Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming XI
Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming XI
Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming XI
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Biomechanics</strong><strong>and</strong>medic<strong>in</strong>e<strong>in</strong>swimm<strong>in</strong>gXi<br />
The Effects of Rubber Swimsuits on Swimmers<br />
Us<strong>in</strong>g a Lactic Acid Curve Test<br />
shiraki, t. 1 , Wakayoshi, K. 1 , hata, h. 1 , Yamamoto, t. 2 , tomikawa,<br />
M. 3<br />
1 Biwako Seikei Sport College, Japan<br />
2 YAMAMOTO CORPORATION CO., LTD., Japan<br />
3 University of Tsukuba, Japan<br />
The rubber swimsuit, made from Neoprene rubber, was one of the causes<br />
of the swimm<strong>in</strong>g record rush <strong>in</strong> 2009. The benefits of wear<strong>in</strong>g a wetsuit<br />
on swimmers were widely reported. This study verified the <strong>in</strong>fluence of<br />
wear<strong>in</strong>g the rubber swimsuit on a swimm<strong>in</strong>g exercise load. Eight female<br />
university swimmers performed 4 x 200 m crawl swimm<strong>in</strong>g at <strong>in</strong>cremental<br />
speeds, set from the best record of each 200 m freestyle race<br />
(80%V 200 , 85% V 200 , 90% V 200 , 95% V 200 ). Four different suits (three<br />
types of rubber suits <strong>and</strong> a cloth swimsuit) were used <strong>and</strong> lactic acid<br />
curve tests were conducted. The blood lactate concentration after 90%<br />
V 200 <strong>and</strong> 95% V 200 trials with rubber swimsuits tended to be lower than<br />
those with a cloth swimsuit. An exam<strong>in</strong>ation of the trials revealed that<br />
the total number of arm strokes tended to decrease due to the use of the<br />
rubber swimsuits. It is suggested that the rubber swimsuits might improve<br />
propulsion efficiency <strong>and</strong> decreased the swimmer’s exercise load,<br />
<strong>in</strong>dicat<strong>in</strong>g that the rubber swimsuit may improve the race performance<br />
of swimmers.<br />
Key words: rubber swimsuit, lactic acid curve test<br />
IntroductIon<br />
Forty-three new world records were set <strong>in</strong> 13 th FINA World Championships<br />
<strong>in</strong> Rome 2009. It was not just a historical co<strong>in</strong>cidence that<br />
the 43 new world records were established <strong>in</strong> just one meet<strong>in</strong>g. These<br />
records were reached with new swimsuits with high technology. In fact,<br />
the rubber swimsuit was one of the causes of this record rush. Be<strong>in</strong>g<br />
similar to wetsuits, the rubber swimsuit was made from Neoprene rubber.<br />
So, rubber swimsuits probably present beneficial characteristics similar<br />
to wetsuits. The effects of us<strong>in</strong>g wetsuits on swimmers were widely<br />
reported:(i) triathletes are able to hold their bodies <strong>in</strong> a more horizontal<br />
position because of the added buoyancy (Chatard et al., 1996, Chatard<br />
et al., 1995, Toussa<strong>in</strong>t et al., 1989) <strong>and</strong> (ii) drag force is reduced by the<br />
smooth surface provided by a wetsuit (Chatard et al., 1995, Toussa<strong>in</strong>t<br />
et al., 1989).<br />
Additionally, Tomikawa et al. (2008) showed that swimm<strong>in</strong>g velocity<br />
at maximal oxygen consumption with a wetsuit was 5.4% higher than<br />
with a swimsuit, <strong>and</strong> that the swimm<strong>in</strong>g energy cost of swimm<strong>in</strong>g with<br />
a wetsuit was lower by 14.4% at 60% of the velocity correspond<strong>in</strong>g to<br />
VO 2 max <strong>and</strong> 7.5% at 80% of the velocity correspond<strong>in</strong>g to VO 2 max.<br />
These results suggest that the benefits of wear<strong>in</strong>g a wetsuit <strong>in</strong>clude not<br />
only the improvement <strong>in</strong> swimm<strong>in</strong>g propulsion efficiency, but also the<br />
reduction <strong>in</strong> energy consumption. While the thickness of a wetsuit is<br />
2-5mm, a rubber swimsuit is only 0.3mm thick, which seems to imply<br />
that the benefits of wear<strong>in</strong>g a rubber swimsuit might be less than those<br />
of us<strong>in</strong>g a wetsuit.<br />
A lactic acid curve test is usually used to determ<strong>in</strong>e the anaerobic<br />
threshold to monitor tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g (Maglischo, 2003). The test is an <strong>in</strong>cremental<br />
