- Page 1 and 2: NX Nastran DMAP Programmer’s Guid
- Page 3 and 4: 1 Direct Matrix Abstraction C O N T
- Page 5 and 6: ❑ Miscellaneous Modules and State
- Page 7 and 8: - MODEPT, 1209 - MODGDN, 1210 - MOD
- Page 9 and 10: CHAPTER 1 NX Nastran DMAP Programme
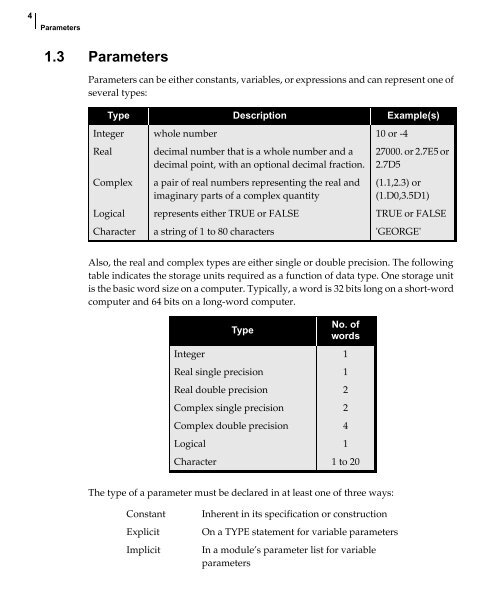
- Page 11: 1.2 The NX Nastran DMAP Language Th
- Page 15 and 16: Parameters 4. Value from the NAME=v
- Page 17 and 18: Parameters For example, the followi
- Page 19 and 20: Relational Operators Parameters Rel
- Page 21 and 22: 1.4 Data Blocks Data Blocks A data
- Page 23 and 24: Form is defined as one of the follo
- Page 25 and 26: 1.5 Instructions Instructions A DMA
- Page 27 and 28: MPYAD A , B , / D $ Instructions Ac
- Page 29 and 30: Instructions Type conversions can b
- Page 31 and 32: Format Definition Result ATAN2( x1,
- Page 33 and 34: Format Definition Result DIM( x1, x
- Page 35 and 36: Format Definition Result LLT( a1, a
- Page 37 and 38: Format Definition Result NUMGT(x1,x
- Page 39 and 40: Format Definition Result Instructio
- Page 41 and 42: Control Statement The NX Nastran DM
- Page 43 and 44: DO WHILE(expression) $ . . . ENDDO
- Page 45 and 46: SUBDMAP TEST X,Y,Z/L,M,N/A1/A2/A3 $
- Page 47 and 48: 1.6 “Output from a Previous Modul
- Page 49 and 50: 1.8 Preface Modules and SOLution 10
- Page 51 and 52: SubDMAPs DBMGR, DBSTORE, and DBFETC
- Page 53 and 54: 1.11 WHERE and CONVERT Clauses WHER
- Page 55 and 56: Examples of the CONVERT clause are:
- Page 57 and 58: What's New in DMAP? Option 39: Remo
- Page 59 and 60: CHAPTER 2 NX Nastran DMAP Programme
- Page 61 and 62: 2.2 Matrix Data Blocks The rows and
- Page 63 and 64:
2.3 Table Data Blocks This section
- Page 65 and 66:
OFP Tables The header record of all
- Page 67 and 68:
Examples: Therefore, MOD(approach_c
- Page 69 and 70:
Type Chapter 2 Name 23 OELOP1 Summa
- Page 71 and 72:
Stress_code In the OES data block d
- Page 73 and 74:
Type Name Description 23 DAMP4 Scal
- Page 75 and 76:
Type Name Description 76 HEXPR Acou
- Page 77 and 78:
Type Name Description 129 Unused (P
- Page 79 and 80:
Type Name Description 183 Unused (P
- Page 81 and 82:
Type Name Description 223 QUADXFD H
- Page 83 and 84:
2.5 Data Block Descriptions BGPDT B
- Page 85 and 86:
BGPDT68 Basic grid point definition
- Page 87 and 88:
Word Name Type Description CASECC C
- Page 89 and 90:
Word Name Type Description CASECC C
- Page 91 and 92:
Word Name Type Description CASECC C
- Page 93 and 94:
Word Name Type Description CASECC C
- Page 95 and 96:
Word Name Type Description CASECC C
- Page 97 and 98:
Word Name Type Description 318 UNDE
- Page 99 and 100:
Word Name Type Description CASECC C
- Page 101 and 102:
Word Name Type Description CASECC C
- Page 103 and 104:
• 4 = punch and their sums; e.g.,
- Page 105 and 106:
CLAMA Complex eigenvalue summary ta
- Page 107 and 108:
CONTAB Design constraint table CONT
- Page 109 and 110:
CONTACT Table of Bulk Data entry re
- Page 111 and 112:
CSTM Coordinate system transformati
- Page 113 and 114:
CSTM68 Coordinate system transforma
- Page 115 and 116:
CSTM68 Coordinate system transforma
- Page 117 and 118:
CSTM68 Coordinate system transforma
- Page 119 and 120:
Record 2 - TRAILER Notes: 1. Coordi
- Page 121 and 122:
Record 5 - INITV DBCOPT Design opti
- Page 123 and 124:
DESTAB Design variable attributes R
- Page 125 and 126:
Word Name Type Description 5 F0 RS
- Page 127 and 128:
Record 12 - TABLES1(3105,31,97) Wor
- Page 129 and 130:
DSCMCOL Design sensitivity paramete
- Page 131 and 132:
Word Name Type Description 5 COMP I
- Page 133 and 134:
Word Name Type Description 5 COMP I
- Page 135 and 136:
Word Name Type Description 6 UNDEF(
- Page 137 and 138:
DVPTAB Designed property table Reco
- Page 139 and 140:
DYNAMIC Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 141 and 142:
Record 7 - EIGB(107,1,86) DYNAMIC T
- Page 143 and 144:
DYNAMIC Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 145 and 146:
DYNAMIC Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 147 and 148:
DYNAMIC Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 149 and 150:
DYNAMIC Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 151 and 152:
DYNAMIC Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 153 and 154:
EGPSF Table of element to grid poin
- Page 155 and 156:
3. Possible values for items in REC
- Page 157 and 158:
EGPSTR Element grid point stress ta
- Page 159 and 160:
Word Name Type Description End TYPE
- Page 161 and 162:
ELDCT Element stress discontinuity
- Page 163 and 164:
EPT Element property table Record 0
- Page 165 and 166:
Word Name Type Description Record 5
- Page 167 and 168:
Word Name Type Description EPT Elem
- Page 169 and 170:
Word Name Type Description EPT Elem
- Page 171 and 172:
Word Name Type Description EPT Elem
- Page 173 and 174:
Word Name Type Description Record 7
- Page 175 and 176:
Word Name Type Description Record 8
- Page 177 and 178:
Word Name Type Description 21 K1 RS
- Page 179 and 180:
Word Name Type Description EPT Elem
- Page 181 and 182:
Word Name Type Description Record 1
- Page 183 and 184:
Record 18 - PDAMPT(1202,12,33) Word
- Page 185 and 186:
Record 29 - PELAS(302,3,46) Word Na
- Page 187 and 188:
Record 35 - PLPLANE(4606,46,375) Wo
- Page 189 and 190:
Record 41 - PSOLID(2402,24,281) Wor
- Page 191 and 192:
Record 46 - PVAL(10201,102,400) Wor
- Page 193 and 194:
Word Name Type Description Record 5
- Page 195 and 196:
EQEXIN Equivalence between external
- Page 197 and 198:
ERROR Table of p-element error tole
- Page 199 and 200:
GEOM1 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 201 and 202:
Record 5 - CORD2R(2101,21,8) GEOM1
