Attention! Your ePaper is waiting for publication!
By publishing your document, the content will be optimally indexed by Google via AI and sorted into the right category for over 500 million ePaper readers on YUMPU.
This will ensure high visibility and many readers!

Your ePaper is now published and live on YUMPU!
You can find your publication here:
Share your interactive ePaper on all platforms and on your website with our embed function

NX Nastran DMAP Programmer's Guide - Kxcad.net
NX Nastran DMAP Programmer's Guide - Kxcad.net
NX Nastran DMAP Programmer's Guide - Kxcad.net
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
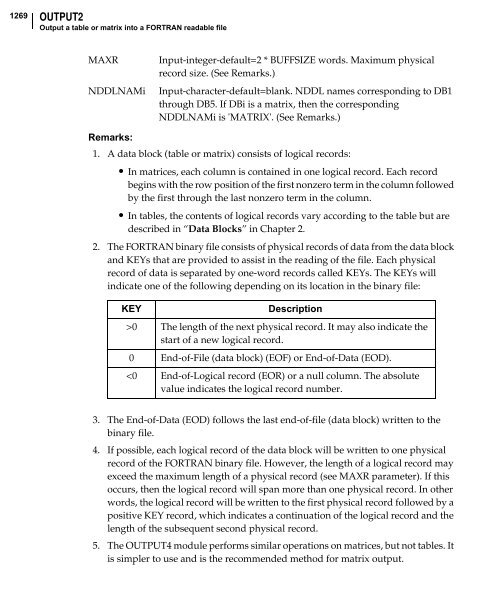
1269<br />
OUTPUT2<br />
Output a table or matrix into a FORTRAN readable file<br />
MAXR Input-integer-default=2 * BUFFSIZE words. Maximum physical<br />
record size. (See Remarks.)<br />
NDDLNAMi Input-character-default=blank. NDDL names corresponding to DB1<br />
through DB5. If DBi is a matrix, then the corresponding<br />
NDDLNAMi is 'MATRIX'. (See Remarks.)<br />
Remarks:<br />
1. A data block (table or matrix) consists of logical records:<br />
• In matrices, each column is contained in one logical record. Each record<br />
begins with the row position of the first nonzero term in the column followed<br />
by the first through the last nonzero term in the column.<br />
• In tables, the contents of logical records vary according to the table but are<br />
described in “Data Blocks” in Chapter 2.<br />
2. The FORTRAN binary file consists of physical records of data from the data block<br />
and KEYs that are provided to assist in the reading of the file. Each physical<br />
record of data is separated by one-word records called KEYs. The KEYs will<br />
indicate one of the following depending on its location in the binary file:<br />
KEY Description<br />
>0 The length of the next physical record. It may also indicate the<br />
start of a new logical record.<br />
0 End-of-File (data block) (EOF) or End-of-Data (EOD).<br />
OUTPUT2 Output a table or matrix into a FORTRAN readable file OUTPUT2 Output a table or matrix into a FORTRAN readable file Writes a table or matrix data block(s) onto a binary or "compressed ASCII" (or “neutral”) file for user postprocessing or for subsequent input (via INPUTT2) into another <strong>NX</strong> <strong>Nastran</strong> run. Format: OUTPUT2 DB1,DB2,DB3,DB4,DB5//ITAPE/IUNIT/LABL/MAXR/ NDDLNAM1/NDDLNAM2/NDDLNAM3/NDDLNAM4/ NDDLNAM5 $ Input Data Blocks: DBi Any data block (table or matrix) name to be output. DBi cannot be a factor matrix (forms 4, 5, 10, 11, 13, and 15). Any or all of the input data blocks may be purged. Parameters: ITAPE Input-integer-default=0. ITAPE is used to select the file positioning option as follows: +n Skip forward n data blocks before writing (only used if file has no label). 0 Data blocks are written starting at the current position. If this is the first use, no label is written. -1 Rewind IUNIT before writing and label file. -3 Rewind IUNIT, print data block names and then write after the last data block on IUNIT (file must have a label). -9 Write a final EOF on IUNIT (must be used before -3 option and as last I/O use of unit) then rewind IUNIT. IUNIT Input-integer-no default. IUNIT is the FORTRAN unit number on which the data blocks are to be written. IUNIT=0 is not recommended. See Remark 7. LABL Input-character-default = 'XXXXXXXX'. LABL is used for file identification. The label is written only if ITAPE=-1 and is checked only if ITAPE=-3. 126
1269 OUTPUT2 Output a table or matrix into a FORTRAN readable file MAXR Input-integer-default=2 * BUFFSIZE words. Maximum physical record size. (See Remarks.) NDDLNAMi Input-character-default=blank. NDDL names corresponding to DB1 through DB5. If DBi is a matrix, then the corresponding NDDLNAMi is 'MATRIX'. (See Remarks.) Remarks: 1. A data block (table or matrix) consists of logical records: • In matrices, each column is contained in one logical record. Each record begins with the row position of the first nonzero term in the column followed by the first through the last nonzero term in the column. • In tables, the contents of logical records vary according to the table but are described in “Data Blocks” in Chapter 2. 2. The FORTRAN binary file consists of physical records of data from the data block and KEYs that are provided to assist in the reading of the file. Each physical record of data is separated by one-word records called KEYs. The KEYs will indicate one of the following depending on its location in the binary file: KEY Description >0 The length of the next physical record. It may also indicate the start of a new logical record. 0 End-of-File (data block) (EOF) or End-of-Data (EOD).
