Xilinx UG194 Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Tri-Mode Ethernet MAC ...
Xilinx UG194 Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Tri-Mode Ethernet MAC ...
Xilinx UG194 Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Tri-Mode Ethernet MAC ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Appendix B: <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> Clocks<br />
TX<br />
Client<br />
Logic CE<br />
RX CE<br />
Client<br />
Logic<br />
GND<br />
GND<br />
<strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> Block<br />
E<strong>MAC</strong>#CLIENTTXCLIENTCLKOUT<br />
E<strong>MAC</strong>#CLIENTRXCLIENTCLKOUT<br />
PHYE<strong>MAC</strong>#GTXCLK<br />
CLIENTE<strong>MAC</strong>#TXCLIENTCLKIN<br />
CLIENTE<strong>MAC</strong>#RXCLIENTCLKIN<br />
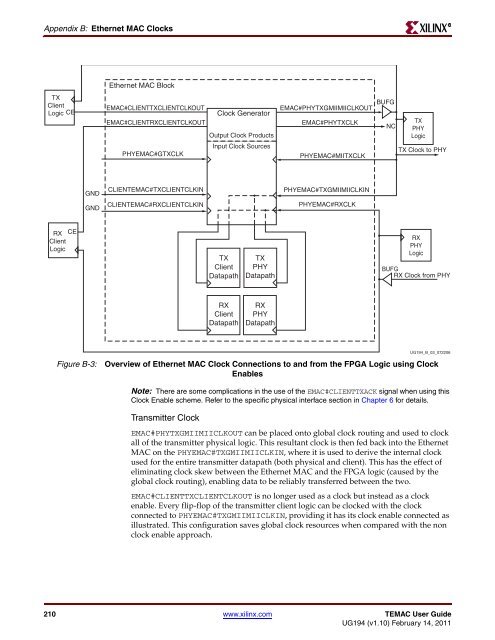
Figure B-3: Overview of <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> Clock Connections to and from the <strong>FPGA</strong> Logic using Clock<br />
Enables<br />
Note: There are some complications in the use of the E<strong>MAC</strong>#CLIENTTXACK signal when using this<br />
Clock Enable scheme. Refer to the specific physical interface section in Chapter 6 for details.<br />
Transmitter Clock<br />
Clock Generator<br />
Output Clock Products<br />
Input Clock Sources<br />
TX<br />
Client<br />
Datapath<br />
RX<br />
Client<br />
Datapath<br />
TX<br />
PHY<br />
Datapath<br />
RX<br />
PHY<br />
Datapath<br />
E<strong>MAC</strong>#PHYTXGMIIMIICLKOUT<br />
E<strong>MAC</strong>#PHYTXCLK<br />
PHYE<strong>MAC</strong>#MIITXCLK<br />
PHYE<strong>MAC</strong>#TXGMIIMIICLKIN<br />
PHYE<strong>MAC</strong>#RXCLK<br />
<strong>UG194</strong>_B_03_072206<br />
E<strong>MAC</strong>#PHYTXGMIIMIICLKOUT can be placed onto global clock routing and used to clock<br />
all of the transmitter physical logic. This resultant clock is then fed back into the <strong>Ethernet</strong><br />
<strong>MAC</strong> on the PHYE<strong>MAC</strong>#TXGMIIMIICLKIN, where it is used to derive the internal clock<br />
used for the entire transmitter datapath (both physical and client). This has the effect of<br />
eliminating clock skew between the <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> and the <strong>FPGA</strong> logic (caused by the<br />
global clock routing), enabling data to be reliably transferred between the two.<br />
E<strong>MAC</strong>#CLIENTTXCLIENTCLKOUT is no longer used as a clock but instead as a clock<br />
enable. Every flip-flop of the transmitter client logic can be clocked with the clock<br />
connected to PHYE<strong>MAC</strong>#TXGMIIMIICLKIN, providing it has its clock enable connected as<br />
illustrated. This configuration saves global clock resources when compared with the non<br />
clock enable approach.<br />
210 www.xilinx.com TE<strong>MAC</strong> User Guide<br />
<strong>UG194</strong> (v1.10) February 14, 2011<br />
BUFG<br />
NC<br />
TX<br />
PHY<br />
Logic<br />
TX Clock to PHY<br />
RX<br />
PHY<br />
Logic<br />
BUFG RX Clock from PHY<br />
R