- Page 203 and 204:
Record 10 - FEEDGE(6101,61,388) GEO
- Page 205 and 206:
Record 15 - GMCORD(6401,64,402) GEO
- Page 207 and 208:
Record 20 - SEELT(7902,79,302) GEOM
- Page 209 and 210:
Record 25 - SENQSET(1327,13,464) GE
- Page 211 and 212:
Record 32 - CSUPUP(5801,58,324) Thi
- Page 213 and 214:
GEOM168 Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 215 and 216:
GEOM168 Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 217 and 218:
GEOM168 Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 219 and 220:
Record 16 - GRID(4501,45,1) GEOM168
- Page 221 and 222:
Record 22 - SELABEL(1027,10,459) GE
- Page 223 and 224:
Record 28 - SESET(5601,56,296) GEOM
- Page 225 and 226:
Record 33 - TRAILER GEOM168 Table o
- Page 227 and 228:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 229 and 230:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 231 and 232:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 233 and 234:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 235 and 236:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 237 and 238:
Record 19 - CDUM2(6208,62,108) GEOM
- Page 239 and 240:
Record 29 - CELAS3(801,8,75) GEOM2
- Page 241 and 242:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 243 and 244:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 245 and 246:
Record 43 - CHEXAFD(14000,140,9990)
- Page 247 and 248:
Record 51 - CMFREE(2508,25,0) GEOM2
- Page 249 and 250:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 251 and 252:
Record 65 - CQUAD4(2958,51,177) Rec
- Page 253 and 254:
Record 72 - CROD(3001,30,48) GEOM2
- Page 255 and 256:
Record 81 - CTRIA3(5959,59,282) GEO
- Page 257 and 258:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 259 and 260:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 261 and 262:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 263 and 264:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 265 and 266:
Record104 - SINT(7801,78,8883) GEOM
- Page 267 and 268:
Record110 - TRAILER Notes: 1. Recor
- Page 269 and 270:
Record 4 - GMLOAD(6309,63,391) GEOM
- Page 271 and 272:
GEOM3 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 273 and 274:
Record 13 - MOMENT2(4701,47,23) GEO
- Page 275 and 276:
Record 20 - PLOADX1(7309,73,351) GE
- Page 277 and 278:
Record 27 - QVOL(2309,23,416) GEOM3
- Page 279 and 280:
Record 35 - TEMPP1(8109,81,201) GEO
- Page 281 and 282:
GEOM3 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 283 and 284:
GEOM4 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 285 and 286:
GEOM4 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 287 and 288:
GEOM4 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 289 and 290:
GEOM4 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 291 and 292:
Record 19 - OMIT1(4951,63,92) GEOM4
- Page 293 and 294:
Record 24 - RBE2(6901,69,295) GEOM4
- Page 295 and 296:
GEOM4 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 297 and 298:
Record 31 - RWELD(11901,119,561) GE
- Page 299 and 300:
Record 37 - SEQSET1(1210,12,322) GE
- Page 301 and 302:
GEOM4 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 303 and 304:
Record 49 - SPCEB(9101,91,9025) GEO
- Page 305 and 306:
Record 56 - SUPORT(5601,56,14) GEOM
- Page 307 and 308:
GPDT68 Grid point definition table
- Page 309 and 310:
HIS Table of design iteration histo
- Page 311 and 312:
Record 2 - TRAILER KDICT Element st
- Page 313 and 314:
Record 3 - TRAILER LAMA Normal mode
- Page 315 and 316:
MPT Table of Bulk Data entry images
- Page 317 and 318:
MPT Table of Bulk Data entry images
- Page 319 and 320:
MPT Table of Bulk Data entry images
- Page 321 and 322:
MPT Table of Bulk Data entry images
- Page 323 and 324:
Record 13 - MATHP(4506,45,374) MPT
- Page 325 and 326:
MPT Table of Bulk Data entry images
- Page 327 and 328:
MPT Table of Bulk Data entry images
- Page 329 and 330:
Record 24 - RADMT(8902,89,423) MPT
- Page 331 and 332:
MPT Table of Bulk Data entry images
- Page 333 and 334:
OBC Output contact pressure and tra
- Page 335 and 336:
OBJTAB Design objective table OBJTA
- Page 337 and 338:
OEE Output element energy (strain,
- Page 339 and 340:
OEE Output element energy (strain,
- Page 341 and 342:
OEF Table of element forces OEF Tab
- Page 343 and 344:
Word Name Type Description 6 UNDEF(
- Page 345 and 346:
Word Name Type Description 5 FREECO
- Page 347 and 348:
Word Name Type Description 12 YFLUX
- Page 349 and 350:
Word Name Type Description OEF Tabl
- Page 351 and 352:
Word Name Type Description 8 F34R R
- Page 353 and 354:
Word Name Type Description OEF Tabl
- Page 355 and 356:
Word Name Type Description TCODE,7
- Page 357 and 358:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 359 and 360:
Word Name Type Description TCODE,7
- Page 361 and 362:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 363 and 364:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 365 and 366:
Word Name Type Description 2 AXR RS
- Page 367 and 368:
Word Name Type Description OEF Tabl
- Page 369 and 370:
Word Name Type Description TCODE,7
- Page 371 and 372:
Word Name Type Description 10 PRESS
- Page 373 and 374:
Word Name Type Description 7 BMX RS
- Page 375 and 376:
Word Name Type Description 10 AZI R
- Page 377 and 378:
Word Name Type Description 7 AF RS
- Page 379 and 380:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 381 and 382:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 383 and 384:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 385 and 386:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 387 and 388:
Word Name Type Description 23 UNDEF
- Page 389 and 390:
Word Name Type Description OEF Tabl