- Page 1 and 2:
NX Nastran DMAP Programmer’s Guid
- Page 3 and 4:
1 Direct Matrix Abstraction C O N T
- Page 5 and 6:
❑ Miscellaneous Modules and State
- Page 7 and 8:
- MODEPT, 1209 - MODGDN, 1210 - MOD
- Page 9 and 10:
CHAPTER 1 NX Nastran DMAP Programme
- Page 11 and 12:
1.2 The NX Nastran DMAP Language Th
- Page 13 and 14:
Constant Parameters Parameters A co
- Page 15 and 16:
Parameters 4. Value from the NAME=v
- Page 17 and 18:
Parameters For example, the followi
- Page 19 and 20:
Relational Operators Parameters Rel
- Page 21 and 22:
1.4 Data Blocks Data Blocks A data
- Page 23 and 24:
Form is defined as one of the follo
- Page 25 and 26:
1.5 Instructions Instructions A DMA
- Page 27 and 28:
MPYAD A , B , / D $ Instructions Ac
- Page 29 and 30:
Instructions Type conversions can b
- Page 31 and 32:
Format Definition Result ATAN2( x1,
- Page 33 and 34:
Format Definition Result DIM( x1, x
- Page 35 and 36:
Format Definition Result LLT( a1, a
- Page 37 and 38:
Format Definition Result NUMGT(x1,x
- Page 39 and 40:
Format Definition Result Instructio
- Page 41 and 42:
Control Statement The NX Nastran DM
- Page 43 and 44:
DO WHILE(expression) $ . . . ENDDO
- Page 45 and 46:
SUBDMAP TEST X,Y,Z/L,M,N/A1/A2/A3 $
- Page 47 and 48:
1.6 “Output from a Previous Modul
- Page 49 and 50:
1.8 Preface Modules and SOLution 10
- Page 51 and 52:
SubDMAPs DBMGR, DBSTORE, and DBFETC
- Page 53 and 54:
1.11 WHERE and CONVERT Clauses WHER
- Page 55 and 56:
Examples of the CONVERT clause are:
- Page 57 and 58:
What's New in DMAP? Option 39: Remo
- Page 59 and 60:
CHAPTER 2 NX Nastran DMAP Programme
- Page 61 and 62:
2.2 Matrix Data Blocks The rows and
- Page 63 and 64:
2.3 Table Data Blocks This section
- Page 65 and 66:
OFP Tables The header record of all
- Page 67 and 68:
Examples: Therefore, MOD(approach_c
- Page 69 and 70:
Type Chapter 2 Name 23 OELOP1 Summa
- Page 71 and 72:
Stress_code In the OES data block d
- Page 73 and 74:
Type Name Description 23 DAMP4 Scal
- Page 75 and 76:
Type Name Description 76 HEXPR Acou
- Page 77 and 78:
Type Name Description 129 Unused (P
- Page 79 and 80:
Type Name Description 183 Unused (P
- Page 81 and 82:
Type Name Description 223 QUADXFD H
- Page 83 and 84:
2.5 Data Block Descriptions BGPDT B
- Page 85 and 86:
BGPDT68 Basic grid point definition
- Page 87 and 88:
Word Name Type Description CASECC C
- Page 89 and 90:
Word Name Type Description CASECC C
- Page 91 and 92:
Word Name Type Description CASECC C
- Page 93 and 94:
Word Name Type Description CASECC C
- Page 95 and 96:
Word Name Type Description CASECC C
- Page 97 and 98:
Word Name Type Description 318 UNDE
- Page 99 and 100:
Word Name Type Description CASECC C
- Page 101 and 102:
Word Name Type Description CASECC C
- Page 103 and 104:
• 4 = punch and their sums; e.g.,
- Page 105 and 106:
CLAMA Complex eigenvalue summary ta
- Page 107 and 108:
CONTAB Design constraint table CONT
- Page 109 and 110:
CONTACT Table of Bulk Data entry re
- Page 111 and 112:
CSTM Coordinate system transformati
- Page 113 and 114:
CSTM68 Coordinate system transforma
- Page 115 and 116:
CSTM68 Coordinate system transforma
- Page 117 and 118:
CSTM68 Coordinate system transforma
- Page 119 and 120:
Record 2 - TRAILER Notes: 1. Coordi
- Page 121 and 122:
Record 5 - INITV DBCOPT Design opti
- Page 123 and 124:
DESTAB Design variable attributes R
- Page 125 and 126:
Word Name Type Description 5 F0 RS
- Page 127 and 128:
Record 12 - TABLES1(3105,31,97) Wor
- Page 129 and 130:
DSCMCOL Design sensitivity paramete
- Page 131 and 132:
Word Name Type Description 5 COMP I
- Page 133 and 134:
Word Name Type Description 5 COMP I
- Page 135 and 136:
Word Name Type Description 6 UNDEF(
- Page 137 and 138:
DVPTAB Designed property table Reco
- Page 139 and 140:
DYNAMIC Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 141 and 142:
Record 7 - EIGB(107,1,86) DYNAMIC T
- Page 143 and 144:
DYNAMIC Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 145 and 146:
DYNAMIC Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 147 and 148:
DYNAMIC Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 149 and 150:
DYNAMIC Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 151 and 152:
DYNAMIC Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 153 and 154:
EGPSF Table of element to grid poin
- Page 155 and 156:
3. Possible values for items in REC
- Page 157 and 158:
EGPSTR Element grid point stress ta
- Page 159 and 160:
Word Name Type Description End TYPE
- Page 161 and 162:
ELDCT Element stress discontinuity
- Page 163 and 164:
EPT Element property table Record 0
- Page 165 and 166:
Word Name Type Description Record 5
- Page 167 and 168:
Word Name Type Description EPT Elem
- Page 169 and 170:
Word Name Type Description EPT Elem
- Page 171 and 172:
Word Name Type Description EPT Elem
- Page 173 and 174:
Word Name Type Description Record 7
- Page 175 and 176:
Word Name Type Description Record 8
- Page 177 and 178:
Word Name Type Description 21 K1 RS
- Page 179 and 180:
Word Name Type Description EPT Elem
- Page 181 and 182:
Word Name Type Description Record 1
- Page 183 and 184:
Record 18 - PDAMPT(1202,12,33) Word
- Page 185 and 186:
Record 29 - PELAS(302,3,46) Word Na
- Page 187 and 188:
Record 35 - PLPLANE(4606,46,375) Wo
- Page 189 and 190:
Record 41 - PSOLID(2402,24,281) Wor
- Page 191 and 192:
Record 46 - PVAL(10201,102,400) Wor
- Page 193 and 194:
Word Name Type Description Record 5
- Page 195 and 196:
EQEXIN Equivalence between external
- Page 197 and 198:
ERROR Table of p-element error tole
- Page 199 and 200:
GEOM1 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 201 and 202:
Record 5 - CORD2R(2101,21,8) GEOM1
- Page 203 and 204:
Record 10 - FEEDGE(6101,61,388) GEO
- Page 205 and 206:
Record 15 - GMCORD(6401,64,402) GEO
- Page 207 and 208:
Record 20 - SEELT(7902,79,302) GEOM
- Page 209 and 210:
Record 25 - SENQSET(1327,13,464) GE
- Page 211 and 212:
Record 32 - CSUPUP(5801,58,324) Thi
- Page 213 and 214:
GEOM168 Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 215 and 216:
GEOM168 Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 217 and 218:
GEOM168 Table of Bulk Data entry im
- Page 219 and 220:
Record 16 - GRID(4501,45,1) GEOM168
- Page 221 and 222:
Record 22 - SELABEL(1027,10,459) GE
- Page 223 and 224:
Record 28 - SESET(5601,56,296) GEOM
- Page 225 and 226:
Record 33 - TRAILER GEOM168 Table o
- Page 227 and 228:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 229 and 230:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 231 and 232:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 233 and 234:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 235 and 236:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 237 and 238:
Record 19 - CDUM2(6208,62,108) GEOM
- Page 239 and 240:
Record 29 - CELAS3(801,8,75) GEOM2
- Page 241 and 242:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 243 and 244:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 245 and 246:
Record 43 - CHEXAFD(14000,140,9990)
- Page 247 and 248:
Record 51 - CMFREE(2508,25,0) GEOM2
- Page 249 and 250:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 251 and 252:
Record 65 - CQUAD4(2958,51,177) Rec
- Page 253 and 254:
Record 72 - CROD(3001,30,48) GEOM2
- Page 255 and 256:
Record 81 - CTRIA3(5959,59,282) GEO
- Page 257 and 258:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 259 and 260:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 261 and 262:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 263 and 264:
GEOM2 Table of Bulk Data entries re
- Page 265 and 266:
Record104 - SINT(7801,78,8883) GEOM
- Page 267 and 268:
Record110 - TRAILER Notes: 1. Recor
- Page 269 and 270:
Record 4 - GMLOAD(6309,63,391) GEOM
- Page 271 and 272:
GEOM3 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 273 and 274:
Record 13 - MOMENT2(4701,47,23) GEO
- Page 275 and 276:
Record 20 - PLOADX1(7309,73,351) GE
- Page 277 and 278:
Record 27 - QVOL(2309,23,416) GEOM3
- Page 279 and 280:
Record 35 - TEMPP1(8109,81,201) GEO
- Page 281 and 282:
GEOM3 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 283 and 284:
GEOM4 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 285 and 286:
GEOM4 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 287 and 288:
GEOM4 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 289 and 290:
GEOM4 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 291 and 292:
Record 19 - OMIT1(4951,63,92) GEOM4
- Page 293 and 294:
Record 24 - RBE2(6901,69,295) GEOM4
- Page 295 and 296:
GEOM4 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 297 and 298:
Record 31 - RWELD(11901,119,561) GE
- Page 299 and 300:
Record 37 - SEQSET1(1210,12,322) GE
- Page 301 and 302:
GEOM4 Table of Bulk Data entry imag
- Page 303 and 304:
Record 49 - SPCEB(9101,91,9025) GEO
- Page 305 and 306:
Record 56 - SUPORT(5601,56,14) GEOM
- Page 307 and 308:
GPDT68 Grid point definition table
- Page 309 and 310:
HIS Table of design iteration histo
- Page 311 and 312:
Record 2 - TRAILER KDICT Element st
- Page 313 and 314:
Record 3 - TRAILER LAMA Normal mode
- Page 315 and 316:
MPT Table of Bulk Data entry images
- Page 317 and 318:
MPT Table of Bulk Data entry images
- Page 319 and 320:
MPT Table of Bulk Data entry images
- Page 321 and 322:
MPT Table of Bulk Data entry images
- Page 323 and 324:
Record 13 - MATHP(4506,45,374) MPT
- Page 325 and 326:
MPT Table of Bulk Data entry images
- Page 327 and 328:
MPT Table of Bulk Data entry images
- Page 329 and 330:
Record 24 - RADMT(8902,89,423) MPT
- Page 331 and 332:
MPT Table of Bulk Data entry images
- Page 333 and 334:
OBC Output contact pressure and tra
- Page 335 and 336:
OBJTAB Design objective table OBJTA
- Page 337 and 338:
OEE Output element energy (strain,
- Page 339 and 340:
OEE Output element energy (strain,
- Page 341 and 342:
OEF Table of element forces OEF Tab
- Page 343 and 344:
Word Name Type Description 6 UNDEF(
- Page 345 and 346:
Word Name Type Description 5 FREECO
- Page 347 and 348:
Word Name Type Description 12 YFLUX
- Page 349 and 350:
Word Name Type Description OEF Tabl
- Page 351 and 352:
Word Name Type Description 8 F34R R
- Page 353 and 354:
Word Name Type Description OEF Tabl
- Page 355 and 356:
Word Name Type Description TCODE,7
- Page 357 and 358:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 359 and 360:
Word Name Type Description TCODE,7
- Page 361 and 362:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 363 and 364:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 365 and 366:
Word Name Type Description 2 AXR RS
- Page 367 and 368:
Word Name Type Description OEF Tabl
- Page 369 and 370:
Word Name Type Description TCODE,7
- Page 371 and 372:
Word Name Type Description 10 PRESS
- Page 373 and 374:
Word Name Type Description 7 BMX RS
- Page 375 and 376:
Word Name Type Description 10 AZI R
- Page 377 and 378:
Word Name Type Description 7 AF RS
- Page 379 and 380:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 381 and 382:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 383 and 384:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 385 and 386:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 387 and 388:
Word Name Type Description 23 UNDEF
- Page 389 and 390:
Word Name Type Description OEF Tabl
- Page 391 and 392:
Word Name Type Description 9 TRQ RS
- Page 393 and 394:
Word Name Type Description 15 TS2I
- Page 395 and 396:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 397 and 398:
Word Name Type Description Record 3
- Page 399 and 400:
2 NX Nastran DMAP Modules and Data
- Page 401 and 402:
OES Table of element stresses or st
- Page 403 and 404:
Word Name Type Description 3 NX1 RS
- Page 405 and 406:
Word Name Type Description TCODE,7
- Page 407 and 408:
Word Name Type Description TCODE,7
- Page 409 and 410:
Word Name Type Description 3 AEI RS
- Page 411 and 412:
Word Name Type Description End TCOD
- Page 413 and 414:
Word Name Type Description 2 UNDEF
- Page 415 and 416:
Word Name Type Description 3 SX1R R
- Page 417 and 418:
Word Name Type Description 2 SX1A R
- Page 419 and 420:
Word Name Type Description TCODE,7
- Page 421 and 422:
Word Name Type Description 16 EP2 R
- Page 423 and 424:
Word Name Type Description 25 P3Z R
- Page 425 and 426:
Word Name Type Description 2 RA RS
- Page 427 and 428:
Word Name Type Description 11 TE4 R
- Page 429 and 430:
Word Name Type Description 4 TE1R R
- Page 431 and 432:
Word Name Type Description 2 SR(9)
- Page 433 and 434:
Word Name Type Description 12 FD2 R
- Page 435 and 436:
Word Name Type Description 6 SX1I R
- Page 437 and 438:
Word Name Type Description 8 EZR RS
- Page 439 and 440:
Word Name Type Description 16 TYZI
- Page 441 and 442:
Word Name Type Description 2 CID I
- Page 443 and 444:
Word Name Type Description 8 EMAX R
- Page 445 and 446:
Word Name Type Description 8 A1 RS
- Page 447 and 448:
Word Name Type Description 2 TERM C
- Page 449 and 450:
Word Name Type Description 12 EY2R
- Page 451 and 452:
Word Name Type Description 14 EY2 R
- Page 453 and 454:
Word Name Type Description 8 SY1I R
- Page 455 and 456:
Word Name Type Description 7 EY1R R
