PLANT PROTECTION 1 â Pests, Diseases and Weeds
PLANT PROTECTION 1 â Pests, Diseases and Weeds
PLANT PROTECTION 1 â Pests, Diseases and Weeds
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>PLANT</strong> <strong>PROTECTION</strong> 1 – <strong>Pests</strong>, <strong>Diseases</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Weeds</strong><br />
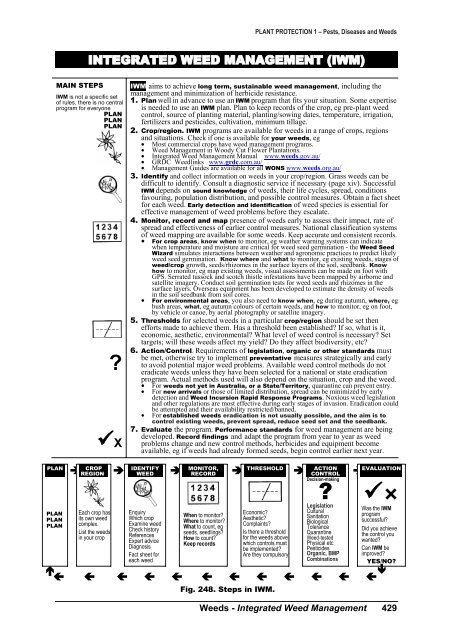
INTEGRATED WEED MANAGEMENT (IWM)<br />
MAIN STEPS<br />
IWM is not a specific set<br />
of rules, there is no central<br />
program for everyone<br />
PLAN<br />
PLAN<br />
PLAN<br />
?<br />
X<br />
IWM aims to achieve long term, sustainable weed management, including the<br />
management <strong>and</strong> minimization of herbicide resistance.<br />
1. Plan well in advance to use an IWM program that fits your situation. Some expertise<br />
is needed to use an IWM plan. Plan to keep records of the crop, eg pre-plant weed<br />
control, source of planting material, planting/sowing dates, temperature, irrigation,<br />
fertilizers <strong>and</strong> pesticides, cultivation, minimum tillage.<br />
2. Crop/region. IWM programs are available for weeds in a range of crops, regions<br />
<strong>and</strong> situations. Check if one is available for your weeds, eg<br />
Most commercial crops have weed management programs.<br />
Weed Management in Woody Cut Flower Plantations.<br />
Integrated Weed Management Manual www.weeds.gov.au/<br />
GRDC Weedlinks www.grdc.com.au/<br />
Management Guides are available for all WONS www.weeds.org.au/<br />
3. Identify <strong>and</strong> collect information on weeds in your crop/region. Grass weeds can be<br />
difficult to identify. Consult a diagnostic service if necessary (page xiv). Successful<br />
IWM depends on sound knowledge of weeds, their life cycles, spread, conditions<br />
favouring, population distribution, <strong>and</strong> possible control measures. Obtain a fact sheet<br />
for each weed. Early detection <strong>and</strong> identification of weed species is essential for<br />
effective management of weed problems before they escalate.<br />
4. Monitor, record <strong>and</strong> map presence of weeds early to assess their impact, rate of<br />
spread <strong>and</strong> effectiveness of earlier control measures. National classification systems<br />
of weed mapping are available for some weeds. Keep accurate <strong>and</strong> consistent records.<br />
For crop areas, know when to monitor, eg weather warning systems can indicate<br />
when temperature <strong>and</strong> moisture are critical for weed seed germination - the Weed Seed<br />
Wizard simulates interactions between weather <strong>and</strong> agronomic practices to predict likely<br />
weed seed germination. Know where <strong>and</strong> what to monitor, eg existing weeds, stages of<br />
weed/crop growth, seeds/rhizomes in the surface layers of the soil, seedbank. Know<br />
how to monitor, eg map existing weeds, visual assessments can be made on foot with<br />
GPS. Serrated tussock <strong>and</strong> scotch thistle infestations have been mapped by airborne <strong>and</strong><br />
satellite imagery. Conduct soil germination tests for weed seeds <strong>and</strong> rhizomes in the<br />
surface layers. Overseas equipment has been developed to estimate the density of weeds<br />
in the soil seedbank from soil cores.<br />
For environmental areas, you also need to know when, eg during autumn, where, eg<br />
