Effet chez le porcelet d'une exposition à un régime co-contaminé en ...
Effet chez le porcelet d'une exposition à un régime co-contaminé en ...
Effet chez le porcelet d'une exposition à un régime co-contaminé en ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
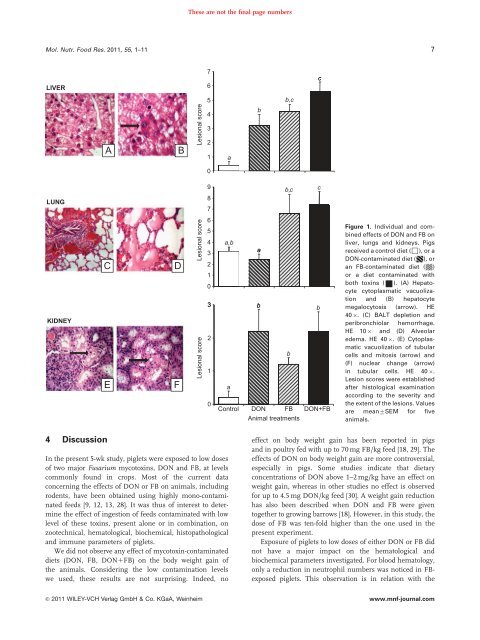
These are not the final page numbersMol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 1–11 7LIVER76cABLesional s<strong>co</strong>re54321abb,c0LUNGKIDNEYCDLesional s<strong>co</strong>reLesional s<strong>co</strong>reE F a9b,c c87654 a,b3a2103 bb2b10Control DON FB DON+FBAnimal treatm<strong>en</strong>tsFigure 1. Individual and <strong>co</strong>mbinedeffects of DON and FB onliver, l<strong>un</strong>gs and kidneys. Pigsreceived a <strong>co</strong>ntrol diet (&), or aDON-<strong>co</strong>ntaminated diet ( ), oran FB-<strong>co</strong>ntaminated diet ( )or a diet <strong>co</strong>ntaminated withboth toxins (&). (A) Hepatocytecytoplasmatic vacuolizationand (B) hepatocytemegalocytosis (arrow). HE40 . (C) BALT dep<strong>le</strong>tion andperibronchiolar hemorrhage.HE 10 and (D) Alveolaredema. HE 40 . (E) Cytoplasmaticvacuolization of tubularcells and mitosis (arrow) and(F) nuc<strong>le</strong>ar change (arrow)in tubular cells. HE 40 .Lesion s<strong>co</strong>res were establishedafter histological examinationac<strong>co</strong>rding to the severity andthe ext<strong>en</strong>t of the <strong>le</strong>sions. Valuesare mean7SEM for fiveanimals.4 DiscussionIn the pres<strong>en</strong>t 5-wk study, pig<strong>le</strong>ts were exposed to low dosesof two major Fusarium my<strong>co</strong>toxins, DON and FB, at <strong>le</strong>vels<strong>co</strong>mmonly fo<strong>un</strong>d in crops. Most of the curr<strong>en</strong>t data<strong>co</strong>ncerning the effects of DON or FB on animals, includingrod<strong>en</strong>ts, have be<strong>en</strong> obtained using highly mono-<strong>co</strong>ntaminatedfeeds [9, 12, 13, 28]. It was thus of interest to determinethe effect of ingestion of feeds <strong>co</strong>ntaminated with low<strong>le</strong>vel of these toxins, pres<strong>en</strong>t alone or in <strong>co</strong>mbination, onzootechnical, hematological, biochemical, histopathologicaland imm<strong>un</strong>e parameters of pig<strong>le</strong>ts.We did not observe any effect of my<strong>co</strong>toxin-<strong>co</strong>ntaminateddiets (DON, FB, DON1FB) on the body weight gain ofthe animals. Considering the low <strong>co</strong>ntamination <strong>le</strong>velswe used, these results are not surprising. Indeed, noeffect on body weight gain has be<strong>en</strong> reported in pigsand in poultry fed with up to 70 mg FB/kg feed [18, 29]. Theeffects of DON on body weight gain are more <strong>co</strong>ntroversial,especially in pigs. Some studies indicate that dietary<strong>co</strong>nc<strong>en</strong>trations of DON above 1–2 mg/kg have an effect onweight gain, whereas in other studies no effect is observedfor up to 4.5 mg DON/kg feed [30]. A weight gain reductionhas also be<strong>en</strong> described wh<strong>en</strong> DON and FB were giv<strong>en</strong>together to growing barrows [18]. However, in this study, thedose of FB was t<strong>en</strong>-fold higher than the one used in thepres<strong>en</strong>t experim<strong>en</strong>t.Exposure of pig<strong>le</strong>ts to low doses of either DON or FB didnot have a major impact on the hematological andbiochemical parameters investigated. For blood hematology,only a reduction in neutrophil numbers was noticed in FBexposedpig<strong>le</strong>ts. This observation is in relation with the& 2011 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheimwww.mnf-journal.<strong>co</strong>m