Xilinx UG194 Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Tri-Mode Ethernet MAC ...
Xilinx UG194 Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Tri-Mode Ethernet MAC ...
Xilinx UG194 Virtex-5 FPGA Embedded Tri-Mode Ethernet MAC ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Generic<br />
Host Bus<br />
DCR Bus<br />
R<br />
Flow Control<br />
Interface<br />
Host<br />
Interface<br />
DCR Bridge<br />
E<strong>MAC</strong>#<br />
TX<br />
RX<br />
16- or 8-bit Client Interface<br />
Transmit Engine<br />
Flow Control<br />
Receive Engine<br />
Address Filter<br />
Registers<br />
MDIO Interface<br />
<strong>MAC</strong> Configuration<br />
Registers<br />
TX RX<br />
Statistics<br />
Clock Management<br />
Architecture Description<br />
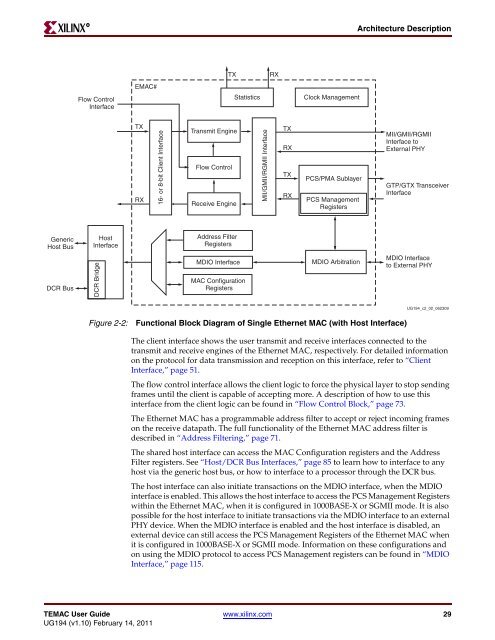
Figure 2-2: Functional Block Diagram of Single <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> (with Host Interface)<br />
MII/GMII/RGMII<br />
Interface to<br />
External PHY<br />
GTP/GTX Transceiver<br />
Interface<br />
MDIO Interface<br />
to External PHY<br />
The client interface shows the user transmit and receive interfaces connected to the<br />
transmit and receive engines of the <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong>, respectively. For detailed information<br />
on the protocol for data transmission and reception on this interface, refer to “Client<br />
Interface,” page 51.<br />
The flow control interface allows the client logic to force the physical layer to stop sending<br />
frames until the client is capable of accepting more. A description of how to use this<br />
interface from the client logic can be found in “Flow Control Block,” page 73.<br />
The <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> has a programmable address filter to accept or reject incoming frames<br />
on the receive datapath. The full functionality of the <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> address filter is<br />
described in “Address Filtering,” page 71.<br />
The shared host interface can access the <strong>MAC</strong> Configuration registers and the Address<br />
Filter registers. See “Host/DCR Bus Interfaces,” page 85 to learn how to interface to any<br />
host via the generic host bus, or how to interface to a processor through the DCR bus.<br />
The host interface can also initiate transactions on the MDIO interface, when the MDIO<br />
interface is enabled. This allows the host interface to access the PCS Management Registers<br />
within the <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong>, when it is configured in 1000BASE-X or SGMII mode. It is also<br />
possible for the host interface to initiate transactions via the MDIO interface to an external<br />
PHY device. When the MDIO interface is enabled and the host interface is disabled, an<br />
external device can still access the PCS Management Registers of the <strong>Ethernet</strong> <strong>MAC</strong> when<br />
it is configured in 1000BASE-X or SGMII mode. Information on these configurations and<br />
on using the MDIO protocol to access PCS Management registers can be found in “MDIO<br />
Interface,” page 115.<br />
TE<strong>MAC</strong> User Guide www.xilinx.com 29<br />
<strong>UG194</strong> (v1.10) February 14, 2011<br />
MII/GMII/RGMII Interface<br />
TX<br />
RX<br />
TX<br />
RX<br />
PCS/PMA Sublayer<br />
PCS Management<br />
Registers<br />
MDIO Arbitration<br />
<strong>UG194</strong>_c2_02_062309