- Page 1 and 2:
Authors Michaela Raab Jasmin Rocha
- Page 3 and 4:
4.7 Reality check: reviewing the ca
- Page 5 and 6:
1. INTRODUCTION AND KEY CONCEPTS 1.
- Page 7 and 8:
control, it enhances the efficiency
- Page 9 and 10:
communication channels to focus on
- Page 11 and 12:
� Challenge and influence change
- Page 13 and 14:
Men and boys must be engaged as key
- Page 15 and 16:
Source: Appiah, K., Oct. 2010. The
- Page 17 and 18:
criminalizing VAW, is necessary so
- Page 19 and 20: compelling campaign messages, and s
- Page 21 and 22: 1.6 WHAT CAN ONE EXPECT FROM A CAMP
- Page 23 and 24: 2. GUIDING PRINCIPLES 2.1 GROUNDING
- Page 25 and 26: experience the campaign issue in th
- Page 27 and 28: For further information, see the Do
- Page 29 and 30: 2006. Linking Gender-Based Violence
- Page 31 and 32: - Competence: The subject must be a
- Page 33 and 34: 3. CAMPAIGN PLANNING 3.1 STRATEGIC
- Page 35 and 36: Read the external evaluation. See t
- Page 37 and 38: a tight budget can obtain quality s
- Page 39 and 40: 3.2 WHEN DOES IT MAKE SENSE TO STAR
- Page 41 and 42: effort in their own countries (on k
- Page 43 and 44: Campaign achievements: Organizers s
- Page 45 and 46: intimate partners, traditional heal
- Page 47 and 48: In sum, in a campaign there are sim
- Page 49 and 50: - Seek advice from experts in colle
- Page 51 and 52: Problem trees visualize the causes
- Page 53 and 54: - What other possible solutions are
- Page 55 and 56: (2) A “help” message that would
- Page 57 and 58: Mapping opportunities helps to dete
- Page 59 and 60: Economic factors may include issues
- Page 61 and 62: 2. For each risk that is probable a
- Page 63 and 64: stakeholder mapping and identifying
- Page 65 and 66: elationships), dotted lines more in
- Page 67 and 68: elationships that men and women can
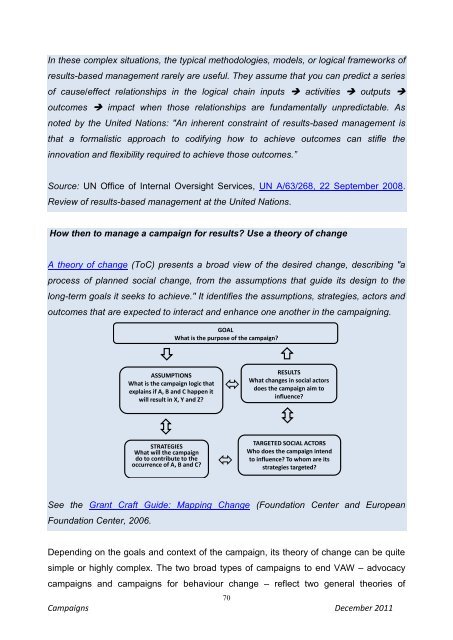
- Page 69: 3.7 THEORIES OF CHANGE IN CAMPAIGNI
- Page 73 and 74: gun violence against women by creat
- Page 75 and 76: Examples: Campaigns that aim to tri
- Page 77 and 78: Campaign Evaluation, and O’Sulliv
- Page 79 and 80: BEHAVIOUR CHANGE CAMPAIGN APPROACHE
- Page 81 and 82: first 21 months of the campaign, th
- Page 83 and 84: � The Legislation Module provides
- Page 85 and 86: The campaign achieved that (i) the
- Page 87 and 88: Further information on campaign act
- Page 89 and 90: The campaign was considered a succe
- Page 91 and 92: 3.9 RESOURCE MAPPING Resource mappi
- Page 93 and 94: 4. CAMPAIGN STRATEGY 4.1 ESSENTIAL
- Page 95 and 96: o The resource mobilization strateg
- Page 97 and 98: campaigns that seek to improve poli
- Page 99 and 100: “Specific” doesn’t imply “u
- Page 101 and 102: Bear in mind: Campaigns are inheren
- Page 103 and 104: opinion-makers, including mass medi
- Page 105 and 106: Source: Making Rights a Reality: Bu
- Page 107 and 108: Example: It’s Against All the Rul
- Page 109 and 110: If the aim of a campaign is to prom
- Page 111 and 112: special care to invite journalists,
- Page 113 and 114: networks. In addition, donors may b
- Page 115 and 116: � Determine what you need the all
- Page 117 and 118: insights if it is shaped by the per
- Page 119 and 120: eports are planned, is a key source
- Page 121 and 122:
DV taking place. The campaign’s i
- Page 123 and 124:
Have we discussed the hypotheses fo
- Page 125 and 126:
Seeking feedback from others should
- Page 127 and 128:
- Which are the core tasks that nee
- Page 129 and 130:
call for different skills in the ca
- Page 131 and 132:
(FAQs) that they can use during pub
- Page 133 and 134:
5.3 THE ART OF COLLABORATION IN ALL
- Page 135 and 136:
� It should allow for learning fr
- Page 137 and 138:
than others, or when costs are disp
- Page 139 and 140:
- Milestones, i.e. specific moments
- Page 141 and 142:
5.6 ADJUSTING A CAMPAIGN There are
- Page 143 and 144:
misunderstandings and conflicts. On
- Page 145 and 146:
alliance has overcome them, generat
- Page 147 and 148:
What is my role? To what extent am
- Page 149 and 150:
Example: The We Can end all violenc
- Page 151 and 152:
and ethics of campaigning to end VA
- Page 153 and 154:
To draw lessons for the future, it
- Page 155 and 156:
6. CAMPAIGN COMMUNICATIONS OVERVIEW
- Page 157 and 158:
friends. Additional precautions mus
- Page 159 and 160:
and others to increase their traini
- Page 161 and 162:
sub-themes for the campaign were id
- Page 163 and 164:
issues of sustainability. The docum
