TABLE OF CONTENTS - Lindbergh School District
TABLE OF CONTENTS - Lindbergh School District
TABLE OF CONTENTS - Lindbergh School District
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
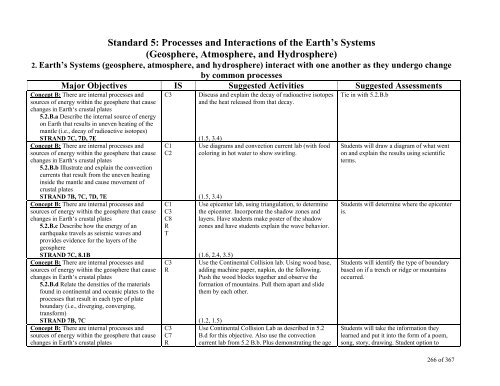
Standard 5: Processes and Interactions of the Earth’s Systems<br />
(Geosphere, Atmosphere, and Hydrosphere)<br />
2. Earth’s Systems (geosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere) interact with one another as they undergo change<br />
by common processes<br />
Major Objectives IS Suggested Activities Suggested Assessments<br />
Concept B: There are internal processes and<br />
sources of energy within the geosphere that cause<br />
changes in Earth‘s crustal plates<br />
5.2.B.a Describe the internal source of energy<br />
on Earth that results in uneven heating of the<br />
mantle (i.e., decay of radioactive isotopes)<br />
STRAND 7C, 7D, 7E<br />
Concept B: There are internal processes and<br />
sources of energy within the geosphere that cause<br />
changes in Earth‘s crustal plates<br />
5.2.B.b Illustrate and explain the convection<br />
currents that result from the uneven heating<br />
inside the mantle and cause movement of<br />
crustal plates<br />
STRAND 7B, 7C, 7D, 7E<br />
Concept B: There are internal processes and<br />
sources of energy within the geosphere that cause<br />
changes in Earth‘s crustal plates<br />
5.2.B.c Describe how the energy of an<br />
earthquake travels as seismic waves and<br />
provides evidence for the layers of the<br />
geosphere<br />
STRAND 7C, 8.1B<br />
Concept B: There are internal processes and<br />
sources of energy within the geosphere that cause<br />
changes in Earth‘s crustal plates<br />
5.2.B.d Relate the densities of the materials<br />
found in continental and oceanic plates to the<br />
processes that result in each type of plate<br />
boundary (i.e., diverging, converging,<br />
transform)<br />
STRAND 7B, 7C<br />
Concept B: There are internal processes and<br />
sources of energy within the geosphere that cause<br />
changes in Earth‘s crustal plates<br />
C3<br />
C1<br />
C2<br />
C1<br />
C3<br />
C8<br />
R<br />
T<br />
C3<br />
R<br />
C3<br />
C7<br />
R<br />
Discuss and explain the decay of radioactive isotopes<br />
and the heat released from that decay.<br />
(1.5, 3.4)<br />
Use diagrams and convection current lab (with food<br />
coloring in hot water to show swirling.<br />
(1.5, 3.4)<br />
Use epicenter lab, using triangulation, to determine<br />
the epicenter. Incorporate the shadow zones and<br />
layers. Have students make poster of the shadow<br />
zones and have students explain the wave behavior.<br />
(1.6, 2.4, 3.5)<br />
Use the Continental Collision lab. Using wood base,<br />
adding machine paper, napkin, do the following.<br />
Push the wood blocks together and observe the<br />
formation of mountains. Pull them apart and slide<br />
them by each other.<br />
(1.2, 1.5)<br />
Use Continental Collision Lab as described in 5.2<br />
B.d for this objective. Also use the convection<br />
current lab from 5.2 B.b. Plus demonstrating the age<br />
Tie in with 5.2.B.b<br />
Students will draw a diagram of what went<br />
on and explain the results using scientific<br />
terms.<br />
Students will determine where the epicenter<br />
is.<br />
Students will identify the type of boundary<br />
based on if a trench or ridge or mountains<br />
occurred.<br />
Students will take the information they<br />
learned and put it into the form of a poem,<br />
song, story, drawing. Student option to<br />
266 of 367