one, allow<strong>in</strong>g that the values of blood lactate concentration be<br />
plotted on a graph <strong>in</strong> comb<strong>in</strong>ation with the swimm<strong>in</strong>g velocity. If the<br />
lactate-velocity curve will move to the right when wear<strong>in</strong>g a wetsuit,<br />
the swimm<strong>in</strong>g performance is improved. This study aimed to verify the<br />
<strong>in</strong>fluence of wear<strong>in</strong>g a rubber swimsuit on the swimm<strong>in</strong>g exercise load<br />
by us<strong>in</strong>g a lactic-velocity curve test.<br />
226<br />
Methods<br />
Eight female university swimmers participated <strong>in</strong> this study. The average<br />
of their best records for 200 m freestyle swimm<strong>in</strong>g was 129.8 ± 4.5 seconds.<br />
They attended the Japanese <strong>in</strong>ter-college swim meet 2009. Their<br />
age, height <strong>and</strong> weight were 19.8 ± 0.9 years, 160.8 ± 4.2 cm <strong>and</strong><br />
58.0 ± 2.8 kg, respectively, <strong>and</strong> they had a body fat % of 28.4 ± 3.6.<br />
Four types of suits were used <strong>in</strong> this study. Three rubber suits were<br />
made from Neoprene rubber: (i) rubber suit A was a commercially available<br />
suit: (ii) rubber suit B was made from Neoprene rubber, <strong>and</strong> metallic<br />
m<strong>in</strong>erals were conta<strong>in</strong>ed between rubber <strong>and</strong> back fabric layers: (iii)<br />
rubber suit C was also made from Neoprene rubber, <strong>in</strong> which titanium<br />
was <strong>in</strong>cluded <strong>in</strong> bond part between rubber <strong>and</strong> back fabric layers. Rubber<br />
suit B <strong>and</strong> C were not commercially available. The 4 th suit type was a<br />
cloth swimsuit, be<strong>in</strong>g a common water-repellent competitive swimsuit<br />
with. All swimsuits were the full-length type, cover<strong>in</strong>g from shoulder<br />
to ankle.<br />
Swimmers performed a 4 x 200 m <strong>in</strong>cremental swimm<strong>in</strong>g protocol,<br />
the speed of the four stages set from the best record of each 200 m<br />
freestyle race (80%V 200 , 85% V 200 , 90% V 200 , 95% V 200 ). The speed was<br />
controlled by a pace maker set on the bottom of pool. Blood from the<br />
f<strong>in</strong>gertip was taken at 0, 3 <strong>and</strong> 5 m<strong>in</strong> after each trial. The blood lactate<br />
concentration was determ<strong>in</strong>ed us<strong>in</strong>g Lactate Pro analyzer (ARKRAY,<br />
Inc.). Arm strokes <strong>in</strong> the trials were counted each 25 m (LAP 1 to 8).<br />
The mean <strong>and</strong> st<strong>and</strong>ard deviation were computed for all variables.<br />
ANOVA with repeated measures was used to compare the data obta<strong>in</strong>ed<br />
<strong>in</strong> the wetsuits <strong>and</strong> a swimsuit condition. A probability level of 5% was<br />
selected for tests of statistical significance.<br />
results<br />
The mean ± SD values of blood lactate concentrations <strong>in</strong> each trial are<br />
shown <strong>in</strong> Table 1. No significant differences were found <strong>in</strong> blood lactate<br />
concentration between different rubber suit conditions.<br />
Table 1. Means ± SD of Blood lactate concentration <strong>in</strong> each suit<br />
condition<br />
NS<br />
mmol·L -1<br />
RS-A<br />
mmol·L -1<br />
RS-B<br />
mmol·L -1<br />
RS-C<br />
mmol·L -1<br />
80%V200 1.49 ± 0.45 1.61 ± 0.54 1.54 ± 0.51 1.30 ± 0.47<br />
85%V200 2.11 ± 0.59 1.95 ± 0.88 1.83 ± 0.69 1.78 ± 0.61<br />
90%V200 3.89 ± 1.37 3.20 ± 1.73 2.89 ± 1.21 2.95 ± 1.45<br />
95%V200 10.46 ± 2.37 8.68 ± 2.66 9.35 ± 2.24 8.18 ± 2.98<br />
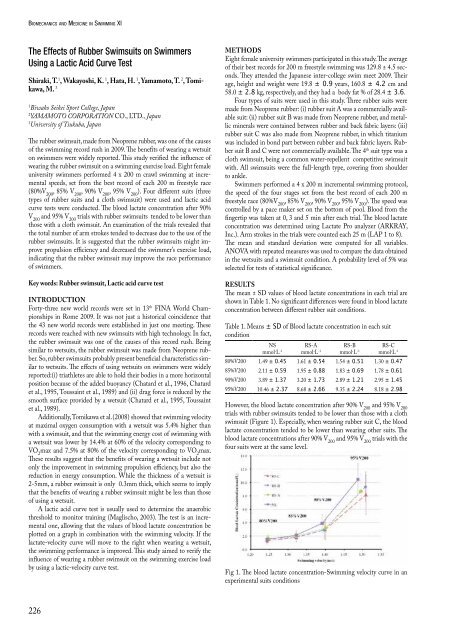
However, the blood lactate concentration after 90% V 200 <strong>and</strong> 95% V 200<br />
trials with rubber swimsuits tended to be lower than those with a cloth<br />
swimsuit (Figure 1). Especially, when wear<strong>in</strong>g rubber suit C, the blood<br />
lactate concentration tended to be lower than wear<strong>in</strong>g other suits. The<br />
blood lactate concentrations after 90% V 200 <strong>and</strong> 95% V 200 trials with the<br />
four suits were at the same level.<br />
Fig 1. The blood lactate concentration-Swimm<strong>in</strong>g velocity curve <strong>in</strong> an<br />
experimental suits conditions