PLANT PROTECTION 1 â Pests, Diseases and Weeds
PLANT PROTECTION 1 â Pests, Diseases and Weeds
PLANT PROTECTION 1 â Pests, Diseases and Weeds
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>PLANT</strong> <strong>PROTECTION</strong> 1 – <strong>Pests</strong>, <strong>Diseases</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Weeds</strong><br />
Timing. Outdoor tree/bush crops. Commence in<br />
early spring at first sign of mite infestation (from<br />
September onwards). If this spray can be applied<br />
before mites have settled on leaves <strong>and</strong> before<br />
they have produced webbing, control is better.<br />
Different life stages. of mites (Table 41).<br />
– Information on using miticides on some crops is<br />
available (Learmonth 2008).<br />
– Some miticides are more effective against eggs<br />
than motile stages (nymphs <strong>and</strong> adults) <strong>and</strong> vice<br />
versa. The miticide chosen depends on the most<br />
abundant stage present at a particular time.<br />
– Ovicides (effective against eggs) <strong>and</strong> larvicides<br />
(effective against nymphs) reduce mite populations<br />
more slowly than those that are effective against<br />
all motile stages (nymphs <strong>and</strong> adults). Remember<br />
this lag time. Ovicides ideally should be applied<br />
when egg numbers are high <strong>and</strong> significant<br />
populations of active stages have developed.<br />
– Adulticides (effective against adults) quickly<br />
eliminate the feeding stages of mites <strong>and</strong> damage<br />
stops soon after the spray is applied. Their use can<br />
be delayed right up to the point where economic<br />
damage is imminent. Some adulticides are sloweracting<br />
than others <strong>and</strong> need to be applied earlier<br />
than more effective products to prevent damage.<br />
Where predatory mites. are being used<br />
to control twospotted mites. Suppliers indicate<br />
which pesticides may be used to control other pests<br />
<strong>and</strong> to supplement the control of twospotted mites<br />
by predatory mites. Avoid spray drift.<br />
Where only. pesticides are used. Use<br />
selective pesticides, eg miticides not toxic to<br />
naturally occurring predators of other pests. Avoid<br />
indiscriminate use of broad spectrum insecticides,<br />
eg carbaryl, synthetic pyrethroids.<br />
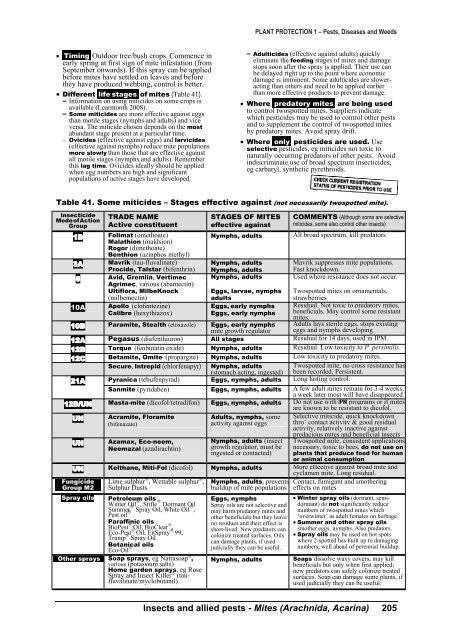
Table 41. Some miticides – Stages effective against (not necessarily twospotted mite).<br />
Insecticide<br />
ModeofAction<br />
Group<br />
TRADE NAME<br />
Active constituent<br />
1B Folimat (omethoate)<br />
Malathion (maldsion)<br />
Rogor (dimethoate)<br />
Benthion (azinphos methyl)<br />
3A Mavrik (tau-fluvalinate)<br />
Procide, Talstar (bifenthrin)<br />
6 Avid, Gremlin, Vertimec<br />
Agrimec, various (abamectin)<br />
Ultiflora, MilbeKnock<br />
(milbemectin)<br />
10A Apollo (clofentezine)<br />
Calibre (hexythiazox)<br />
STAGES OF MITES<br />
effective against<br />
Nymphs, adults<br />
Nymphs, adults<br />
Nymphs, adults<br />
Nymphs, adults<br />
Eggs, larvae, nymphs<br />
adults<br />
Eggs, early nymphs<br />
Eggs, early nymphs<br />
10B Paramite, Stealth (etoxazole) Eggs, early nymphs<br />
mite growth regulator<br />
COMMENTS (Although some are selective<br />
miticides, some also control other insects)<br />
All broad spectrum, kill predators<br />
Mavrik suppresses mite populations.<br />
Fast knockdown.<br />
Used where resistance does not occur.<br />
Twospotted mites on ornamentals,<br />
strawberries<br />