- Page 391 and 392:
Word Name Type Description 9 TRQ RS
- Page 393 and 394:
Word Name Type Description 15 TS2I
- Page 395 and 396:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 397 and 398:
Word Name Type Description Record 3
- Page 399 and 400:
2 NX Nastran DMAP Modules and Data
- Page 401 and 402:
OES Table of element stresses or st
- Page 403 and 404:
Word Name Type Description 3 NX1 RS
- Page 405 and 406:
Word Name Type Description TCODE,7
- Page 407 and 408:
Word Name Type Description TCODE,7
- Page 409 and 410:
Word Name Type Description 3 AEI RS
- Page 411 and 412:
Word Name Type Description End TCOD
- Page 413 and 414:
Word Name Type Description 2 UNDEF
- Page 415 and 416:
Word Name Type Description 3 SX1R R
- Page 417 and 418:
Word Name Type Description 2 SX1A R
- Page 419 and 420:
Word Name Type Description TCODE,7
- Page 421 and 422:
Word Name Type Description 16 EP2 R
- Page 423 and 424:
Word Name Type Description 25 P3Z R
- Page 425 and 426:
Word Name Type Description 2 RA RS
- Page 427 and 428:
Word Name Type Description 11 TE4 R
- Page 429 and 430:
Word Name Type Description 4 TE1R R
- Page 431 and 432:
Word Name Type Description 2 SR(9)
- Page 433 and 434:
Word Name Type Description 12 FD2 R
- Page 435 and 436:
Word Name Type Description 6 SX1I R
- Page 437 and 438:
Word Name Type Description 8 EZR RS
- Page 439 and 440:
Word Name Type Description 16 TYZI
- Page 441 and 442:
Word Name Type Description 2 CID I
- Page 443 and 444:
Word Name Type Description 8 EMAX R
- Page 445 and 446:
Word Name Type Description 8 A1 RS
- Page 447 and 448:
Word Name Type Description 2 TERM C
- Page 449 and 450:
Word Name Type Description 12 EY2R
- Page 451 and 452:
Word Name Type Description 14 EY2 R
- Page 453 and 454:
Word Name Type Description 8 SY1I R
- Page 455 and 456:
Word Name Type Description 7 EY1R R
- Page 457 and 458:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 459 and 460:
Word Name Type Description 2 FD1 RS
- Page 461 and 462:
Word Name Type Description 11 EY1 R
- Page 463 and 464:
Word Name Type Description 13 EX RS
- Page 465 and 466:
Word Name Type Description 49 TEFB
- Page 467 and 468:
Word Name Type Description 5 ET1 RS
- Page 469 and 470:
Word Name Type Description 9 EMIN R
- Page 471 and 472:
Word Name Type Description 4 ABSORB
- Page 473 and 474:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 475 and 476:
Word Name Type Description 3 GRID I
- Page 477 and 478:
Word Name Type Description OES Tabl
- Page 479 and 480:
Word Name Type Description 11 YNORM
- Page 481 and 482:
Word Name Type Description 8 TYZ RS
- Page 483 and 484:
Word Name Type Description 2 UNDEF
- Page 485 and 486:
Word Name Type Description 9 SMI RS
- Page 487 and 488:
Word Name Type Description 20 CX RS
- Page 489 and 490:
Word Name Type Description 8 SMJ RS
- Page 491 and 492:
Word Name Type Description 19 TYZR
- Page 493 and 494:
Word Name Type Description 20 TZX1R
- Page 495 and 496:
Word Name Type Description 25 UNDEF
- Page 497 and 498:
Word Name Type Description 26 TXY2R
- Page 499 and 500:
Word Name Type Description 2 UNDEF
- Page 501 and 502:
Word Name Type Description 7 SXY RS
- Page 503 and 504:
Word Name Type Description 11 VOLST
- Page 505 and 506:
Word Name Type Description 15 EXY R
- Page 507 and 508:
Word Name Type Description 9 VOLSTR
- Page 509 and 510:
Word Name Type Description 3 ID I 4
- Page 511 and 512:
Word Name Type Description 7 SXY RS
- Page 513 and 514:
Word Name Type Description 10 ETZ R
- Page 515 and 516:
Word Name Type Description 11 SX2 R
- Page 517 and 518:
Word Name Type Description 14 EXY2R
- Page 519 and 520:
Word Name Type Description 7 SL2 RS
- Page 521 and 522:
OGF Table of grid point forces Tabl
- Page 523 and 524:
Word Name Type Description OGF Tabl
- Page 525 and 526:
OGK Output gasket element results F
- Page 527 and 528:
OGS Table of grid point stresses/st
- Page 529 and 530:
OGS Table of grid point stresses/st
- Page 531 and 532:
OGS Table of grid point stresses/st
- Page 533 and 534:
4. Output coordinate system code 1
- Page 535 and 536:
Record 2 - DATA Record 3 - TRAILER
- Page 537 and 538:
OMEOSCTable of oscillating total mo
- Page 539 and 540:
5 = print and punch 4. Approach cod
- Page 541 and 542:
Record 2 - DATA Record 3 - TRAILER
- Page 543 and 544:
OMKEO Table of oscillating modal ki
- Page 545 and 546:
5 = print and punch 4. Approach cod
- Page 547 and 548:
Record 2 - DATA Record 3 - TRAILER
- Page 549 and 550:
OMSEO Table of oscillating modal st
- Page 551 and 552:
5 = print and punch 4. Approach cod
- Page 553 and 554:
Word Name Type Description ACODE =0
- Page 555 and 556:
Word Name Type Description OPG Tabl
- Page 557 and 558:
OPTPRM Table of optimization parame
- Page 559 and 560:
OQG OQG Table of single or multipoi
- Page 561 and 562:
OQG Table of single or multipoint c
- Page 563 and 564:
OQG Table of single or multipoint c
- Page 565 and 566:
OUG Table of displacements, velocit
- Page 567 and 568:
OUG Table of displacements, velocit
- Page 569 and 570:
OUG Table of displacements, velocit
- Page 571 and 572:
OUG Table of displacements, velocit
- Page 573 and 574:
OUG Table of displacements, velocit
- Page 575 and 576:
OUG Table of displacements, velocit
- Page 577 and 578:
R1MAP Table of mapping from origina
- Page 579 and 580:
R1TAB Table of type one response at
- Page 581 and 582:
R1TAB Table of type one response at
- Page 583 and 584:
Record 2 - TRAILER R1TAB Table of t
- Page 585 and 586:
RESP12 Table of second level (synth
- Page 587 and 588:
Record 2 - TRAILER RESP12 Table of
- Page 589 and 590:
Word Name Type Description Word 13