bush areas, what, eg autumn colours of certain weeds, <strong>and</strong> how to monitor, eg on foot,<br />
by vehicle or canoe, by aerial photography or satellite imagery.<br />
5. Thresholds for selected weeds in a particular crop/region should be set then<br />
efforts made to achieve them. Has a threshold been established? If so, what is it,<br />
economic, aesthetic, environmental? What level of weed control is necessary? Set<br />
targets; will these weeds affect my yield? Do they affect biodiversity, etc?<br />
6. Action/Control. Requirements of legislation, organic or other st<strong>and</strong>ards must<br />
be met, otherwise try to implement preventative measures strategically <strong>and</strong> early<br />
to avoid potential major weed problems. Available weed control methods do not<br />
eradicate weeds unless they have been selected for a national or state eradication<br />
program. Actual methods used will also depend on the situation, crop <strong>and</strong> the weed.<br />
For weeds not yet in Australia, or a State/Territory, quarantine can prevent entry.<br />
For new arrivals or those of limited distribution, spread can be minimized by early<br />
detection <strong>and</strong> Weed Incursion Rapid Response Programs. Noxious weed legislation<br />
<strong>and</strong> other regulations are most effective during early stages of invasion. Eradication could<br />
be attempted <strong>and</strong> their availability restricted/banned.<br />
<br />
For established weeds eradication is not usually possible, <strong>and</strong> the aim is to<br />
control existing weeds, prevent spread, reduce seed set <strong>and</strong> the seedbank.<br />
7. Evaluate the program. Performance st<strong>and</strong>ards for weed management are being<br />
developed. Record findings <strong>and</strong> adapt the program from year to year as weed<br />
problems change <strong>and</strong> new control methods, herbicides <strong>and</strong> equipment become<br />
available, eg if weeds had already formed seeds, begin control earlier next year.<br />
PLAN<br />
PLAN<br />
PLAN<br />
PLAN<br />
<br />
CROP<br />
REGION<br />
Each crop has<br />
its own weed<br />
complex.<br />
List the weeds<br />
in your crop<br />
IDENTIFY<br />
WEED<br />
Enquiry<br />
Which crop<br />
Examine weed<br />
Check history<br />
References<br />
Expert advice<br />
Diagnosis<br />
Fact sheet for<br />
each weed<br />
MONITOR,<br />
RECORD<br />
When to monitor?<br />
Where to monitor?<br />
What to count, eg<br />
seeds, seedlings?<br />
How to count?<br />
Keep records<br />
THRESHOLD<br />
Economic?<br />
Aesthetic?<br />
Complaints?<br />
Is there a threshold<br />
for the weeds above<br />
which controls must<br />
be implemented?<br />
Are they compulsory?<br />
<br />
CONTROL<br />
ACTION<br />
Decision-making<br />
?<br />
Legislation<br />
Cultural<br />
Sanitation<br />
Biological<br />
Tolerance<br />
Quarantine<br />
Weed-tested<br />
Physical etc<br />
Pesticides<br />
Organic, BMP<br />
Combinations<br />
EVALUATION<br />
<br />
Fig. 248. Steps in IWM.<br />
<br />
Was the IWM<br />
program<br />
successful?<br />
Did you achieve<br />
the control you<br />
wanted?<br />
Can IWM be<br />
improved?<br />
YES/NO?<br />
<strong>Weeds</strong> - Integrated Weed Management 429





![[Compatibility Mode].pdf](https://img.yumpu.com/27318716/1/190x135/compatibility-modepdf.jpg?quality=85)










