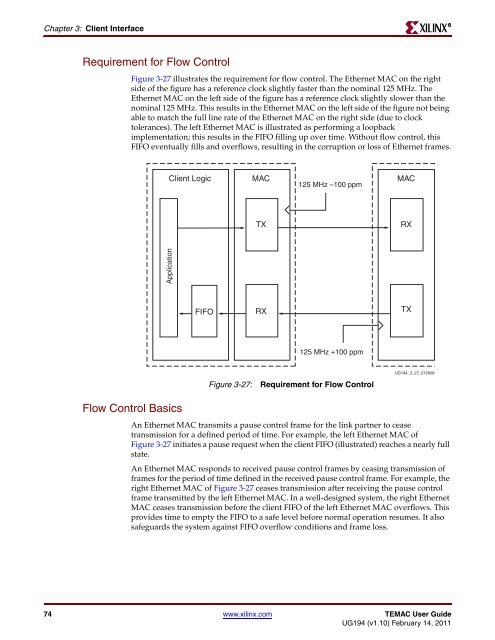
Figure 3-27 illustrates the requirement for flow control. The <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> on the right<br />
side of the figure has a reference clock slightly faster than the nominal 125 MHz. The<br />
<strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> on the left side of the figure has a reference clock slightly slower than the<br />
nominal 125 MHz. This results in the <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> on the left side of the figure not being<br />
able to match the full line rate of the <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> on the right side (due to clock<br />
tolerances). The left <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> is illustrated as performing a loopback<br />
implementation; this results in the FIFO filling up over time. Without flow control, this<br />
FIFO eventually fills and overflows, resulting in the corruption or loss of <strong>Ethernet</strong> frames.<br />
Application<br />
Flow Control Basics<br />
Client Logic<br />
FIFO<br />
Figure 3-27: Requirement for Flow Control<br />
An <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> transmits a pause control frame for the link partner to cease<br />
transmission for a defined period of time. For example, the left <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> of<br />
Figure 3-27 initiates a pause request when the client FIFO (illustrated) reaches a nearly full<br />
state.<br />
An <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> responds to received pause control frames by ceasing transmission of<br />
frames for the period of time defined in the received pause control frame. For example, the<br />
right <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> of Figure 3-27 ceases transmission after receiving the pause control<br />
frame transmitted by the left <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong>. In a well-designed system, the right <strong>Ethernet</strong><br />
<strong>MAC</strong> ceases transmission before the client FIFO of the left <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> overflows. This<br />
provides time to empty the FIFO to a safe level before normal operation resumes. It also<br />
safeguards the system against FIFO overflow conditions and frame loss.<br />
74 www.xilinx.com TE<strong>MAC</strong> User Guide<br />
<strong>UG194</strong> (v1.10) February 14, 2011<br />
<strong>MAC</strong><br />
TX<br />
RX<br />
125 MHz –100 ppm<br />
125 MHz +100 ppm<br />
<strong>MAC</strong><br />
RX<br />
TX<br />
<strong>UG194</strong>_3_27_072606<br />
R