- Page 591 and 592:
SEMAP Superelement Definition Table
- Page 593 and 594:
SET Table of combined sets Record 0
- Page 595 and 596:
VIEWTB View information table VIEWT
- Page 597 and 598:
Word Name Type Description Record 4
- Page 599 and 600:
Chapter 4 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 601 and 602:
Chapter 4 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 603 and 604:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 605 and 606:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 607 and 608:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 609 and 610:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 611 and 612:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 613 and 614:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 615 and 616:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 617 and 618:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 619 and 620:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 621 and 622:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 623 and 624:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 625 and 626:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 627 and 628:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 629 and 630:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 631 and 632:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 633 and 634:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 635 and 636:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 637 and 638:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 639 and 640:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 641 and 642:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 643 and 644:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 645 and 646:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 647 and 648:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 649 and 650:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 651 and 652:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 653 and 654:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 655 and 656:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 657 and 658:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 659 and 660:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 661 and 662:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 663 and 664:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 665 and 666:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 667 and 668:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 669 and 670:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 671 and 672:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 673 and 674:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 675 and 676:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 677 and 678:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 679 and 680:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 681 and 682:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 683 and 684:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 685 and 686:
Data Block Naming Conventions Stiff
- Page 687 and 688:
Solutions: ___U___ Static and dynam
- Page 689 and 690:
Solution Output Tables: O__ES__ Ele
- Page 691 and 692:
Inconsistent Names: BUG Buckling ei
- Page 693 and 694:
Name Type and Description 'DYNAMICS
- Page 695 and 696:
Name Type and Description BUCKCC Lo
- Page 697 and 698:
Name Type and Description -1 Lumped
- Page 699 and 700:
Name Type and Description DFRQCC Lo
- Page 701 and 702:
Name Type and Description DTMi Inte
- Page 703 and 704:
Name Type and Description EXISTS Ch
- Page 705 and 706:
Name Type and Description FOUND Int
- Page 707 and 708:
Name Type and Description 2 Cubic s
- Page 709 and 710:
Name Type and Description 2 Insuffi
- Page 711 and 712:
Name Type and Description LINC Inte
- Page 713 and 714:
Name Type and Description MAXSET In
- Page 715 and 716:
Name Type and Description MPFSORT I
- Page 717 and 718:
Name Type and Description NE Intege
- Page 719 and 720:
Name Type and Description NOA Integ
- Page 721 and 722:
Name Type and Description NOGOIFPi
- Page 723 and 724:
Name Type and Description NOMR Inte
- Page 725 and 726:
Name Type and Description NORM Char
- Page 727 and 728:
Name Type and Description NOUNIT In
- Page 729 and 730:
Name Type and Description NLITER an
- Page 731 and 732:
Name Type and Description 'WHOLE' R
- Page 733 and 734:
Name Type and Description POUTF Int
- Page 735 and 736:
Name Type and Description RCOLLBLi
- Page 737 and 738:
Name Type and Description SEFLAG Lo
- Page 739 and 740:
Name Type and Description SID Integ
- Page 741 and 742:
Name Type and Description 2 Maximum
- Page 743 and 744:
Name Type and Description TINY Real
- Page 745 and 746:
Name Type and Description VUTRIA3 C
- Page 747 and 748:
CHAPTER 3 NX Nastran DMAP Programme
- Page 749 and 750:
3.2 Detailed Description of NDDL St
- Page 751 and 752:
DATABLK Describes data blocks used
- Page 753 and 754:
where: Keywords: Variables: DATABLK
- Page 755 and 756:
DATABLK Describes data blocks used
- Page 757 and 758:
ENTRY, SET,I, ENDENTRY,COUNT=LSET,
- Page 759 and 760:
Examples: 1. EPTS example: DEPEN Sp
- Page 761 and 762:
PARAM Defines parameters requiring
- Page 763 and 764:
QUAL Defines qualifiers referenced
- Page 765 and 766:
CHAPTER 4 NX Nastran DMAP Programme
- Page 767 and 768:
Utility Modules APPEND COPY DBC DBD
- Page 769 and 770:
761 GETCOL GETMKL GI GKAM GNFM GP0
- Page 771 and 772:
UMERGE1 UPARTN Module Basic Operati
- Page 773 and 774:
Executive Modules and Statements Mo
- Page 775 and 776:
ACMG Computes fluid/structure coupl
