Poverty and Human Development Report 2009 - UNDP in Tanzania
Poverty and Human Development Report 2009 - UNDP in Tanzania
Poverty and Human Development Report 2009 - UNDP in Tanzania
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
POVERTY AND HUMAN DEVELOPMENT REPORT <strong>2009</strong><br />
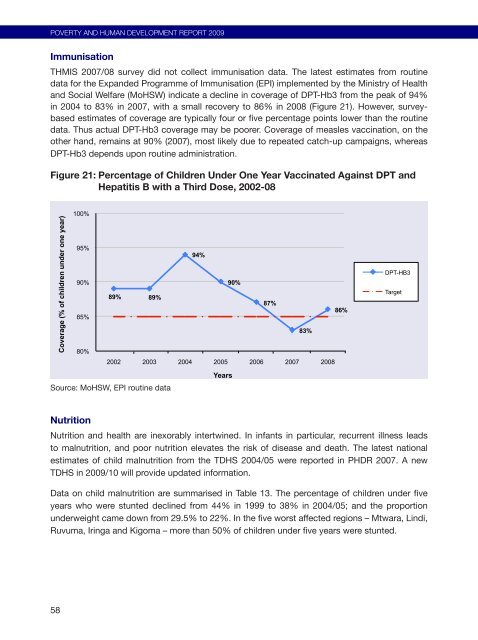
Immunisation<br />
THMIS 2007/08 survey did not collect immunisation data. The latest estimates from rout<strong>in</strong>e<br />
data for the Exp<strong>and</strong>ed Programme of Immunisation (EPI) implemented by the M<strong>in</strong>istry of Health<br />
<strong>and</strong> Social Welfare (MoHSW) <strong>in</strong>dicate a decl<strong>in</strong>e <strong>in</strong> coverage of DPT-Hb3 from the peak of 94%<br />
<strong>in</strong> 2004 to 83% <strong>in</strong> 2007, with a small recovery to 86% <strong>in</strong> 2008 (Figure 21). However, surveybased<br />
estimates of coverage are typically four or five percentage po<strong>in</strong>ts lower than the rout<strong>in</strong>e<br />
data. Thus actual DPT-Hb3 coverage may be poorer. Coverage of measles vacc<strong>in</strong>ation, on the<br />
other h<strong>and</strong>, rema<strong>in</strong>s at 90% (2007), most likely due to repeated catch-up campaigns, whereas<br />
DPT-Hb3 depends upon rout<strong>in</strong>e adm<strong>in</strong>istration.<br />
Figure 21: Percentage of Children Under One Year Vacc<strong>in</strong>ated Aga<strong>in</strong>st DPT <strong>and</strong><br />
Hepatitis B with a Third Dose, 2002-08<br />
Coverage (% of children under one year)<br />
58<br />
100%<br />
95%<br />
90%<br />
85%<br />
80%<br />
89% 89%<br />
94%<br />
90%<br />
87%<br />
83%<br />
2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008<br />
Source: MoHSW, EPI rout<strong>in</strong>e data<br />
Nutrition<br />
Years<br />
86%<br />
DPT-HB3<br />
Nutrition <strong>and</strong> health are <strong>in</strong>exorably <strong>in</strong>tertw<strong>in</strong>ed. In <strong>in</strong>fants <strong>in</strong> particular, recurrent illness leads<br />
to malnutrition, <strong>and</strong> poor nutrition elevates the risk of disease <strong>and</strong> death. The latest national<br />
estimates of child malnutrition from the TDHS 2004/05 were reported <strong>in</strong> PHDR 2007. A new<br />
TDHS <strong>in</strong> <strong>2009</strong>/10 will provide updated <strong>in</strong>formation.<br />
Data on child malnutrition are summarised <strong>in</strong> Table 13. The percentage of children under five<br />
years who were stunted decl<strong>in</strong>ed from 44% <strong>in</strong> 1999 to 38% <strong>in</strong> 2004/05; <strong>and</strong> the proportion<br />
underweight came down from 29.5% to 22%. In the five worst affected regions – Mtwara, L<strong>in</strong>di,<br />
Ruvuma, Ir<strong>in</strong>ga <strong>and</strong> Kigoma – more than 50% of children under five years were stunted.<br />
Target