characterization, modeling, and design of esd protection circuits
characterization, modeling, and design of esd protection circuits
characterization, modeling, and design of esd protection circuits
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
2.3. Overview <strong>of</strong> Protection Circuit Design 39<br />
Input Output<br />
D1<br />
V CC<br />
(a)<br />
Bond pad D2<br />
D2 Bond pad<br />
(b)<br />
Bond pad<br />
V CC<br />
V SS<br />
R diff<br />
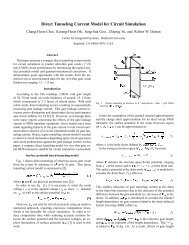
VSS Fig. 2.15 (a) ESD diode <strong>protection</strong> circuit in a CMOS technology; (b)<br />
use <strong>of</strong> a series resistor in combination with diode <strong>protection</strong>. A<br />
diffused resistor has a distributed resistance <strong>and</strong> also forms a<br />
distributed diode.<br />
using larger diode areas, but this takes up valuable chip real estate <strong>and</strong> may increase the<br />
parasitic capacitance to a level no longer negligible compared to the input-gate capacitance,<br />
thus degrading high-frequency performance. Reverse diode resistance can also be<br />
decreased if a diode with a smaller depletion layer can be processed, but the reduction <strong>of</strong><br />
the depletion layer again implies a higher capacitance. Another limitation <strong>of</strong> diodes is that<br />
the breakdown voltage itself may be higher than the dielectric threshold <strong>of</strong> today’s thin<br />
gate oxides. Finally, a diode <strong>of</strong>ten cannot break down quickly enough to protect a circuit<br />
from a fast-rising transient pulse such as that created by the charged-device model.<br />
Fig. 2.16 shows a CMOS-transistor <strong>protection</strong> scheme. These devices, which can be either<br />
thin-gate or thick-gate (field) transistors, have the advantage <strong>of</strong> being built using the<br />
st<strong>and</strong>ard chip process without additional implant or masking steps. (One exception is that<br />
a resist mask which blocks the silicide deposition may be added to increase the drain-togate<br />
<strong>and</strong> source-to-gate resistance.) The drain <strong>of</strong> the NMOS device (M2) is connected to<br />
D1<br />
D2<br />
Input<br />
D1