Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming XI
Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming XI
Biomechanics and Medicine in Swimming XI
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Biomechanics</strong><strong>and</strong>medic<strong>in</strong>e<strong>in</strong>swimm<strong>in</strong>gXi<br />
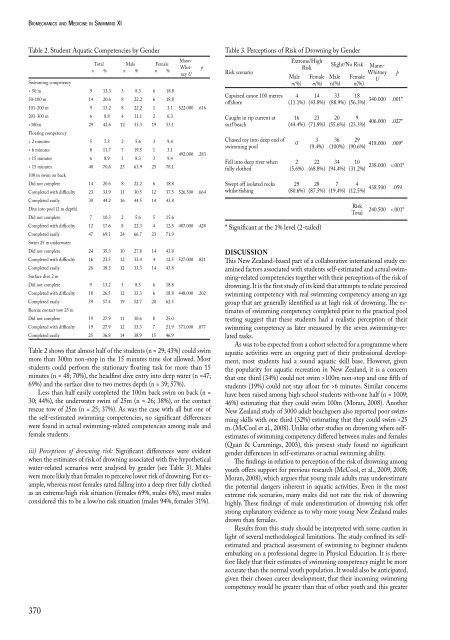
Table 2. Student Aquatic Competencies by Gender<br />
370<br />
Total<br />
n %<br />
Male<br />
n %<br />
Female<br />
n %<br />
Mann-<br />
Whitney<br />
U<br />
Swimm<strong>in</strong>g competency<br />
< 50 m 9 13.3 3 8.3 6 18.8<br />
50-100 m 14 20.6 8 22.2 6 18.8<br />
101-200 m 9 13.2 8 22.2 1 3.1 522.000 .616<br />
201-300 m 6 8.8 4 11.1 2 6.3<br />
>300m<br />
Float<strong>in</strong>g competency<br />
29 42.6 12 33.3 19 53.1<br />
< 2 m<strong>in</strong>utes 5 7.3 2 5.6 3 9.4<br />
< 6 m<strong>in</strong>utes<br />
< 15 m<strong>in</strong>utes<br />
8<br />
6<br />
11.7<br />
8.9<br />
7<br />
3<br />
19.5<br />
8.3<br />
1<br />
3<br />
3.1<br />
9.4<br />
492.000 .283<br />
> 15 m<strong>in</strong>utes<br />
100 m swim on back<br />
48 70.6 23 63.9 25 78.1<br />
Did not complete 14 20.6 8 22.2 6 18.8<br />
Completed with difficulty 23 33.9 11 30.5 12 37.5 526.500 .664<br />
Completed easily<br />
Dive <strong>in</strong>to pool (2 m depth)<br />
30 44.2 16 44.5 14 43.8<br />
Did not complete 7 10.3 2 5.6 5 15.6<br />
Completed with difficulty 12 17.6 8 22.3 4 12.5 487.000 .428<br />
Completed easily<br />
Swim 25 m underwater<br />
47 69.1 24 66.7 23 71.9<br />
Did not complete 24 35.3 10 27.8 14 43.8<br />
Completed with difficulty 16 23.5 12 33.4 4 12.5 527.000 .821<br />
Completed easily<br />
Surface dive 2 m<br />
26 38.3 12 33.3 14 43.8<br />
Did not complete 9 13.2 3 8.3 6 18.8<br />
Completed with difficulty 18 26.5 12 33.3 6 18.8 448.000 .202<br />
Completed easily<br />
Rescue contact tow 25 m<br />
39 57.4 19 52.7 20 62.5<br />
Did not complete 19 27.9 11 30.6 8 25.0<br />
Completed with difficulty 19 27.9 12 33.3 7 21.9 371.000 .077<br />
Completed easily 25 36.8 14 38.9 15 46.9<br />
Table 2 shows that almost half of the students (n = 29; 43%) could swim<br />
more than 300m non-stop <strong>in</strong> the 15 m<strong>in</strong>utes time slot allowed. Most<br />
students could perform the stationary float<strong>in</strong>g task for more than 15<br />
m<strong>in</strong>utes (n = 48; 70%), the headfirst dive entry <strong>in</strong>to deep water (n =47;<br />
69%) <strong>and</strong> the surface dive to two metres depth (n = 39; 57%).<br />
Less than half easily completed the 100m back swim on back (n =<br />
30; 44%), the underwater swim of 25m (n = 26; 38%), or the contact<br />
rescue tow of 25m (n = 25; 37%). As was the case with all but one of<br />
the self-estimated swimm<strong>in</strong>g competencies, no significant differences<br />
were found <strong>in</strong> actual swimm<strong>in</strong>g-related competencies among male <strong>and</strong><br />
female students.<br />
iii) Perceptions of drown<strong>in</strong>g risk: Significant differences were evident<br />
when the estimates of risk of drown<strong>in</strong>g associated with five hypothetical<br />
water-related scenarios were analysed by gender (see Table 3). Males<br />
were more likely than females to perceive lower risk of drown<strong>in</strong>g. For example,<br />
whereas most females rated fall<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>to a deep river fully clothed<br />
as an extreme/high risk situation (females 69%, males 6%), most males<br />
considered this to be a low/no risk situation (males 94%, females 31%).<br />
p<br />
Table 3. Perceptions of Risk of Drown<strong>in</strong>g by Gender<br />
Risk scenario<br />
Extreme/High<br />
Risk<br />
Male Female<br />
n(%) n(%)<br />
Slight/No Risk Mann-<br />
Whitney<br />
Male Female U<br />
n(%) n(%)<br />
Capsized canoe 100 metres<br />
offshore<br />
Caught <strong>in</strong> rip current at<br />
surf beach<br />
Chased toy <strong>in</strong>to deep end of<br />
swimm<strong>in</strong>g pool<br />
Fell <strong>in</strong>to deep river when<br />
fully clothed<br />
Swept off isolated rocks<br />
whilst fish<strong>in</strong>g<br />
4<br />
(11.1%)<br />
16<br />
(44.4%)<br />
0<br />
2<br />
(5.6%)<br />
29<br />
(80.6%)<br />
14<br />
(43.8%)<br />
23<br />
(71.9%)<br />
3<br />
(9.4%)<br />
22<br />
(68.8%)<br />
28<br />
(87.5%)<br />
* Significant at the 1% level (2-tailed)<br />
33<br />
(88.9%)<br />
20<br />
(55.6%)<br />
36<br />
(100%)<br />
34<br />
(94.4%)<br />
7<br />
(19.4%)<br />
18<br />
340.000 .001*<br />
(56.3%)<br />
9<br />
406.000 .027*<br />
(23.3%)<br />
29<br />
418.000 .009*<br />
(90.6%)<br />
10<br />
238.000 6 m<strong>in</strong>utes. Similar concerns<br />
have been raised among high school students with