- Page 457 and 458:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 459 and 460:
Word Name Type Description 2 FD1 RS
- Page 461 and 462:
Word Name Type Description 11 EY1 R
- Page 463 and 464:
Word Name Type Description 13 EX RS
- Page 465 and 466:
Word Name Type Description 49 TEFB
- Page 467 and 468:
Word Name Type Description 5 ET1 RS
- Page 469 and 470:
Word Name Type Description 9 EMIN R
- Page 471 and 472:
Word Name Type Description 4 ABSORB
- Page 473 and 474:
Word Name Type Description ELTYPE =
- Page 475 and 476:
Word Name Type Description 3 GRID I
- Page 477 and 478:
Word Name Type Description OES Tabl
- Page 479 and 480:
Word Name Type Description 11 YNORM
- Page 481 and 482:
Word Name Type Description 8 TYZ RS
- Page 483 and 484:
Word Name Type Description 2 UNDEF
- Page 485 and 486:
Word Name Type Description 9 SMI RS
- Page 487 and 488:
Word Name Type Description 20 CX RS
- Page 489 and 490:
Word Name Type Description 8 SMJ RS
- Page 491 and 492:
Word Name Type Description 19 TYZR
- Page 493 and 494:
Word Name Type Description 20 TZX1R
- Page 495 and 496:
Word Name Type Description 25 UNDEF
- Page 497 and 498:
Word Name Type Description 26 TXY2R
- Page 499 and 500:
Word Name Type Description 2 UNDEF
- Page 501 and 502:
Word Name Type Description 7 SXY RS
- Page 503 and 504:
Word Name Type Description 11 VOLST
- Page 505 and 506:
Word Name Type Description 15 EXY R
- Page 507 and 508:
Word Name Type Description 9 VOLSTR
- Page 509 and 510:
Word Name Type Description 3 ID I 4
- Page 511 and 512:
Word Name Type Description 7 SXY RS
- Page 513 and 514:
Word Name Type Description 10 ETZ R
- Page 515 and 516:
Word Name Type Description 11 SX2 R
- Page 517 and 518:
Word Name Type Description 14 EXY2R
- Page 519 and 520:
Word Name Type Description 7 SL2 RS
- Page 521 and 522:
OGF Table of grid point forces Tabl
- Page 523 and 524:
Word Name Type Description OGF Tabl
- Page 525 and 526:
OGK Output gasket element results F
- Page 527 and 528:
OGS Table of grid point stresses/st
- Page 529 and 530:
OGS Table of grid point stresses/st
- Page 531 and 532:
OGS Table of grid point stresses/st
- Page 533 and 534:
4. Output coordinate system code 1
- Page 535 and 536:
Record 2 - DATA Record 3 - TRAILER
- Page 537 and 538:
OMEOSCTable of oscillating total mo
- Page 539 and 540:
5 = print and punch 4. Approach cod
- Page 541 and 542:
Record 2 - DATA Record 3 - TRAILER
- Page 543 and 544:
OMKEO Table of oscillating modal ki
- Page 545 and 546:
5 = print and punch 4. Approach cod
- Page 547 and 548:
Record 2 - DATA Record 3 - TRAILER
- Page 549 and 550:
OMSEO Table of oscillating modal st
- Page 551 and 552:
5 = print and punch 4. Approach cod
- Page 553 and 554:
Word Name Type Description ACODE =0
- Page 555 and 556:
Word Name Type Description OPG Tabl
- Page 557 and 558:
OPTPRM Table of optimization parame
- Page 559 and 560:
OQG OQG Table of single or multipoi
- Page 561 and 562:
OQG Table of single or multipoint c
- Page 563 and 564:
OQG Table of single or multipoint c
- Page 565 and 566:
OUG Table of displacements, velocit
- Page 567 and 568:
OUG Table of displacements, velocit
- Page 569 and 570:
OUG Table of displacements, velocit
- Page 571 and 572:
OUG Table of displacements, velocit
- Page 573 and 574:
OUG Table of displacements, velocit
- Page 575 and 576:
OUG Table of displacements, velocit
- Page 577 and 578:
R1MAP Table of mapping from origina
- Page 579 and 580:
R1TAB Table of type one response at
- Page 581 and 582:
R1TAB Table of type one response at
- Page 583 and 584:
Record 2 - TRAILER R1TAB Table of t
- Page 585 and 586:
RESP12 Table of second level (synth
- Page 587 and 588:
Record 2 - TRAILER RESP12 Table of
- Page 589 and 590:
Word Name Type Description Word 13
- Page 591 and 592:
SEMAP Superelement Definition Table
- Page 593 and 594:
SET Table of combined sets Record 0
- Page 595 and 596:
VIEWTB View information table VIEWT
- Page 597 and 598:
Word Name Type Description Record 4
- Page 599 and 600:
Chapter 4 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 601 and 602:
Chapter 4 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 603 and 604:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 605 and 606:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 607 and 608:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 609 and 610:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 611 and 612:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 613 and 614:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 615 and 616:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 617 and 618:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 619 and 620:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 621 and 622:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 623 and 624:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 625 and 626:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 627 and 628:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 629 and 630:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 631 and 632:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 633 and 634:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 635 and 636:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 637 and 638:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 639 and 640:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 641 and 642:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 643 and 644:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 645 and 646:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 647 and 648:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 649 and 650:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 651 and 652:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 653 and 654:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 655 and 656:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 657 and 658:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 659 and 660:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 661 and 662:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 663 and 664:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 665 and 666:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 667 and 668:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 669 and 670:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 671 and 672:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 673 and 674:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 675 and 676:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 677 and 678:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 679 and 680:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 681 and 682:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 683 and 684:
Chapter 3 Name Chapter 2 Name Descr
- Page 685 and 686:
Data Block Naming Conventions Stiff
- Page 687 and 688:
Solutions: ___U___ Static and dynam
- Page 689 and 690:
Solution Output Tables: O__ES__ Ele
- Page 691 and 692:
Inconsistent Names: BUG Buckling ei
- Page 693 and 694:
Name Type and Description 'DYNAMICS
- Page 695 and 696:
Name Type and Description BUCKCC Lo
- Page 697 and 698:
Name Type and Description -1 Lumped
- Page 699 and 700:
Name Type and Description DFRQCC Lo
- Page 701 and 702:
Name Type and Description DTMi Inte
- Page 703 and 704:
Name Type and Description EXISTS Ch
- Page 705 and 706:
Name Type and Description FOUND Int
- Page 707 and 708:
Name Type and Description 2 Cubic s
- Page 709 and 710:
Name Type and Description 2 Insuffi
- Page 711 and 712:
Name Type and Description LINC Inte
- Page 713 and 714:
Name Type and Description MAXSET In
- Page 715 and 716:
Name Type and Description MPFSORT I
- Page 717 and 718:
Name Type and Description NE Intege
- Page 719 and 720:
Name Type and Description NOA Integ
- Page 721 and 722:
Name Type and Description NOGOIFPi
- Page 723 and 724:
Name Type and Description NOMR Inte
- Page 725 and 726:
Name Type and Description NORM Char
- Page 727 and 728:
Name Type and Description NOUNIT In
- Page 729 and 730:
Name Type and Description NLITER an
- Page 731 and 732:
Name Type and Description 'WHOLE' R
- Page 733 and 734:
Name Type and Description POUTF Int
- Page 735 and 736:
Name Type and Description RCOLLBLi
- Page 737 and 738:
Name Type and Description SEFLAG Lo
- Page 739 and 740:
Name Type and Description SID Integ
- Page 741 and 742:
Name Type and Description 2 Maximum
- Page 743 and 744:
Name Type and Description TINY Real
- Page 745 and 746:
Name Type and Description VUTRIA3 C
- Page 747 and 748:
CHAPTER 3 NX Nastran DMAP Programme
- Page 749 and 750:
3.2 Detailed Description of NDDL St
- Page 751 and 752:
DATABLK Describes data blocks used
- Page 753 and 754:
where: Keywords: Variables: DATABLK
- Page 755 and 756:
DATABLK Describes data blocks used
- Page 757 and 758:
ENTRY, SET,I, ENDENTRY,COUNT=LSET,
- Page 759 and 760:
Examples: 1. EPTS example: DEPEN Sp
- Page 761 and 762:
PARAM Defines parameters requiring
- Page 763 and 764:
QUAL Defines qualifiers referenced
- Page 765 and 766:
CHAPTER 4 NX Nastran DMAP Programme
- Page 767 and 768:
Utility Modules APPEND COPY DBC DBD
- Page 769 and 770:
761 GETCOL GETMKL GI GKAM GNFM GP0
- Page 771 and 772:
UMERGE1 UPARTN Module Basic Operati
- Page 773 and 774:
Executive Modules and Statements Mo
- Page 775 and 776:
ACMG Computes fluid/structure coupl
- Page 777 and 778:
ACMG Computes fluid/structure coupl
- Page 779 and 780:
ADAPT Performs and prints error est
- Page 781 and 782:
ADD Matrix add Computes [ X] = α[
- Page 783 and 784:
ADD5 Matrix add ADD5 Matrix add To
- Page 785 and 786:
4. Change the type of the real doub
- Page 787 and 788:
Parameters: Remarks: 1. NK, and NJ
- Page 789 and 790:
2. PKF cannot be purged. Examples:
- Page 791 and 792:
Remarks: AELOOP Aerodynamic loop dr
- Page 793 and 794:
AMG Builds aerodynamic influence ma
- Page 795 and 796:
AMP Generates modal aerodynamic mat
- Page 797 and 798:
APD Generates aerodynamic geometry
- Page 799 and 800:
MODLTYPE='AEROSTRC' $ APD EDT,xCSTM
- Page 801 and 802:
APPEND Concatenate two data blocks
- Page 803 and 804:
FILE U=APPEND $ MATGEN ,/US/5/1/7 $
- Page 805 and 806:
ASDR Prints the extra point aerodyn
- Page 807 and 808:
Parameter: ASG Computes the aerodyn
- Page 809 and 810:
AXMPR1 Builds a list of auxiliary m
- Page 811 and 812:
BCDR Drives a boundary condition lo
- Page 813 and 814:
BDRYINFO Generates geometry and con
- Page 815 and 816:
BGP Processes geometry for boundary
- Page 817 and 818:
BNDSPC Processes constraints on sup
- Page 819 and 820:
. CASE Dynamic analysis case contro
- Page 821 and 822:
CASE Dynamic analysis case control
- Page 823 and 824:
Examples: CASE Dynamic analysis cas
- Page 825 and 826:
CEAD Complex or unsymmetric eigenva
- Page 827 and 828:
CMPZPR Generates Bulk Data entry im
- Page 829 and 830:
CURV Transforms elemental centroid
- Page 831 and 832:
CURVPLOT Converts grid point output
- Page 833 and 834:
CYCLIC1 Generates cyclic symmetry t
- Page 835 and 836:
CYCLIC2 Processes degrees-of-freedo
- Page 837 and 838:
CYCLIC3 Forms cyclic matrices CYCLI
- Page 839 and 840:
CYCLIC4 Transforms cyclic component
- Page 841 and 842:
Examples: 1. Static analysis: CYCLI
- Page 843 and 844:
DBC Database converter for model ge
- Page 845 and 846:
Remarks: 1. Data block name table:
- Page 847 and 848:
Generic Name (P1-P20) Chapter 2 Nam
- Page 849 and 850:
DBC Database converter for model ge
- Page 851 and 852:
DBDELETE Deletes NDDL data blocks a
- Page 853 and 854:
DBDICT Prints database directory ta
- Page 855 and 856:
DBDICT Prints database directory ta
- Page 857 and 858:
DBDICT Prints database directory ta
- Page 859 and 860:
Column name Table 4-1 DBDICT DATABL
- Page 861 and 862:
Column name Default column width Ta
- Page 863 and 864:
DBDICT Prints database directory ta
- Page 865 and 866:
DBDICT Prints database directory ta
- Page 867 and 868:
and looks like: COLSPACE=1 ,CDATE=1
- Page 869 and 870:
DBEQUIV Equivalences (or copies) ND
- Page 871 and 872:
DBEQUIV Equivalences (or copies) ND
- Page 873 and 874:
SubDMAP DBMGR Functions on data blo
- Page 875 and 876:
Format: Parameters: SubDMAP DBMGR F
- Page 877 and 878:
SubDMAP DBSTORE Stores data blocks
- Page 879 and 880:
DBVIEW DBVIEW Creates virtual data
- Page 881 and 882:
DCMP Matrix decomposition with exte
- Page 883 and 884:
DCMP Matrix decomposition with exte
- Page 885 and 886:
DDR2 Computes displacements due to
- Page 887 and 888:
DDR2 Computes displacements due to
- Page 889 and 890:
Parameters: DDRMM Performs matrix m
- Page 891 and 892:
0 Use standard decomposition (defau
- Page 893 and 894:
DECOMP Matrix decomposition 3. If t
- Page 895 and 896:
DELETE Deletes data blocks Format:
- Page 897 and 898:
DIAGONAL Extracts diagonal from mat
- Page 899 and 900:
DISDCMP Performs distributed decomp
- Page 901 and 902:
DISOFPM Collects and merges OFP dat
- Page 903 and 904:
DISOPT Performs appropriate discret
- Page 905 and 906:
Output Data Blocks DISOPT Performs
- Page 907 and 908:
Input Data Blocks: DISUTIL Broadcas
- Page 909 and 910:
d. Strain energy (external work) 3.