- Page 777 and 778:
ACMG Computes fluid/structure coupl
- Page 779 and 780:
ADAPT Performs and prints error est
- Page 781 and 782:
ADD Matrix add Computes [ X] = α[
- Page 783 and 784:
ADD5 Matrix add ADD5 Matrix add To
- Page 785 and 786:
4. Change the type of the real doub
- Page 787 and 788:
Parameters: Remarks: 1. NK, and NJ
- Page 789 and 790:
2. PKF cannot be purged. Examples:
- Page 791 and 792:
Remarks: AELOOP Aerodynamic loop dr
- Page 793 and 794:
AMG Builds aerodynamic influence ma
- Page 795 and 796:
AMP Generates modal aerodynamic mat
- Page 797 and 798:
APD Generates aerodynamic geometry
- Page 799 and 800:
MODLTYPE='AEROSTRC' $ APD EDT,xCSTM
- Page 801 and 802:
APPEND Concatenate two data blocks
- Page 803 and 804:
FILE U=APPEND $ MATGEN ,/US/5/1/7 $
- Page 805 and 806:
ASDR Prints the extra point aerodyn
- Page 807 and 808:
Parameter: ASG Computes the aerodyn
- Page 809 and 810:
AXMPR1 Builds a list of auxiliary m
- Page 811 and 812:
BCDR Drives a boundary condition lo
- Page 813 and 814:
BDRYINFO Generates geometry and con
- Page 815 and 816:
BGP Processes geometry for boundary
- Page 817 and 818:
BNDSPC Processes constraints on sup
- Page 819 and 820:
. CASE Dynamic analysis case contro
- Page 821 and 822:
CASE Dynamic analysis case control
- Page 823 and 824:
Examples: CASE Dynamic analysis cas
- Page 825 and 826:
CEAD Complex or unsymmetric eigenva
- Page 827 and 828:
CMPZPR Generates Bulk Data entry im
- Page 829 and 830:
CURV Transforms elemental centroid
- Page 831 and 832:
CURVPLOT Converts grid point output
- Page 833 and 834:
CYCLIC1 Generates cyclic symmetry t
- Page 835 and 836:
CYCLIC2 Processes degrees-of-freedo
- Page 837 and 838:
CYCLIC3 Forms cyclic matrices CYCLI
- Page 839 and 840:
CYCLIC4 Transforms cyclic component
- Page 841 and 842:
Examples: 1. Static analysis: CYCLI
- Page 843 and 844:
DBC Database converter for model ge
- Page 845 and 846:
Remarks: 1. Data block name table:
- Page 847 and 848:
Generic Name (P1-P20) Chapter 2 Nam
- Page 849 and 850:
DBC Database converter for model ge
- Page 851 and 852:
DBDELETE Deletes NDDL data blocks a
- Page 853 and 854:
DBDICT Prints database directory ta
- Page 855 and 856:
DBDICT Prints database directory ta
- Page 857 and 858:
DBDICT Prints database directory ta
- Page 859 and 860:
Column name Table 4-1 DBDICT DATABL
- Page 861 and 862:
Column name Default column width Ta
- Page 863 and 864:
DBDICT Prints database directory ta
- Page 865 and 866:
DBDICT Prints database directory ta
- Page 867 and 868:
and looks like: COLSPACE=1 ,CDATE=1
- Page 869 and 870:
DBEQUIV Equivalences (or copies) ND
- Page 871 and 872:
DBEQUIV Equivalences (or copies) ND
- Page 873 and 874:
SubDMAP DBMGR Functions on data blo
- Page 875 and 876:
Format: Parameters: SubDMAP DBMGR F
- Page 877 and 878:
SubDMAP DBSTORE Stores data blocks
- Page 879 and 880:
DBVIEW DBVIEW Creates virtual data
- Page 881 and 882:
DCMP Matrix decomposition with exte
- Page 883 and 884:
DCMP Matrix decomposition with exte
- Page 885 and 886:
DDR2 Computes displacements due to
- Page 887 and 888:
DDR2 Computes displacements due to
- Page 889 and 890:
Parameters: DDRMM Performs matrix m
- Page 891 and 892:
0 Use standard decomposition (defau
- Page 893 and 894:
DECOMP Matrix decomposition 3. If t
- Page 895 and 896:
DELETE Deletes data blocks Format:
- Page 897 and 898:
DIAGONAL Extracts diagonal from mat
- Page 899 and 900:
DISDCMP Performs distributed decomp
- Page 901 and 902:
DISOFPM Collects and merges OFP dat
- Page 903 and 904:
DISOPT Performs appropriate discret
- Page 905 and 906:
Output Data Blocks DISOPT Performs
- Page 907 and 908:
Input Data Blocks: DISUTIL Broadcas
- Page 909 and 910:
d. Strain energy (external work) 3.
- Page 911 and 912:
Remark: DIVERG Performs aerostatic
- Page 913 and 914:
DOM10 Prints initial and final resu
- Page 915 and 916:
DOM10 Prints initial and final resu
- Page 917 and 918:
GEOM2N Updated (optimized) GEOM2 MP
- Page 919 and 920:
DOM12 Performs soft and hard conver
- Page 921 and 922:
DOM12 Performs soft and hard conver
- Page 923 and 924:
DOM6 Calculates sensitivity of all
- Page 925 and 926:
DOM9 Performs the approximate optim
- Page 927 and 928:
PROPO Matrix of final (optimized) p
- Page 929 and 930:
DOPFS Performs optimization of the
- Page 931 and 932:
PROPI* Family of matrices of initia
- Page 933 and 934:
Parameters: DOPR2 Preprocesses the
- Page 935 and 936:
DOPR3 Preprocesses DCONSTR, DRESP1,
- Page 937 and 938:
DOPR4 Creates design sensitivity ta
- Page 939 and 940:
Parameters: STPSCL Input-real-defau
- Page 941 and 942:
DOPR6 Generates tables relating to
- Page 943 and 944:
DPD DPD Creates tables from Bulk Da
- Page 945 and 946:
UNUSED12 Input-integer-default=0. U
- Page 947 and 948:
DRMH1 Converts data recovery tables
- Page 949 and 950:
DRMH3 Partitions tables for each su
- Page 951 and 952:
4. Directory tables contain the map
- Page 953 and 954:
Parameters: DSABO Incorporates elem
- Page 955 and 956:
DSAD Processes tables related to de
- Page 957 and 958:
DRDUG Matrix of adjoint loads for t
- Page 959 and 960:
DSAD Processes tables related to de
- Page 961 and 962:
XTYPE Input-integer-default=0. Type
- Page 963 and 964:
DSAE Merges tables to evaluate resp
- Page 965 and 966:
Output Data Blocks: DSAF Generates
- Page 967 and 968:
DSAH Generates data blocks required
- Page 969 and 970:
DSAJ Generates g-set size reduced b
- Page 971 and 972:
DSAL Generates design sensitivity c
- Page 973 and 974:
Remark: 1 Eigenvalue (radian/time)
- Page 975 and 976:
DSAN Generates design sensitivity p
- Page 977 and 978:
Parameters: DSAP Computes an inerti
