Online proceedings - EDA Publishing Association
Online proceedings - EDA Publishing Association
Online proceedings - EDA Publishing Association
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
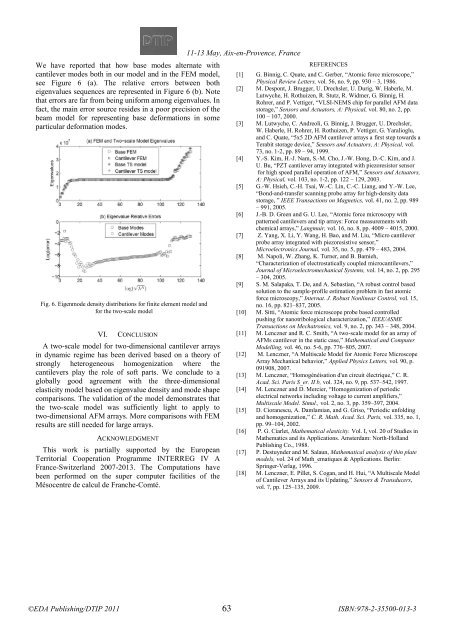
We have reported that how base modes alternate with<br />
cantilever modes both in our model and in the FEM model,<br />
see Figure 6 (a). The relative errors between both<br />
eigenvalues sequences are represented in Figure 6 (b). Note<br />
that errors are far from being uniform among eigenvalues. In<br />
fact, the main error source resides in a poor precision of the<br />
beam model for representing base deformations in some<br />
particular deformation modes.<br />
Fig. 6. Eigenmode density distributions for finite element model and<br />
for the two-scale model<br />
VI. CONCLUSION<br />
A two-scale model for two-dimensional cantilever arrays<br />
in dynamic regime has been derived based on a theory of<br />
strongly heterogeneous homogenization where the<br />
cantilevers play the role of soft parts. We conclude to a<br />
globally good agreement with the three-dimensional<br />
elasticity model based on eigenvalue density and mode shape<br />
comparisons. The validation of the model demonstrates that<br />
the two-scale model was sufficiently light to apply to<br />
two-dimensional AFM arrays. More comparisons with FEM<br />
results are still needed for large arrays.<br />
ACKNOWLEDGMENT<br />
This work is partially supported by the European<br />
Territorial Cooperation Programme INTERREG IV A<br />
France-Switzerland 2007-2013. The Computations have<br />
been performed on the super computer facilities of the<br />
Mésocentre de calcul de Franche-Comté.<br />
<br />
<br />
REFERENCES<br />
[1] G innig, C Quate, and C Ger er, “ tomi for e mi ros ope,”<br />
Physical Review Letters, vol. 56, no. 9, pp. 930 – 3, 1986.<br />
[2] M. Despont, J. Brugger, U. Drechsler, U. Durig, W. Haberle, M.<br />
Lutwyche, H. Rothuizen, R. Stutz, R. Widmer, G. Binnig, H.<br />
Rohrer, and P Vettiger, “V SI-NEMS chip for parallel AFM data<br />
storage,” Sensors and Actuators, A: Physical, vol. 80, no. 2, pp.<br />
100 – 107, 2000.<br />
[3] M. Lutwyche, C. Andreoli, G. Binnig, J. Brugger, U. Drechsler,<br />
W. Haberle, H. Rohrer, H. Rothuizen, P. Vettiger, G. Yaralioglu,<br />
and C Quate, “ x 2D FM antilever arrays a first step towards a<br />
Tera it storage devi e,” Sensors and Actuators, A: Physical, vol.<br />
73, no. 1-2, pp. 89 – 94, 1999.<br />
[4] Y.-S. Kim, H.-J. Nam, S.-M. Cho, J.-W. Hong, D.-C. Kim, and J.<br />
U u, “PZT antilever array integrated with piezoresistor sensor<br />
for high speed parallel operation of FM,” Sensors and Actuators,<br />
A: Physical, vol. 103, no. 1-2, pp. 122 – 129, 2003.<br />
[5] G.-W. Hsieh, C.-H. Tsai, W.-C. Lin, C.-C. Liang, and Y.-W. Lee,<br />
“ ond-and-transfer scanning probe array for high-density data<br />
storage, ” IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 41, no. 2, pp. 989<br />
– 991, 2005.<br />
[6] J.- D Green and G U ee, “ tomi for e mi ros opy with<br />
patterned cantilevers and tip arrays: Force measurements with<br />
hemi al arrays,” Langmuir, vol. 16, no. 8, pp. 4009 – 4015, 2000.<br />
[7] Z Yang, X i, Y Wang, H ao, and M iu, “Mi ro antilever<br />
probe array integrated with piezoresistive sensor,”<br />
Microelectronics Journal, vol. 35, no. 5, pp. 479 – 483, 2004.<br />
[8] M. Napoli, W. Zhang, K. Turner, and B. Bamieh,<br />
“Chara terization of ele trostati ally oupled mi ro antilevers,”<br />
Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 295<br />
– 304, 2005.<br />
[9] S. M Salapaka, T De, and Se astian, “ ro ust ontrol ased<br />
solution to the sample-profile estimation problem in fast atomic<br />
for e mi ros opy,” Internat. J. Robust Nonlinear Control, vol. 15,<br />
no. 16, pp. 821–837, 2005.<br />
[10] M Sitti, “ tomi for e mi roscope probe based controlled<br />
pushing for nanotri ologi al hara terization,” IEEE/ASME<br />
Transactions on Mechatronics, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 343 – 348, 2004.<br />
[11] M en zner and R C Smith, “ two-scale model for an array of<br />
AFMs cantilever in the static ase,” Mathematical and Computer<br />
Modelling, vol. 46, no. 5-6, pp. 776–805, 2007.<br />
[12] M en zner, “ Multis ale Model for tomi For e Mi ros ope<br />
rray Me hani al ehavior,” Applied Physics Letters, vol. 90, p.<br />
091908, 2007.<br />
[13] M. Lenczner, “Homogénéisation d'un circuit éle trique,” C R<br />
Acad. Sci. Paris S_er. II b, vol. 324, no. 9, pp. 537–542, 1997.<br />
[14] M en zner and D Mer ier, “Homogenization of periodi<br />
electrical networks including voltage to current amplifiers,”<br />
Multiscale Model. Simul., vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 359–397, 2004.<br />
[15] D Cioranes u, Damlamian, and G Griso, “Periodi unfolding<br />
and homogenization,” C. R. Math. Acad. Sci. Paris, vol. 335, no. 1,<br />
pp. 99–104, 2002.<br />
[16] P. G. Ciarlet, Mathematical elasticity. Vol. I, vol. 20 of Studies in<br />
Mathematics and its Applications. Amsterdam: North-Holland<br />
<strong>Publishing</strong> Co., 1988.<br />
[17] P. Destuynder and M. Salaun, Mathematical analysis of thin plate<br />
models, vol. 24 of Math_ematiques & Applications. Berlin:<br />
Springer-Verlag, 1996.<br />
[18] M en zner, E Pillet, S Cogan, and H Hui, “ Multis ale Model<br />
of Cantilever Arrays and its Updating,” Sensors & Transducers,<br />
vol. 7, pp. 125–135, 2009.<br />
63