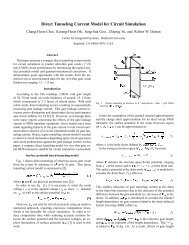
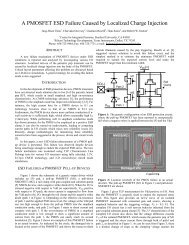
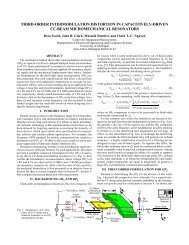
characterization, modeling, and design of esd protection circuits
characterization, modeling, and design of esd protection circuits
characterization, modeling, and design of esd protection circuits
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
140 Chapter 5. Design <strong>and</strong> Optimization <strong>of</strong> ESD Protection Transistor Layout<br />
optimize transistor layout for maximum HBM <strong>and</strong>/or charged-device model (CDM)<br />
robustness, minimum clamping voltage, <strong>and</strong> minimum area [67]. Such work is <strong>of</strong> interest<br />
because NMOS bipolar snapback will continue to be an effective ESD <strong>protection</strong><br />
mechanism in future technologies [68].<br />
This chapter explores the use <strong>of</strong> empirical <strong>modeling</strong> <strong>of</strong> ESD <strong>protection</strong>-transistor<br />
performance to optimize transistor layout <strong>and</strong> quantify the trade-<strong>of</strong>fs in layout parameters.<br />
As an example <strong>of</strong> these trade-<strong>of</strong>fs, suppose that the ESD robustness <strong>of</strong> a previously<br />
<strong>design</strong>ed multiple-finger NMOS clamp must be increased, but there is only limited area<br />
for expansion. A <strong>design</strong>er may choose to either add another poly finger to increase the<br />
total transistor width or to increase the contact-to-gate spacing <strong>of</strong> the existing fingers,<br />
thereby presumably increasing the robustness per unit width. It is not obvious which<br />
option will yield the greater ESD withst<strong>and</strong> level, but accurate <strong>characterization</strong> <strong>of</strong> a large<br />
<strong>design</strong> space over all critical layout parameters will lead directly to this answer. Chapters<br />
3 <strong>and</strong> 4 demonstrated how electrothermal simulation is used to study the dependence <strong>of</strong><br />
ESD robustness on layout parameters, <strong>and</strong> other work has been published on this<br />
application <strong>of</strong> two-dimensional [24,32] <strong>and</strong> even three-dimensional [69] simulation.<br />
However, in all <strong>of</strong> these studies the simulations have been <strong>of</strong> simple circuit elements such<br />
as single-finger transistors or diodes rather than <strong>of</strong> multifinger transistors, mainly because<br />
<strong>of</strong> the greatly increased computation time <strong>and</strong> resources required for simulating large<br />
devices. Therefore, while numerical simulation <strong>of</strong>fers much underst<strong>and</strong>ing <strong>of</strong> the ESD<br />
response <strong>of</strong> individual transistors, empirical <strong>modeling</strong> <strong>of</strong> an adequate layout <strong>design</strong> space<br />
may be the best approach to characterizing <strong>and</strong> optimizing multifingered ESD <strong>circuits</strong>.<br />
In the next section, an ESD-circuit <strong>design</strong> methodology is presented by reviewing the TLP<br />
<strong>characterization</strong> <strong>of</strong> ESD test structures, investigating the correlation between TLP<br />
withst<strong>and</strong> current <strong>and</strong> HBM withst<strong>and</strong> voltage, developing second-order linear models <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>protection</strong>-transistor performance, <strong>and</strong> discussing the importance <strong>of</strong> identifying critical<br />
ESD current paths in an integrated circuit. To verify the methodology, a model is extracted<br />
from <strong>characterization</strong> <strong>of</strong> a 0.35µm CMOS process <strong>and</strong> its predicted responses are<br />
compared to experimental HBM withst<strong>and</strong> levels <strong>of</strong> SRAM <strong>protection</strong> <strong>circuits</strong>. These<br />
results are analyzed, <strong>and</strong> optimization <strong>of</strong> circuit layout is discussed. Conclusions are<br />
drawn regarding the effectiveness <strong>of</strong> the methodology <strong>and</strong> how it may be enhanced in the<br />
future.