- Page 911 and 912:
Remark: DIVERG Performs aerostatic
- Page 913 and 914:
DOM10 Prints initial and final resu
- Page 915 and 916:
DOM10 Prints initial and final resu
- Page 917 and 918:
GEOM2N Updated (optimized) GEOM2 MP
- Page 919 and 920:
DOM12 Performs soft and hard conver
- Page 921 and 922:
DOM12 Performs soft and hard conver
- Page 923 and 924:
DOM6 Calculates sensitivity of all
- Page 925 and 926:
DOM9 Performs the approximate optim
- Page 927 and 928:
PROPO Matrix of final (optimized) p
- Page 929 and 930:
DOPFS Performs optimization of the
- Page 931 and 932:
PROPI* Family of matrices of initia
- Page 933 and 934:
Parameters: DOPR2 Preprocesses the
- Page 935 and 936:
DOPR3 Preprocesses DCONSTR, DRESP1,
- Page 937 and 938:
DOPR4 Creates design sensitivity ta
- Page 939 and 940:
Parameters: STPSCL Input-real-defau
- Page 941 and 942:
DOPR6 Generates tables relating to
- Page 943 and 944:
DPD DPD Creates tables from Bulk Da
- Page 945 and 946:
UNUSED12 Input-integer-default=0. U
- Page 947 and 948:
DRMH1 Converts data recovery tables
- Page 949 and 950:
DRMH3 Partitions tables for each su
- Page 951 and 952:
4. Directory tables contain the map
- Page 953 and 954:
Parameters: DSABO Incorporates elem
- Page 955 and 956:
DSAD Processes tables related to de
- Page 957 and 958:
DRDUG Matrix of adjoint loads for t
- Page 959 and 960:
DSAD Processes tables related to de
- Page 961 and 962:
XTYPE Input-integer-default=0. Type
- Page 963 and 964:
DSAE Merges tables to evaluate resp
- Page 965 and 966:
Output Data Blocks: DSAF Generates
- Page 967 and 968:
DSAH Generates data blocks required
- Page 969 and 970:
DSAJ Generates g-set size reduced b
- Page 971 and 972:
DSAL Generates design sensitivity c
- Page 973 and 974:
Remark: 1 Eigenvalue (radian/time)
- Page 975 and 976:
DSAN Generates design sensitivity p
- Page 977 and 978:
Parameters: DSAP Computes an inerti
- Page 979 and 980:
DSAR Extracts and truncates data fr
- Page 981 and 982:
DSARLP DSARLP Calculates pseudo-dis
- Page 983 and 984:
DSARME Computes RMS values Computes
- Page 985 and 986:
DSARSN Calculates delta response va
- Page 987 and 988:
DSDVRG DSDVRG Computes weighting fa
- Page 989 and 990:
DSFLTF Calculates sensitivity of ac
- Page 991 and 992:
Remarks: 1. DSMA is applicable only
- Page 993 and 994:
DSPRM Sets design sensitivity param
- Page 995 and 996:
DSTA Creates tables for Old Design
- Page 997 and 998:
DSTA Creates tables for Old Design
- Page 999 and 1000:
DSVG1 Creates pseudo loads or scala
- Page 1001 and 1002:
DSVG1P DSVG1P Creates pseudo loads
- Page 1003 and 1004:
DSVG2 Generates pseudo-load matrix
- Page 1005 and 1006:
DSVG3 DSVG3 Combines and appends so
- Page 1007 and 1008:
Remark: DSVGP4 Generates a perturbe
- Page 1009 and 1010:
Remark: DSVGP5 Performs multiplicat
- Page 1011 and 1012:
DUMMOD1 DUMMOD1 Provides dummy modu
- Page 1013 and 1014:
DUMMOD3 DUMMOD3 Provides dummy modu
- Page 1015 and 1016:
DVIEWP DVIEWP Generates view-elemen
- Page 1017 and 1018:
DYNREDU Computes approximate eigenv
- Page 1019 and 1020:
EFFMASS Computes modal effective ma
- Page 1021 and 1022:
. ELTPRT Prints element summary inf
- Page 1023 and 1024:
ELTPRT Prints element summary infor
- Page 1025 and 1026:
EMAKFR Generates stiffness for foll
- Page 1027 and 1028:
Output Data Blocks: EMG Computes el
- Page 1029 and 1030:
EMG Computes elemental matrices ALT
- Page 1031 and 1032:
EQUIVX Data block name equivalence
- Page 1033 and 1034:
FA1 Prepares the modal matrices for
- Page 1035 and 1036:
FA2 Collects aeroelastic flutter da
- Page 1037 and 1038:
FBS Matrix forward/backward substit
- Page 1039 and 1040:
FILE Data block declaration Declare
- Page 1041 and 1042:
FORTIO Opens or closes a FORTRAN fi
- Page 1043 and 1044:
FRLG Generates frequency-dependent
- Page 1045 and 1046:
FRLGEN Creates frequency response l
- Page 1047 and 1048:
FRRD1 Solves for the steady-state f
- Page 1049 and 1050:
FRRD1 Solves for the steady-state f
- Page 1051 and 1052:
Output Data Blocks: Parameters: FRR
- Page 1053 and 1054:
GETCOL Reads STATSUB Case Control c
- Page 1055 and 1056:
Generates the aerodynamic spline tr
- Page 1057 and 1058:
GKAM Assembles modal mass, damping
- Page 1059 and 1060:
GP0 Modifies tables to include p-el
- Page 1061 and 1062:
GP1 Performs basic geometry process
- Page 1063 and 1064:
GP2 Processes element connectivity
- Page 1065 and 1066:
3. ETT may be purged if there are n
- Page 1067 and 1068:
Output Data Blocks: RMG Multipoint
- Page 1069 and 1070:
GP5 GP5 Creates table of static loa
- Page 1071 and 1072:
Computes grid point forces and elem
- Page 1073 and 1074:
GPFDR Computes grid point forces an
- Page 1075 and 1076:
GPSP Performs auto-SPC operation Pe
- Page 1077 and 1078:
Remarks: 1. YS0 and YS may be purge
- Page 1079 and 1080:
GPSTR2 Computes grid point stresses
- Page 1081 and 1082:
GPWG Computes center of mass of str
- Page 1083 and 1084:
GUST Computes loads for aerodynamic
- Page 1085 and 1086:
IFP Reads Bulk Data Section Reads i
- Page 1087 and 1088:
Example: IFP Reads Bulk Data Sectio
- Page 1089 and 1090:
IFP1 Reads Case Control Section Rea
- Page 1091 and 1092:
IFP3 Modifies Bulk Data entry recor
- Page 1093 and 1094:
Processes hydroelastic-related Bulk
- Page 1095 and 1096:
Process acoustic cavity-related Bul
- Page 1097 and 1098:
IFP6 Creates PSHELL and MAT2 Bulk D
- Page 1099 and 1100:
IFP7 Creates PBEAM Bulk Data entry
- Page 1101 and 1102:
IFP9 Creates PBAR and PBEAM Bulk Da
- Page 1103 and 1104:
IFT Performs an inverse Fourier tra
- Page 1105 and 1106:
ITAPE Value +n No 0 No -1 Yes Tape
- Page 1107 and 1108:
INPUTT4 Inputs a matrix from a FORT
- Page 1109 and 1110:
INTERR Generates modal components o
- Page 1111 and 1112:
ISHELL Invokes an external program
- Page 1113 and 1114:
Parameters: LAMX Eigenvalue Table E
- Page 1115 and 1116:
LAMX Eigenvalue Table Editor Exampl
- Page 1117 and 1118:
LANCZOS Performs real eigenvalue an
- Page 1119 and 1120:
3 Detailed output on cost and conve
- Page 1121 and 1122:
LMATPRT Prints combined design sens
- Page 1123 and 1124:
1115 MAKAEFA Extracts data specifie
- Page 1125 and 1126:
1117 MAKAEFS Generates an index and
- Page 1127 and 1128:
1119 MAKCOMP Extracts components fr
- Page 1129 and 1130:
1121 MAKENEW Converts tables from p
- Page 1131 and 1132:
1123 MAKEOLD Converts tables from V
- Page 1133 and 1134:
1125 MAKETR Generates transformatio
- Page 1135 and 1136:
1127 MATGEN Matrix generator MATGEN
- Page 1137 and 1138:
1129 MATGEN Matrix generator Input
- Page 1139 and 1140:
1131 MATGEN Matrix generator MATGEN
- Page 1141 and 1142:
1133 MATGEN Matrix generator Option
- Page 1143 and 1144:
1135 MATGEN Matrix generator The eq
- Page 1145 and 1146:
1137 MATGEN Matrix generator Option
- Page 1147 and 1148:
1139 MATGPR Degree-of-freedom matri
- Page 1149 and 1150:
1141 MATGPR Degree-of-freedom matri
- Page 1151 and 1152:
1143 MATGPR Degree-of-freedom matri
- Page 1153 and 1154:
1145 MATMOD Matrix modification MAT
- Page 1155 and 1156:
1147 MATMOD Matrix modification Out
- Page 1157 and 1158:
1149 MATMOD Matrix modification Opt
- Page 1159 and 1160:
1151 MATMOD Matrix modification Inp
- Page 1161 and 1162:
1153 MATMOD Matrix modification For
- Page 1163 and 1164:
1155 MATMOD Matrix modification Rem
- Page 1165 and 1166:
1157 MATMOD Matrix modification Opt
- Page 1167 and 1168:
1159 MATMOD Matrix modification Par
- Page 1169 and 1170:
1161 MATMOD Matrix modification Inp
- Page 1171 and 1172:
1163 MATMOD Matrix modification Inp
- Page 1173 and 1174:
1165 MATMOD Matrix modification 2.
- Page 1175 and 1176:
1167 MATMOD Matrix modification MAT
- Page 1177 and 1178:
1169 MATMOD Matrix modification Par
- Page 1179 and 1180:
1171 MATMOD Matrix modification Opt
- Page 1181 and 1182:
1173 MATMOD Matrix modification P1=
- Page 1183 and 1184:
1175 MATMOD Matrix modification Rem
- Page 1185 and 1186:
1177 MATMOD Matrix modification Par
- Page 1187 and 1188:
1179 MATPCH Punches contents of Mat
- Page 1189 and 1190:
1181 MATPRT Matrix printer MATPRT M
- Page 1191 and 1192:
1183 MATREDU Reduces square matrix
- Page 1193 and 1194:
1185 MCE2 Performs multipoint const
- Page 1195 and 1196:
1187 MDCASE Partitions the Case Con
- Page 1197 and 1198:
1189 MDCASE Partitions the Case Con
- Page 1199 and 1200:
1191 MERGE Matrix merge MERGE Matri
- Page 1201 and 1202:
1193 MERGE Matrix merge Case 4: Nei
- Page 1203 and 1204:
1195 MERGE Matrix merge then the re
- Page 1205 and 1206:
1197 MESSAGE Prints messages MESSAG
- Page 1207 and 1208:
1199 MKCNTRL Creates virtual fluid
- Page 1209 and 1210:
1201 MKSPLINE Generates splines to
- Page 1211 and 1212:
1203 MODACC OFREQ and OTIME command
- Page 1213 and 1214:
1205 MODEPF OFREQ and OTIME command
- Page 1215 and 1216:
1207 MODEPOUT OFREQ and OTIME comma
- Page 1217 and 1218:
1209 MODEPT Updates PACABS and PACA
- Page 1219 and 1220:
1211 MODGM2 Create table entries fo
- Page 1221 and 1222:
1213 MODGM4 Reads SPCs and SPCDs an
- Page 1223 and 1224:
1215 MODTRK Reorders eigenvalues an
- Page 1225 and 1226: 1217 MODTRL Modify trailer Examples
- Page 1227 and 1228: 1219 MODUSET Modifies the degree-of
- Page 1229 and 1230: 1221 MPP Prints monitor point resul
- Page 1231 and 1232: 1223 MPYAD Matrix multiply and add
- Page 1233 and 1234: 1225 MPYAD Matrix multiply and add
- Page 1235 and 1236: 1227 MPYAD Matrix multiply and add
- Page 1237 and 1238: 1229 MRGCOMP Merges two existing ae
- Page 1239 and 1240: 1231 MSGHAN Passes message number f
- Page 1241 and 1242: 1233 MTRXIN Converts DMIG entries t
- Page 1243 and 1244: 1235 MTRXIN Converts DMIG entries t
- Page 1245 and 1246: 1237 MTRXIN Converts DMIG entries t
- Page 1247 and 1248: 1239 NASSETS Combines all element s
- Page 1249 and 1250: 1241 NLCOMB Consolidates tables rel
- Page 1251 and 1252: 1243 NLITER Computes nonlinear anal
- Page 1253 and 1254: 1245 NLITER Computes nonlinear anal
- Page 1255 and 1256: 1247 NLITER Computes nonlinear anal
- Page 1257 and 1258: 1249 NLTRD Computes transient nonli
- Page 1259 and 1260: 1251 NLTRD Computes transient nonli
- Page 1261 and 1262: 1253 NLTRD2 Computes transient nonl
- Page 1263 and 1264: 1255 NLTRD2 Computes transient nonl
- Page 1265 and 1266: 1257 NORM Normalize a matrix NORM N
- Page 1267 and 1268: 1259 NXNADAMS Creates an ADAMS MNF
- Page 1269 and 1270: 1261 OFP Output file processor OFP
- Page 1271 and 1272: 1263 OPTGP0 p-element analysis prep
- Page 1273 and 1274: 1265 ORTHOG Generates orthonormal s
- Page 1275: 1267 OUTPRT Constructs sparse load
- Page 1279 and 1280: 1271 OUTPUT2 Output a table or matr
- Page 1281 and 1282: 1273 OUTPUT2 Output a table or matr
- Page 1283 and 1284: 1275 OUTPUT2 Output a table or matr
- Page 1285 and 1286: 1277 OUTPUT2 Output a table or matr
- Page 1287 and 1288: 1279 OUTPUT2 Output a table or matr
- Page 1289 and 1290: 1281 OUTPUT4 Output matrices onto a
- Page 1291 and 1292: 1283 OUTPUT4 Output matrices onto a
- Page 1293 and 1294: 1285 OUTPUT4 Output matrices onto a
- Page 1295 and 1296: 1287 PARAML Sets parameters from a
- Page 1297 and 1298: 1289 PARAML Sets parameters from a
- Page 1299 and 1300: 1291 PARAML Sets parameters from a
- Page 1301 and 1302: 1293 PARAML Sets parameters from a
- Page 1303 and 1304: 1295 PARAML Sets parameters from a
- Page 1305 and 1306: 1297 PARAML Sets parameters from a
- Page 1307 and 1308: 1299 PARTN Matrix partition PARTN M
- Page 1309 and 1310: 1301 PARTN Matrix partition 4. If {
- Page 1311 and 1312: 1303 PARTN Matrix partition 1 2 3 5
- Page 1313 and 1314: 1305 PCOPY Tests parallel copy PCOP
- Page 1315 and 1316: 1307 PLOT Creates a table of plot i
- Page 1317 and 1318: 1309 PLTSET Generates element sets
- Page 1319 and 1320: 1311 PRESOL Prepares special tables
- Page 1321 and 1322: 1313 PRTMSG Prints plotting informa
- Page 1323 and 1324: 1315 PRTPARM Parameter and DMAP mes
- Page 1325 and 1326: 1317 PVT Sets parameter values PVT
- Page 1327 and 1328:
1319 RANDOM Computes functions from
- Page 1329 and 1330:
1321 RANDOM Computes functions from
- Page 1331 and 1332:
1323 RBMG3 Computes rigid body info
- Page 1333 and 1334:
1325 READ Extracts real symmetric s
- Page 1335 and 1336:
1327 READ Extracts real symmetric s
- Page 1337 and 1338:
1329 READ Extracts real symmetric s
- Page 1339 and 1340:
1331 READ Extracts real symmetric s
- Page 1341 and 1342:
1333 RESTART Data block comparison
- Page 1343 and 1344:
1335 RMAXMIN Searches result tables
- Page 1345 and 1346:
1337 RMG2 Processes radiation excha
- Page 1347 and 1348:
1339 RSPEC Converts transient respo
- Page 1349 and 1350:
1341 SCALAR Matrix element extracto
- Page 1351 and 1352:
1343 SDP Calculates nondimensional
- Page 1353 and 1354:
1345 SDR1 Computes solution and sin
- Page 1355 and 1356:
1347 SDR2 Creates output tables EDT
- Page 1357 and 1358:
1349 SDR2 Creates output tables MET