Residual. Not toxic to predatory mites,<br />
beneficials. May control some resistant<br />
mites.<br />
Adults lays sterile eggs, stops existing<br />
eggs <strong>and</strong> nymphs developing<br />
12A Pegasus (diafenthiuron) All stages Residual for 14 days, used in IPM.<br />
12B Torque (fenbutatin oxide) Nymphs, adults Residual. Low toxicity to P. persimilis.<br />
12C Betamite, Omite (propargite) Nymphs, adults Low toxicity to predatory mites.<br />
Secure, Intrepid (chlorfenapyr) Nymphs, adults Twospotted mite, no cross resistance has<br />
(stomach acting, ingested) been recorded. Persistent.<br />
21A Pyranica (tebufenpyrad) Eggs, nymphs, adults Long lasting control.<br />
Sanmite (pyridaben) Eggs, nymphs, adults A few adult mites remain for 3-4 weeks,<br />
a week later most will have disappeared.<br />
12D/UN Masta-mite (dicofol/tetradifon) Eggs, nymphs, adults Do not use with IPM programs or if mites<br />
are known to be resistant to dicofol.<br />
UN<br />
Acramite, Floramite<br />
(bifenazate)<br />
Adults, nymphs, some<br />
activity against eggs<br />
Selective miticide, quick knockdown<br />
thro’ contact activity & good residual<br />
activity, relatively inactive against<br />
predacious mites <strong>and</strong> beneficial insects<br />
UN Azamax, Eco-neem,<br />
Nymphs, adults (insect Twospotted mite, consistent applications<br />
Neemazal (azadirachtin) growth regulator, must be necessary, toxic to bees, do not use on<br />
ingested or contacted) plants that produce food for human<br />
or animal consumption<br />
UN Kelthane, Miti-Fol (dicofol) Nymphs, adults More effective against broad mite <strong>and</strong><br />
Fungicide<br />
Group M2<br />
Lime sulphur , Wettable sulphur ,<br />
Sulphur Dusts<br />
Spray oils Petroleum oils<br />
Winter Oil , Stifle Dormant Oil<br />
Summer Spray Oil, White Oil ,<br />
Pest oil <br />
Paraffinic oils<br />
BioPest Oil, BioClear ,<br />
Eco-Pest Oil, EnSpray 99,<br />
Trump Spray Oil<br />
Botanical oils<br />
Eco-Oil <br />
Other sprays Soap sprays, eg Natrasoap ,<br />
various (potassium salts)<br />
Home garden sprays, eg Rose<br />
Spray <strong>and</strong> Insect Killer (taufluvalinate/myclobutanil)<br />
Nymphs, adults, prevents<br />
buildup of mite populations<br />
Eggs, nymphs<br />
Spray oils are not selective <strong>and</strong><br />
may harm predatory mites <strong>and</strong><br />
other beneficials but they leave<br />
no residues <strong>and</strong> their effect is<br />
short-lived. New predators can<br />
colonize treated surfaces. Oils<br />
can damage plants, if used<br />
judicially they can be useful.<br />
Nymphs, adults<br />
cyclamen mite. Long residual.<br />
Contact, fumigant <strong>and</strong> smothering<br />
effects on mites<br />
Winter spray oils (dormant, semidormant)<br />
do not significantly reduce<br />
numbers of twospotted mites which<br />
‘overwinter’ as adult females on herbage.<br />
Summer <strong>and</strong> other spray oils<br />
smother eggs, nymphs. Also predators.<br />
Spray oils may be used on hot spots<br />
where 2-spotted has built up to damaging<br />
numbers, well ahead of perennial buildup.<br />
Soaps dissolve waxy covers, may kill<br />
beneficials but only when first applied;<br />
new predators can safely colonize treated<br />
surfaces. Soap can damage some plants, if<br />
used judicially they can be useful.<br />
Insects <strong>and</strong> allied pests - Mites (Arachnida, Acarina) 205





![[Compatibility Mode].pdf](https://img.yumpu.com/27318716/1/190x135/compatibility-modepdf.jpg?quality=85)