- Page 165 and 166:
Effective campaigning is built arou
- Page 167 and 168:
QUESTIONS TO CONSIDER WHEN CRAFTING
- Page 169 and 170:
� If the audience is highly diver
- Page 171 and 172:
Bear in mind: � All communication
- Page 173 and 174:
~~~~~ The Southern Africa Counter-T
- Page 175 and 176:
(VAW). The guide presents a variety
- Page 177 and 178:
Source: Making a Difference: Strate
- Page 179 and 180:
See the video. Visit the Say No-UNi
- Page 181 and 182:
constructive guidance should be off
- Page 183 and 184:
� Avoid being long-winded since a
- Page 185 and 186:
� If a prominent individual (poli
- Page 187 and 188:
6. Follow up with the media. Follow
- Page 189 and 190:
Practical tips for op-eds - Humaniz
- Page 191 and 192:
� Less is more: the design of vis
- Page 193 and 194:
Read the White Ribbon Campaign case
- Page 195 and 196:
Source: Lacayo, V. & Singhal, A., P
- Page 197 and 198:
UNIFEM Say No Campaign T-shirts fro
- Page 199 and 200:
Participation - Government of Catal
- Page 201 and 202:
- Picture scenes that target audien
- Page 203 and 204:
The ‘Say No - Unite to End Violen
- Page 205 and 206:
Refer to the section on Community M
- Page 207 and 208:
media specialists need to be involv
- Page 209 and 210:
video material that is easily disse
- Page 211 and 212:
Tools for digital video: � The in
- Page 213 and 214:
and South Asian audiences, it conta
- Page 215 and 216:
cyber-bullying of teenage girls, th
- Page 217 and 218:
The colorful campaign site is desig
- Page 219 and 220:
and tactics for communicating your
- Page 221 and 222:
� Provide an opt-out function for
- Page 223 and 224:
Chat/cyber dialoguing Many social w
- Page 225 and 226:
Mobile phones in campaigns - exampl
- Page 227 and 228:
applied to other issues and used by
- Page 229 and 230:
KEY ISSUES IN COMMUNITY MOBILIZATIO
- Page 231 and 232:
Raising Voices has developed a deta
- Page 233 and 234:
the My Strength Campaign in Califor
- Page 235 and 236:
(Oxfam murals with messages painted
- Page 237 and 238:
Read more in the publication: Gaye,
- Page 239 and 240:
comprehensive series of guides such
- Page 241 and 242:
GAMES FOR CHANGE Games for Change i
- Page 243 and 244:
*Items 4 and 6 can be omitted if th
- Page 245 and 246:
other visual means to capture the r
- Page 247 and 248:
audience so as to garner public sup
- Page 249 and 250:
� If it is highly likely to rally
- Page 251 and 252:
screened, a documentary film about
- Page 253 and 254:
special care to invite journalists,
- Page 255 and 256:
(e.g. CEDAW) must submit regular re
- Page 257 and 258:
to online complaint forms for the I
- Page 259 and 260:
Bear in mind: Before signing up for
- Page 261 and 262:
eached. In campaigns, external fact
- Page 263 and 264:
the changes in the individuals, gro
- Page 265 and 266:
4. Choose benchmarks and indicators
- Page 267 and 268:
violence). Sample question: How man
- Page 269 and 270:
participatory assessment tools adap
- Page 271 and 272:
espondents through probability samp
- Page 273 and 274:
elow, from Oxfam GB Bangladesh Offi
- Page 275 and 276:
hesitate to talk about it. Surveys
- Page 277 and 278:
LEVELS OF MONITORING Monitoring the
- Page 279 and 280:
three sets of questions: (1) Is the
- Page 281 and 282:
Another aspect is to monitor media
- Page 283 and 284:
� Conducting a Participatory Eval
- Page 285 and 286:
Kenya, Uganda and Venezuela. In add
- Page 287 and 288:
Matters, a free, hour-long online t
- Page 289 and 290:
communication campaign evaluation i
- Page 291 and 292:
Advanced research designs for impac
- Page 293 and 294:
Different stakeholders may require
- Page 295 and 296:
include a request for feedback on s
- Page 297 and 298:
� Domestic Violence Campaign - Ma
- Page 299 and 300:
challenges that exist. It provides
- Page 301 and 302:
� Operational costs, i.e. the cos
- Page 303 and 304:
Grant from donor B Community contri
- Page 305 and 306:
2. Mapping internal and community r
- Page 307 and 308:
information on the expected results
- Page 309 and 310:
Example: Urgent Action Fund Africa,
- Page 311 and 312:
Where campaign funds are held in th
- Page 313 and 314:
REFERENCES Advocacy Online, 2009. E
- Page 315 and 316:
Communication for Change, 2010. A L
- Page 317 and 318:
Heifetz, R. and Laurie, D., 1997.
- Page 319 and 320:
Guide to Designing a Health Communi
- Page 321 and 322:
Advocacy and Lobbying Manual Shapir
- Page 323 and 324:
2001.“Bold rape-awareness posters