- Page 1359 and 1360:
1351 SDR3 Converts tables in SORT1
- Page 1361 and 1362:
1353 SDRCOMP Calculates laminar str
- Page 1363 and 1364:
1355 SDRHT Combines heat flow for C
- Page 1365 and 1366:
1357 SDRNL Performs stress data rec
- Page 1367 and 1368:
1359 SDRP Computes data for p-eleme
- Page 1369 and 1370:
1361 SDRX Modifies CBAR, CBEAM and
- Page 1371 and 1372:
1363 SDRXD Modifies CBAR, CBEAM and
- Page 1373 and 1374:
1365 SDSA Partitions design model t
- Page 1375 and 1376:
1367 SDSB Generates superelement pr
- Page 1377 and 1378:
1369 SECONVRT Modifies Bulk Data en
- Page 1379 and 1380:
1371 SEDR Partitions tables for sup
- Page 1381 and 1382:
1373 SEDRDR Drives superelement dat
- Page 1383 and 1384:
1375 SELA Assembles static load mat
- Page 1385 and 1386:
1377 SEMA Assembles square symmetri
- Page 1387 and 1388:
1379 SEP1 Constructs superelement m
- Page 1389 and 1390:
1381 SEP1X Constructs superelement
- Page 1391 and 1392:
1383 SEP1X Constructs superelement
- Page 1393 and 1394:
1385 SEP2 Partitions tables for eac
- Page 1395 and 1396:
1387 SEP2DR Drives superelement gen
- Page 1397 and 1398:
1389 SEP2DR Drives superelement gen
- Page 1399 and 1400:
1391 SEP2X Partitions tables for ea
- Page 1401 and 1402:
1393 SEP3 Examines Case Control and
- Page 1403 and 1404:
1395 SEP4 Examines table and data b
- Page 1405 and 1406:
1397 SEPLOT Assembles plot displace
- Page 1407 and 1408:
1399 SEPR1 Builds a list of partiti
- Page 1409 and 1410:
1401 SEQP Resequencing processor Ou
- Page 1411 and 1412:
1403 SEQP Resequencing processor NT
- Page 1413 and 1414:
1405 SEQP Resequencing processor 8.
- Page 1415 and 1416:
1407 SMA3 Assembles global stiffnes
- Page 1417 and 1418:
1409 SMPYAD Matrix series multiply
- Page 1419 and 1420:
1411 SOLVE Linear system solver Rem
- Page 1421 and 1422:
1413 SOLVIT Iterative solver CASECC
- Page 1423 and 1424:
1415 SOLVIT Iterative solver ADPTIN
- Page 1425 and 1426:
1417 SOLVIT Iterative solver Format
- Page 1427 and 1428:
1419 SSG1 Computes static load matr
- Page 1429 and 1430:
1421 SSG2 Reduces static load and e
- Page 1431 and 1432:
1423 SSG3 Computes static solutions
- Page 1433 and 1434:
1425 SSG4 Updates static loads with
- Page 1435 and 1436:
1427 STATICS Performs static analys
- Page 1437 and 1438:
1429 STDCON Calculate stress discon
- Page 1439 and 1440:
1431 STRSORT Filters and sorts elem
- Page 1441 and 1442:
1433 TA1 Combines element data into
- Page 1443 and 1444:
1435 TABEDIT Performs editing opera
- Page 1445 and 1446:
1437 TABEDIT Performs editing opera
- Page 1447 and 1448:
1439 TABEDIT Performs editing opera
- Page 1449 and 1450:
1441 TABPRT Formatted table printer
- Page 1451 and 1452:
1443 TABPRT Formatted table printer
- Page 1453 and 1454:
1445 TABPRT Formatted table printer
- Page 1455 and 1456:
1447 TABPRT Formatted table printer
- Page 1457 and 1458:
1449 TABPRT Formatted table printer
- Page 1459 and 1460:
1451 TABPT Table printer TABPT Tabl
- Page 1461 and 1462:
1453 TAHT Adds records to element s
- Page 1463 and 1464:
1455 TASNP1 Computes the shell norm
- Page 1465 and 1466:
1457 TASNP2 Computes grid point she
- Page 1467 and 1468:
1459 TIMETEST Provide timing data I
- Page 1469 and 1470:
1461 TIMETEST Provide timing data I
- Page 1471 and 1472:
1463 TIMETEST Provide timing data I
- Page 1473 and 1474:
1465 TIMETEST Provide timing data C
- Page 1475 and 1476:
1467 TOLAPP Appends nonlinear data
- Page 1477 and 1478:
1469 TRD1 Solves for modal/direct,
- Page 1479 and 1480:
1471 TRD2 Solves for modal/direct,
- Page 1481 and 1482:
1473 TRLG Generates applied loads i
- Page 1483 and 1484:
1475 TRNSP Matrix transpose TRNSP M
- Page 1485 and 1486:
1477 TYPE Declares NDDL data blocks
- Page 1487 and 1488:
1479 TYPE Declares NDDL data blocks
- Page 1489 and 1490:
1481 UEIGL Solves both linear and q
- Page 1491 and 1492:
1483 UGVADD Adds two displacement v
- Page 1493 and 1494:
1485 UMERGE Merges two matrices bas
- Page 1495 and 1496:
1487 UMERGE1 Merges two matrices ba
- Page 1497 and 1498:
1489 UMERGE1 Merges two matrices ba
- Page 1499 and 1500:
1491 UPARTN Partitions a matrix bas
- Page 1501 and 1502:
1493 UPARTN Partitions a matrix bas
- Page 1503 and 1504:
1495 UREDUC Reduces rectangular mat
- Page 1505 and 1506:
1497 VDR Creates tables based on so
- Page 1507 and 1508:
1499 VEC Creates partitioning vecto
- Page 1509 and 1510:
1501 VECPLOT Transforms, searches,
- Page 1511 and 1512:
1503 VECPLOT Transforms, searches,
- Page 1513 and 1514:
1505 VECPLOT Transforms, searches,
- Page 1515 and 1516:
1507 VIEW Computes heat transfer ra
- Page 1517 and 1518:
1509 VIEWP Generates geometry table
- Page 1519 and 1520:
XSORT Reads and sorts Bulk Data sec
- Page 1521 and 1522:
XYPLOT Writes plot information to p
- Page 1523 and 1524:
XYTRAN Creates table of plot instru
- Page 1525 and 1526:
X Nastran MAP rogrammer’s uide I
Inappropriate
Loading...
Inappropriate
You have already flagged this document.
Thank you, for helping us keep this platform clean.
The editors will have a look at it as soon as possible.
Mail this publication
Loading...
Embed
Loading...
Delete template?
Are you sure you want to delete your template?
DOWNLOAD ePAPER
This ePaper is currently not available for download.
You can find similar magazines on this topic below under ‘Recommendations’.