Artemisinin-based combination therapy for ... - The Cochrane Library
Artemisinin-based combination therapy for ... - The Cochrane Library
Artemisinin-based combination therapy for ... - The Cochrane Library
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
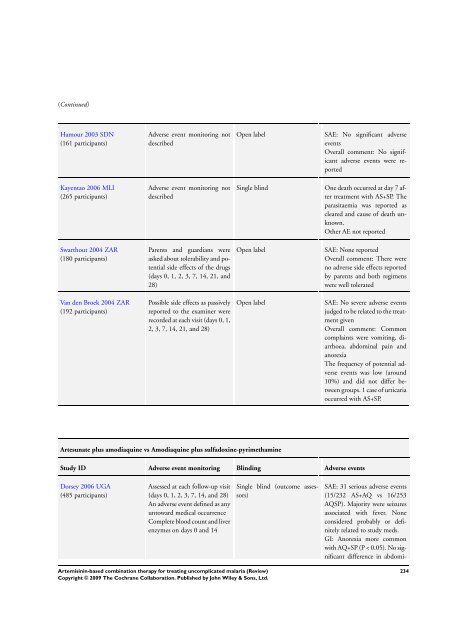
(Continued)<br />
Hamour 2003 SDN<br />
(161 participants)<br />
Kayentao 2006 MLI<br />
(265 participants)<br />
Swarthout 2004 ZAR<br />
(180 participants)<br />
Van den Broek 2004 ZAR<br />
(192 participants)<br />
Adverse event monitoring not<br />
described<br />
Adverse event monitoring not<br />
described<br />
Parents and guardians were<br />
asked about tolerability and potential<br />
side effects of the drugs<br />
(days 0, 1, 2, 3, 7, 14, 21, and<br />
28)<br />
Possible side effects as passively<br />
reported to the examiner were<br />
recorded at each visit (days 0, 1,<br />
2, 3, 7, 14, 21, and 28)<br />
Artesunate plus amodiaquine vs Amodiaquine plus sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine<br />
Open label SAE: No significant adverse<br />
events<br />
Overall comment: No significant<br />
adverse events were reported<br />
Single blind One death occurred at day 7 after<br />
treatment with AS+SP. <strong>The</strong><br />
parasitaemia was reported as<br />
cleared and cause of death unknown.<br />
Other AE not reported<br />
Open label SAE: None reported<br />
Overall comment: <strong>The</strong>re were<br />
no adverse side effects reported<br />
by parents and both regimens<br />
were well tolerated<br />
Open label SAE: No severe adverse events<br />
judged to be related to the treatment<br />
given<br />
Overall comment: Common<br />
complaints were vomiting, diarrhoea,<br />
abdominal pain and<br />
anorexia<br />
<strong>The</strong> frequency of potential adverse<br />
events was low (around<br />
10%) and did not differ between<br />
groups. 1 case of urticaria<br />
occurred with AS+SP.<br />
Study ID Adverse event monitoring Blinding Adverse events<br />
Dorsey 2006 UGA<br />
(485 participants)<br />
Assessed at each follow-up visit<br />
(days 0, 1, 2, 3, 7, 14, and 28)<br />
An adverse event defined as any<br />
untoward medical occurrence<br />
Complete blood count and liver<br />
enzymes on days 0 and 14<br />
<strong>Artemisinin</strong>-<strong>based</strong> <strong>combination</strong> <strong>therapy</strong> <strong>for</strong> treating uncomplicated malaria (Review)<br />
Copyright © 2009 <strong>The</strong> <strong>Cochrane</strong> Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.<br />
Single blind (outcome assessors)<br />
SAE: 31 serious adverse events<br />
(15/232 AS+AQ vs 16/253<br />
AQSP). Majority were seizures<br />
associated with fever. None<br />
considered probably or definitely<br />
related to study meds.<br />
GI: Anorexia more common<br />
with AQ+SP (P < 0.05). No significant<br />
difference in abdomi-<br />
234