- Page 979 and 980:
DSAR Extracts and truncates data fr
- Page 981 and 982:
DSARLP DSARLP Calculates pseudo-dis
- Page 983 and 984:
DSARME Computes RMS values Computes
- Page 985 and 986:
DSARSN Calculates delta response va
- Page 987 and 988:
DSDVRG DSDVRG Computes weighting fa
- Page 989 and 990:
DSFLTF Calculates sensitivity of ac
- Page 991 and 992:
Remarks: 1. DSMA is applicable only
- Page 993 and 994:
DSPRM Sets design sensitivity param
- Page 995 and 996:
DSTA Creates tables for Old Design
- Page 997 and 998:
DSTA Creates tables for Old Design
- Page 999 and 1000:
DSVG1 Creates pseudo loads or scala
- Page 1001 and 1002:
DSVG1P DSVG1P Creates pseudo loads
- Page 1003 and 1004:
DSVG2 Generates pseudo-load matrix
- Page 1005 and 1006:
DSVG3 DSVG3 Combines and appends so
- Page 1007 and 1008:
Remark: DSVGP4 Generates a perturbe
- Page 1009 and 1010:
Remark: DSVGP5 Performs multiplicat
- Page 1011 and 1012:
DUMMOD1 DUMMOD1 Provides dummy modu
- Page 1013 and 1014:
DUMMOD3 DUMMOD3 Provides dummy modu
- Page 1015 and 1016:
DVIEWP DVIEWP Generates view-elemen
- Page 1017 and 1018:
DYNREDU Computes approximate eigenv
- Page 1019 and 1020:
EFFMASS Computes modal effective ma
- Page 1021 and 1022:
. ELTPRT Prints element summary inf
- Page 1023 and 1024:
ELTPRT Prints element summary infor
- Page 1025 and 1026:
EMAKFR Generates stiffness for foll
- Page 1027 and 1028:
Output Data Blocks: EMG Computes el
- Page 1029 and 1030:
EMG Computes elemental matrices ALT
- Page 1031 and 1032:
EQUIVX Data block name equivalence
- Page 1033 and 1034:
FA1 Prepares the modal matrices for
- Page 1035 and 1036:
FA2 Collects aeroelastic flutter da
- Page 1037 and 1038:
FBS Matrix forward/backward substit
- Page 1039 and 1040:
FILE Data block declaration Declare
- Page 1041 and 1042:
FORTIO Opens or closes a FORTRAN fi
- Page 1043 and 1044:
FRLG Generates frequency-dependent
- Page 1045 and 1046:
FRLGEN Creates frequency response l
- Page 1047 and 1048:
FRRD1 Solves for the steady-state f
- Page 1049 and 1050:
FRRD1 Solves for the steady-state f
- Page 1051 and 1052:
Output Data Blocks: Parameters: FRR
- Page 1053 and 1054:
GETCOL Reads STATSUB Case Control c
- Page 1055 and 1056:
Generates the aerodynamic spline tr
- Page 1057 and 1058:
GKAM Assembles modal mass, damping
- Page 1059 and 1060:
GP0 Modifies tables to include p-el
- Page 1061 and 1062:
GP1 Performs basic geometry process
- Page 1063 and 1064:
GP2 Processes element connectivity
- Page 1065 and 1066:
3. ETT may be purged if there are n
- Page 1067 and 1068:
Output Data Blocks: RMG Multipoint
- Page 1069 and 1070:
GP5 GP5 Creates table of static loa
- Page 1071 and 1072:
Computes grid point forces and elem
- Page 1073 and 1074:
GPFDR Computes grid point forces an
- Page 1075 and 1076:
GPSP Performs auto-SPC operation Pe
- Page 1077 and 1078:
Remarks: 1. YS0 and YS may be purge
- Page 1079 and 1080:
GPSTR2 Computes grid point stresses
- Page 1081 and 1082:
GPWG Computes center of mass of str
- Page 1083 and 1084:
GUST Computes loads for aerodynamic
- Page 1085 and 1086:
IFP Reads Bulk Data Section Reads i
- Page 1087 and 1088:
Example: IFP Reads Bulk Data Sectio
- Page 1089 and 1090:
IFP1 Reads Case Control Section Rea
- Page 1091 and 1092:
IFP3 Modifies Bulk Data entry recor
- Page 1093 and 1094:
Processes hydroelastic-related Bulk
- Page 1095 and 1096:
Process acoustic cavity-related Bul
- Page 1097 and 1098:
IFP6 Creates PSHELL and MAT2 Bulk D
- Page 1099 and 1100:
IFP7 Creates PBEAM Bulk Data entry
- Page 1101 and 1102:
IFP9 Creates PBAR and PBEAM Bulk Da
- Page 1103 and 1104:
IFT Performs an inverse Fourier tra
- Page 1105 and 1106:
ITAPE Value +n No 0 No -1 Yes Tape
- Page 1107 and 1108:
INPUTT4 Inputs a matrix from a FORT
- Page 1109 and 1110:
INTERR Generates modal components o
- Page 1111 and 1112:
ISHELL Invokes an external program
- Page 1113 and 1114:
Parameters: LAMX Eigenvalue Table E
- Page 1115 and 1116:
LAMX Eigenvalue Table Editor Exampl
- Page 1117 and 1118:
LANCZOS Performs real eigenvalue an
- Page 1119 and 1120:
3 Detailed output on cost and conve
- Page 1121 and 1122:
LMATPRT Prints combined design sens
- Page 1123 and 1124:
1115 MAKAEFA Extracts data specifie
- Page 1125 and 1126:
1117 MAKAEFS Generates an index and
- Page 1127 and 1128:
1119 MAKCOMP Extracts components fr
- Page 1129 and 1130:
1121 MAKENEW Converts tables from p
- Page 1131 and 1132:
1123 MAKEOLD Converts tables from V
- Page 1133 and 1134:
1125 MAKETR Generates transformatio
- Page 1135 and 1136:
1127 MATGEN Matrix generator MATGEN
- Page 1137 and 1138:
1129 MATGEN Matrix generator Input
- Page 1139 and 1140:
1131 MATGEN Matrix generator MATGEN
- Page 1141 and 1142:
1133 MATGEN Matrix generator Option
- Page 1143 and 1144:
1135 MATGEN Matrix generator The eq
- Page 1145 and 1146:
1137 MATGEN Matrix generator Option
- Page 1147 and 1148:
1139 MATGPR Degree-of-freedom matri
- Page 1149 and 1150:
1141 MATGPR Degree-of-freedom matri
- Page 1151 and 1152:
1143 MATGPR Degree-of-freedom matri
- Page 1153 and 1154:
1145 MATMOD Matrix modification MAT
- Page 1155 and 1156:
1147 MATMOD Matrix modification Out
- Page 1157 and 1158:
1149 MATMOD Matrix modification Opt
- Page 1159 and 1160:
1151 MATMOD Matrix modification Inp
- Page 1161 and 1162:
1153 MATMOD Matrix modification For
- Page 1163 and 1164:
1155 MATMOD Matrix modification Rem
- Page 1165 and 1166:
1157 MATMOD Matrix modification Opt
- Page 1167 and 1168:
1159 MATMOD Matrix modification Par
- Page 1169 and 1170:
1161 MATMOD Matrix modification Inp
- Page 1171 and 1172:
1163 MATMOD Matrix modification Inp
- Page 1173 and 1174:
1165 MATMOD Matrix modification 2.
- Page 1175 and 1176:
1167 MATMOD Matrix modification MAT
- Page 1177 and 1178:
1169 MATMOD Matrix modification Par
- Page 1179 and 1180:
1171 MATMOD Matrix modification Opt
- Page 1181 and 1182:
1173 MATMOD Matrix modification P1=
- Page 1183 and 1184:
1175 MATMOD Matrix modification Rem
- Page 1185 and 1186:
1177 MATMOD Matrix modification Par
- Page 1187 and 1188:
1179 MATPCH Punches contents of Mat
- Page 1189 and 1190:
1181 MATPRT Matrix printer MATPRT M
- Page 1191 and 1192:
1183 MATREDU Reduces square matrix
- Page 1193 and 1194:
1185 MCE2 Performs multipoint const
- Page 1195 and 1196:
1187 MDCASE Partitions the Case Con
- Page 1197 and 1198:
1189 MDCASE Partitions the Case Con
- Page 1199 and 1200:
1191 MERGE Matrix merge MERGE Matri
- Page 1201 and 1202:
1193 MERGE Matrix merge Case 4: Nei
- Page 1203 and 1204:
1195 MERGE Matrix merge then the re
- Page 1205 and 1206:
1197 MESSAGE Prints messages MESSAG
- Page 1207 and 1208:
1199 MKCNTRL Creates virtual fluid
- Page 1209 and 1210:
1201 MKSPLINE Generates splines to
- Page 1211 and 1212:
1203 MODACC OFREQ and OTIME command
- Page 1213 and 1214:
1205 MODEPF OFREQ and OTIME command
- Page 1215 and 1216:
1207 MODEPOUT OFREQ and OTIME comma
- Page 1217 and 1218:
1209 MODEPT Updates PACABS and PACA
- Page 1219 and 1220:
1211 MODGM2 Create table entries fo
- Page 1221 and 1222:
1213 MODGM4 Reads SPCs and SPCDs an
- Page 1223 and 1224:
1215 MODTRK Reorders eigenvalues an
- Page 1225 and 1226:
1217 MODTRL Modify trailer Examples
- Page 1227 and 1228:
1219 MODUSET Modifies the degree-of
- Page 1229 and 1230:
1221 MPP Prints monitor point resul
- Page 1231 and 1232:
1223 MPYAD Matrix multiply and add
- Page 1233 and 1234:
1225 MPYAD Matrix multiply and add
- Page 1235 and 1236:
1227 MPYAD Matrix multiply and add
- Page 1237 and 1238:
1229 MRGCOMP Merges two existing ae
- Page 1239 and 1240:
1231 MSGHAN Passes message number f
- Page 1241 and 1242:
1233 MTRXIN Converts DMIG entries t
- Page 1243 and 1244:
1235 MTRXIN Converts DMIG entries t
- Page 1245 and 1246:
1237 MTRXIN Converts DMIG entries t
- Page 1247 and 1248:
1239 NASSETS Combines all element s
- Page 1249 and 1250:
1241 NLCOMB Consolidates tables rel
- Page 1251 and 1252:
1243 NLITER Computes nonlinear anal
- Page 1253 and 1254:
1245 NLITER Computes nonlinear anal
- Page 1255 and 1256:
1247 NLITER Computes nonlinear anal
- Page 1257 and 1258:
1249 NLTRD Computes transient nonli
- Page 1259 and 1260:
1251 NLTRD Computes transient nonli
- Page 1261 and 1262:
1253 NLTRD2 Computes transient nonl
- Page 1263 and 1264:
1255 NLTRD2 Computes transient nonl
- Page 1265 and 1266:
1257 NORM Normalize a matrix NORM N
- Page 1267 and 1268:
1259 NXNADAMS Creates an ADAMS MNF
- Page 1269 and 1270:
1261 OFP Output file processor OFP
- Page 1271 and 1272:
1263 OPTGP0 p-element analysis prep
- Page 1273 and 1274:
1265 ORTHOG Generates orthonormal s
- Page 1275 and 1276:
1267 OUTPRT Constructs sparse load
- Page 1277 and 1278:
1269 OUTPUT2 Output a table or matr
- Page 1279 and 1280:
1271 OUTPUT2 Output a table or matr
- Page 1281 and 1282:
1273 OUTPUT2 Output a table or matr
- Page 1283 and 1284:
1275 OUTPUT2 Output a table or matr
- Page 1285 and 1286:
1277 OUTPUT2 Output a table or matr
- Page 1287 and 1288:
1279 OUTPUT2 Output a table or matr
- Page 1289 and 1290:
1281 OUTPUT4 Output matrices onto a
- Page 1291 and 1292:
1283 OUTPUT4 Output matrices onto a
- Page 1293 and 1294:
1285 OUTPUT4 Output matrices onto a
- Page 1295 and 1296:
1287 PARAML Sets parameters from a
- Page 1297 and 1298:
1289 PARAML Sets parameters from a
- Page 1299 and 1300:
1291 PARAML Sets parameters from a
- Page 1301 and 1302:
1293 PARAML Sets parameters from a
- Page 1303 and 1304:
1295 PARAML Sets parameters from a
- Page 1305 and 1306:
1297 PARAML Sets parameters from a
- Page 1307 and 1308:
1299 PARTN Matrix partition PARTN M
- Page 1309 and 1310:
1301 PARTN Matrix partition 4. If {
- Page 1311 and 1312:
1303 PARTN Matrix partition 1 2 3 5
- Page 1313 and 1314:
1305 PCOPY Tests parallel copy PCOP
- Page 1315 and 1316:
1307 PLOT Creates a table of plot i
- Page 1317 and 1318:
1309 PLTSET Generates element sets
- Page 1319 and 1320:
1311 PRESOL Prepares special tables
- Page 1321 and 1322:
1313 PRTMSG Prints plotting informa
- Page 1323 and 1324:
1315 PRTPARM Parameter and DMAP mes
- Page 1325 and 1326:
1317 PVT Sets parameter values PVT
- Page 1327 and 1328:
1319 RANDOM Computes functions from
- Page 1329 and 1330:
1321 RANDOM Computes functions from
- Page 1331 and 1332:
1323 RBMG3 Computes rigid body info
- Page 1333 and 1334:
1325 READ Extracts real symmetric s
- Page 1335 and 1336:
1327 READ Extracts real symmetric s
- Page 1337 and 1338:
1329 READ Extracts real symmetric s
- Page 1339 and 1340:
1331 READ Extracts real symmetric s
- Page 1341 and 1342:
1333 RESTART Data block comparison
- Page 1343 and 1344:
1335 RMAXMIN Searches result tables
- Page 1345 and 1346:
1337 RMG2 Processes radiation excha
- Page 1347 and 1348:
1339 RSPEC Converts transient respo
- Page 1349 and 1350:
1341 SCALAR Matrix element extracto
