TABLE OF CONTENTS - Lindbergh School District
TABLE OF CONTENTS - Lindbergh School District
TABLE OF CONTENTS - Lindbergh School District
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
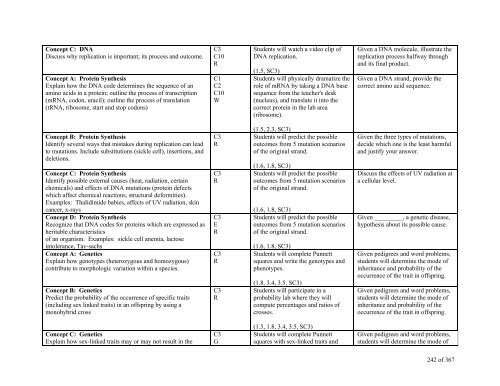
Concept C: DNA<br />
Discuss why replication is important; its process and outcome.<br />
Concept A: Protein Synthesis<br />
Explain how the DNA code determines the sequence of an<br />
amino acids in a protein; outline the process of transcription<br />
(mRNA, codon, uracil); outline the process of translation<br />
(tRNA, ribosome, start and stop codons)<br />
C3<br />
C10<br />
R<br />
C1<br />
C2<br />
C10<br />
W<br />
Students will watch a video clip of<br />
DNA replication.<br />
(1.5, SC3)<br />
Students will physically dramatize the<br />
role of mRNA by taking a DNA base<br />
sequence from the teacher's desk<br />
(nucleus), and translate it into the<br />
correct protein in the lab area<br />
(ribosome).<br />
Given a DNA molecule, illustrate the<br />
replication process halfway through<br />
and its final product.<br />
Given a DNA strand, provide the<br />
correct amino acid sequence.<br />
Concept B: Protein Synthesis<br />
Identify several ways that mistakes during replication can lead<br />
to mutations. Include substitutions (sickle cell), insertions, and<br />
deletions.<br />
Concept C: Protein Synthesis<br />
Identify possible external causes (heat, radiation, certain<br />
chemicals) and effects of DNA mutations (protein defects<br />
which affect chemical reactions, structural deformities).<br />
Examples: Thalidimide babies, affects of UV radiation, skin<br />
cancer, x-rays<br />
Concept D: Protein Synthesis<br />
Recognize that DNA codes for proteins which are expressed as<br />
heritable characteristics<br />
of an organism. Examples: sickle cell anemia, lactose<br />
intolerance, Tay-sachs<br />
Concept A: Genetics<br />
Explain how genotypes (heterozygous and homozygous)<br />
contribute to morphologic variation within a species.<br />
Concept B: Genetics<br />
Predict the probability of the occurrence of specific traits<br />
(including sex linked traits) in an offspring by using a<br />
monohybrid cross<br />
C3<br />
R<br />
C3<br />
R<br />
C3<br />
E<br />
R<br />
C3<br />
R<br />
C3<br />
R<br />
(1.5, 2.3, SC3)<br />
Students will predict the possible<br />
outcomes from 5 mutation scenarios<br />
of the original strand.<br />
(1.6, 1.8, SC3)<br />
Students will predict the possible<br />
outcomes from 5 mutation scenarios<br />
of the original strand.<br />
(1.6, 1.8, SC3)<br />
Students will predict the possible<br />
outcomes from 5 mutation scenarios<br />
of the original strand.<br />
(1.6, 1.8, SC3)<br />
Students will complete Punnett<br />
squares and write the genotypes and<br />
phenotypes.<br />
(1.8, 3.4, 3.5, SC3)<br />
Students will participate in a<br />
probability lab where they will<br />
compute percentages and ratios of<br />
crosses.<br />
Given the three types of mutations,<br />
decide which one is the least harmful<br />
and justify your answer.<br />
Discuss the effects of UV radiation at<br />
a cellular level.<br />
Given _________, a genetic disease,<br />
hypothesis about its possible cause.<br />
Given pedigrees and word problems,<br />
students will determine the mode of<br />
inheritance and probability of the<br />
occurrence of the trait in offspring.<br />
Given pedigrees and word problems,<br />
students will determine the mode of<br />
inheritance and probability of the<br />
occurrence of the trait in offspring.<br />
Concept C: Genetics<br />
Explain how sex-linked traits may or may not result in the<br />
C3<br />
G<br />
(1.5, 1.8, 3.4, 3.5, SC3)<br />
Students will complete Punnett<br />
squares with sex-linked traits and<br />
Given pedigrees and word problems,<br />
students will determine the mode of<br />
242 of 367