Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming XI
Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming XI
Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming XI
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Biomechanics</strong><strong>and</strong>medic<strong>in</strong>e<strong>in</strong>swimm<strong>in</strong>gXi<br />
suit (short made by Lycra) <strong>and</strong> one us<strong>in</strong>g a BlueseventyTM bodysuit that<br />
covered from the shoulders to the ankles. The order of the trials was<br />
r<strong>and</strong>omized <strong>and</strong> the subjects rested for 20 m<strong>in</strong> between the trials. The<br />
subjects used their own bodysuits dur<strong>in</strong>g the trials.<br />
Video sampl<strong>in</strong>g <strong>and</strong> analysis: Two synchronized sub-aquatic video<br />
cameras (SANYO VPC-WH1), operat<strong>in</strong>g at 30 Hz, were used to acquire<br />
images <strong>in</strong> the sagittal plane of the swimmers. The cameras were<br />
positioned on the lateral sides of the pool <strong>and</strong> were carried manually<br />
us<strong>in</strong>g chariots on rails. To determ<strong>in</strong>e the stroke phases, two experienced<br />
researchers made a frame-by-frame analysis as reported before by Chollet<br />
et al. (2000) us<strong>in</strong>g the software VirtualDub v1.8.7.<br />
A third <strong>in</strong>dependent video camera operat<strong>in</strong>g at 25 Hz ( JVC, GR-<br />
DVL9800) was positioned 4 m above the water surface <strong>in</strong> the middle<br />
of the pool deck to measure race parameters. This camera allowed us to<br />
quantify swimm<strong>in</strong>g speed <strong>and</strong> stroke rate, from which stroke length was<br />
calculated. The analysis of the images was performed with the software<br />
Dgeme v.1.0.<br />
Index of coord<strong>in</strong>ation <strong>and</strong> arm stroke phases: Index of coord<strong>in</strong>ation<br />
(IdC) was taken to represent arm coord<strong>in</strong>ation, as proposed by Chollet<br />
et al. (2000). The <strong>in</strong>dex of coord<strong>in</strong>ation was expressed as a percentage of<br />
the duration of one arm stroke <strong>and</strong> represents the time between the end<br />
of propulsive action of one arm <strong>and</strong> the beg<strong>in</strong>n<strong>in</strong>g of propulsion with<br />
the other arm, consider<strong>in</strong>g the mean of both the right <strong>and</strong> left arms.<br />
Therefore it is possible to quantify a catch-up (IdC < 0%), an opposition<br />
(IdC = 0%) or a superposition coord<strong>in</strong>ation mode (IdC > 0%).<br />
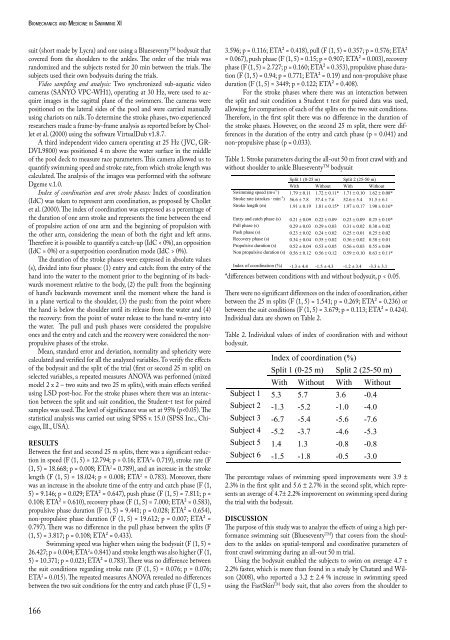
The duration of the stroke phases were expressed <strong>in</strong> absolute values<br />
(s), divided <strong>in</strong>to four phases: (1) entry <strong>and</strong> catch: from the entry of the<br />
h<strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>to the water to the moment prior to the beg<strong>in</strong>n<strong>in</strong>g of its backwards<br />
movement relative to the body, (2) the pull: from the beg<strong>in</strong>n<strong>in</strong>g<br />
of h<strong>and</strong>’s backwards movement until the moment where the h<strong>and</strong> is<br />
<strong>in</strong> a plane vertical to the shoulder, (3) the push: from the po<strong>in</strong>t where<br />
the h<strong>and</strong> is below the shoulder until its release from the water <strong>and</strong> (4)<br />
the recovery: from the po<strong>in</strong>t of water release to the h<strong>and</strong> re-entry <strong>in</strong>to<br />
the water. The pull <strong>and</strong> push phases were considered the propulsive<br />
ones <strong>and</strong> the entry <strong>and</strong> catch <strong>and</strong> the recovery were considered the nonpropulsive<br />
phases of the stroke.<br />
Mean, st<strong>and</strong>ard error <strong>and</strong> deviation, normality <strong>and</strong> sphericity were<br />
calculated <strong>and</strong> verified for all the analyzed variables. To verify the effects<br />
of the bodysuit <strong>and</strong> the split of the trial (first or second 25 m split) on<br />
selected variables, a repeated measures ANOVA was performed (mixed<br />
model 2 x 2 – two suits <strong>and</strong> two 25 m splits), with ma<strong>in</strong> effects verified<br />
us<strong>in</strong>g LSD post-hoc. For the stroke phases where there was an <strong>in</strong>teraction<br />
between the split <strong>and</strong> suit condition, the Student-t test for paired<br />
samples was used. The level of significance was set at 95% (p