- Page 1351 and 1352:
1343 SDP Calculates nondimensional
- Page 1353 and 1354:
1345 SDR1 Computes solution and sin
- Page 1355 and 1356:
1347 SDR2 Creates output tables EDT
- Page 1357 and 1358:
1349 SDR2 Creates output tables MET
- Page 1359 and 1360:
1351 SDR3 Converts tables in SORT1
- Page 1361 and 1362:
1353 SDRCOMP Calculates laminar str
- Page 1363 and 1364:
1355 SDRHT Combines heat flow for C
- Page 1365 and 1366:
1357 SDRNL Performs stress data rec
- Page 1367 and 1368:
1359 SDRP Computes data for p-eleme
- Page 1369 and 1370:
1361 SDRX Modifies CBAR, CBEAM and
- Page 1371 and 1372:
1363 SDRXD Modifies CBAR, CBEAM and
- Page 1373 and 1374:
1365 SDSA Partitions design model t
- Page 1375 and 1376:
1367 SDSB Generates superelement pr
- Page 1377 and 1378:
1369 SECONVRT Modifies Bulk Data en
- Page 1379 and 1380:
1371 SEDR Partitions tables for sup
- Page 1381 and 1382:
1373 SEDRDR Drives superelement dat
- Page 1383 and 1384:
1375 SELA Assembles static load mat
- Page 1385 and 1386:
1377 SEMA Assembles square symmetri
- Page 1387 and 1388:
1379 SEP1 Constructs superelement m
- Page 1389 and 1390:
1381 SEP1X Constructs superelement
- Page 1391 and 1392:
1383 SEP1X Constructs superelement
- Page 1393 and 1394:
1385 SEP2 Partitions tables for eac
- Page 1395 and 1396:
1387 SEP2DR Drives superelement gen
- Page 1397 and 1398:
1389 SEP2DR Drives superelement gen
- Page 1399 and 1400:
1391 SEP2X Partitions tables for ea
- Page 1401 and 1402:
1393 SEP3 Examines Case Control and
- Page 1403 and 1404:
1395 SEP4 Examines table and data b
- Page 1405 and 1406:
1397 SEPLOT Assembles plot displace
- Page 1407 and 1408:
1399 SEPR1 Builds a list of partiti
- Page 1409 and 1410:
1401 SEQP Resequencing processor Ou
- Page 1411 and 1412:
1403 SEQP Resequencing processor NT
- Page 1413 and 1414:
1405 SEQP Resequencing processor 8.
- Page 1415 and 1416:
1407 SMA3 Assembles global stiffnes
- Page 1417 and 1418:
1409 SMPYAD Matrix series multiply
- Page 1419 and 1420:
1411 SOLVE Linear system solver Rem
- Page 1421 and 1422:
1413 SOLVIT Iterative solver CASECC
- Page 1423 and 1424:
1415 SOLVIT Iterative solver ADPTIN
- Page 1425 and 1426:
1417 SOLVIT Iterative solver Format
- Page 1427 and 1428:
1419 SSG1 Computes static load matr
- Page 1429 and 1430:
1421 SSG2 Reduces static load and e
- Page 1431 and 1432:
1423 SSG3 Computes static solutions
- Page 1433 and 1434:
1425 SSG4 Updates static loads with
- Page 1435 and 1436:
1427 STATICS Performs static analys
- Page 1437 and 1438:
1429 STDCON Calculate stress discon
- Page 1439 and 1440:
1431 STRSORT Filters and sorts elem
- Page 1441 and 1442:
1433 TA1 Combines element data into
- Page 1443 and 1444:
1435 TABEDIT Performs editing opera
- Page 1445 and 1446:
1437 TABEDIT Performs editing opera
- Page 1447 and 1448:
1439 TABEDIT Performs editing opera
- Page 1449 and 1450:
1441 TABPRT Formatted table printer
- Page 1451 and 1452:
1443 TABPRT Formatted table printer
- Page 1453 and 1454:
1445 TABPRT Formatted table printer
- Page 1455 and 1456:
1447 TABPRT Formatted table printer
- Page 1457 and 1458:
1449 TABPRT Formatted table printer
- Page 1459 and 1460:
1451 TABPT Table printer TABPT Tabl
- Page 1461 and 1462:
1453 TAHT Adds records to element s
- Page 1463 and 1464:
1455 TASNP1 Computes the shell norm
- Page 1465 and 1466:
1457 TASNP2 Computes grid point she
- Page 1467 and 1468:
1459 TIMETEST Provide timing data I
- Page 1469 and 1470:
1461 TIMETEST Provide timing data I
- Page 1471 and 1472:
1463 TIMETEST Provide timing data I
- Page 1473 and 1474:
1465 TIMETEST Provide timing data C
- Page 1475 and 1476:
1467 TOLAPP Appends nonlinear data
- Page 1477 and 1478:
1469 TRD1 Solves for modal/direct,
- Page 1479 and 1480:
1471 TRD2 Solves for modal/direct,
- Page 1481 and 1482:
1473 TRLG Generates applied loads i
- Page 1483 and 1484:
1475 TRNSP Matrix transpose TRNSP M
- Page 1485 and 1486:
1477 TYPE Declares NDDL data blocks
- Page 1487 and 1488:
1479 TYPE Declares NDDL data blocks
- Page 1489 and 1490:
1481 UEIGL Solves both linear and q
- Page 1491 and 1492:
1483 UGVADD Adds two displacement v
- Page 1493 and 1494:
1485 UMERGE Merges two matrices bas
- Page 1495 and 1496:
1487 UMERGE1 Merges two matrices ba
- Page 1497 and 1498:
1489 UMERGE1 Merges two matrices ba
- Page 1499 and 1500:
1491 UPARTN Partitions a matrix bas
- Page 1501 and 1502:
1493 UPARTN Partitions a matrix bas
- Page 1503 and 1504:
1495 UREDUC Reduces rectangular mat
- Page 1505 and 1506:
1497 VDR Creates tables based on so
- Page 1507 and 1508:
1499 VEC Creates partitioning vecto
- Page 1509 and 1510:
1501 VECPLOT Transforms, searches,
- Page 1511 and 1512:
1503 VECPLOT Transforms, searches,
- Page 1513 and 1514:
1505 VECPLOT Transforms, searches,
- Page 1515 and 1516:
1507 VIEW Computes heat transfer ra
- Page 1517 and 1518:
1509 VIEWP Generates geometry table
- Page 1519 and 1520:
XSORT Reads and sorts Bulk Data sec
- Page 1521 and 1522:
XYPLOT Writes plot information to p
- Page 1523 and 1524:
XYTRAN Creates table of plot instru
- Page 1525 and 1526:
X Nastran MAP rogrammer’s uide I